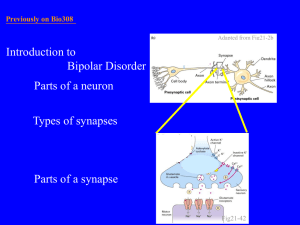
Synaptic Transmission Lecture
... • NO PORE, but binding can initiate: • 2nd messenger system • Other products could open ion channels • Modulate enzyme activity • Regulate ion channels in membrane • Initiate gene transcription/translation ...
... • NO PORE, but binding can initiate: • 2nd messenger system • Other products could open ion channels • Modulate enzyme activity • Regulate ion channels in membrane • Initiate gene transcription/translation ...
Modified Project Summary/Abstract Section
... Psychosocial stress is a major risk factor for the precipitation and exacerbation of mental illness in susceptible individuals. Understanding the neuroadaptations induced by chronic stress could afford new opportunities for therapeutic intervention for stressrelated psychiatric disorders. The candid ...
... Psychosocial stress is a major risk factor for the precipitation and exacerbation of mental illness in susceptible individuals. Understanding the neuroadaptations induced by chronic stress could afford new opportunities for therapeutic intervention for stressrelated psychiatric disorders. The candid ...
Document
... important brain areas, including those that mediate nausea/vomiting, appetite, and neuropathic pain ...
... important brain areas, including those that mediate nausea/vomiting, appetite, and neuropathic pain ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 14
... Signal transuduction cascade Ras and MAP kinase Other pathways Role of scaffolding complexes Dominant negative mutants in research D. Receptor Ser/Thr kinases TGF-b family (transforming growth factor) Smads are used in intracellular signaling DNA binding proteins E. CREB and STATs (Chapter 23; pp. 7 ...
... Signal transuduction cascade Ras and MAP kinase Other pathways Role of scaffolding complexes Dominant negative mutants in research D. Receptor Ser/Thr kinases TGF-b family (transforming growth factor) Smads are used in intracellular signaling DNA binding proteins E. CREB and STATs (Chapter 23; pp. 7 ...
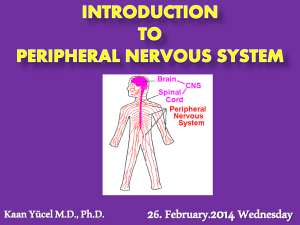
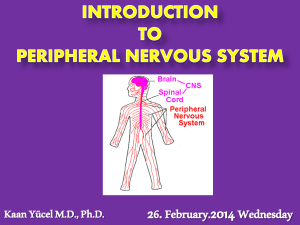
9-18-04 Nervous System Peripheral No1
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
... – All ganglionic transmission is cholinergic (acetylcholine) • Drugs that block ganglionic transmission block either parasympathetic or sympathetic depending on which is active • This is a paradox many have a problem grasping ...
model questions for SCT
... Both have a non-covalently associated signaling subunit. Both have a transmembrane domain. Both consist of heavy and light chains. They recognize epitopes. Generation of several millions of different variable domains is possible. ...
... Both have a non-covalently associated signaling subunit. Both have a transmembrane domain. Both consist of heavy and light chains. They recognize epitopes. Generation of several millions of different variable domains is possible. ...
Powerpoint
... Summary - neurotransmission transmitter is stored in vesicles vesicles released by local Ca influx following action potential transporters are major drug targets multiple kinds of transmitter ...
... Summary - neurotransmission transmitter is stored in vesicles vesicles released by local Ca influx following action potential transporters are major drug targets multiple kinds of transmitter ...
The Truth about Weed - Copley
... Pons – a structure located on the brain stem that conduct signals from the cerebrum down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus Synapse - a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell ...
... Pons – a structure located on the brain stem that conduct signals from the cerebrum down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus Synapse - a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... This study published in the Nature Neuroscience journal reflects a unique mechanism of interaction between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the rodent hippocampus. Our work describes a new form of short-term plasticity of inhibitory synapses that involves glutamate receptors, the major excitato ...
... This study published in the Nature Neuroscience journal reflects a unique mechanism of interaction between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the rodent hippocampus. Our work describes a new form of short-term plasticity of inhibitory synapses that involves glutamate receptors, the major excitato ...
Metabotropic Neurot
... • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA neurons (Ca2+ channel) ...
... • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA neurons (Ca2+ channel) ...
Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... kinds of receptors to glutamates. A receptor called NMDA receptor, and a receptor called the AMPA receptor. Under normal circumstances only the AMPA receptor is active. But if you give a train of stimuli, the NMDA receptor becomes active, it flexes calcium, it allows calcium to come into the cell ...
... kinds of receptors to glutamates. A receptor called NMDA receptor, and a receptor called the AMPA receptor. Under normal circumstances only the AMPA receptor is active. But if you give a train of stimuli, the NMDA receptor becomes active, it flexes calcium, it allows calcium to come into the cell ...
1 OVERVIEW OF EXTRACELLULAR SIGNALING A. Steps of
... 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression triggered by the receptorsignaling molecue complex 6. Removal of the signal ...
... 1. synthesis of signaling molecule 2. Release of signaling molecule 3. Transport of the signal to the target cell 4. Detection of the signal by a specific receptor protein 5. Change in cellular metabolism or gene expression triggered by the receptorsignaling molecue complex 6. Removal of the signal ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... transduce intracellular signals by coupling to GTP-binding proteins • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... transduce intracellular signals by coupling to GTP-binding proteins • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
... it is reabsorbed by the neuron that released it. This reabsorption happens with the help of a protein called the dopamine transporter. Crack interrupts this cycle. It attaches to the dopamine transporter, preventing the normal reabsorption process. As dopamine builds up in the synapse, it continues ...
00216 - UROP
... Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors causes the endocannabinoid system to induce both short- and long-term changes in synaptic strength in the striatum, the hippocampus, and other regions of the brain. Although current electrophysiological evidence suggests a role for the re ...
... Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors causes the endocannabinoid system to induce both short- and long-term changes in synaptic strength in the striatum, the hippocampus, and other regions of the brain. Although current electrophysiological evidence suggests a role for the re ...