Slide ()
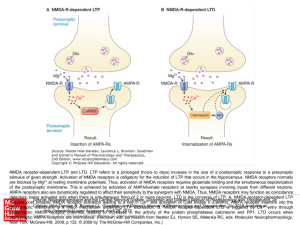
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
Are You suprised ?
... superfamily and is implicated in the generation and modulation of various cognitive, behavioral and developmental functions. We previously demonstrated that membrane cholesterol is necessary for ligand binding, and G-protein coupling of serotonin1A receptors. Interestingly, recently reported crystal ...
... superfamily and is implicated in the generation and modulation of various cognitive, behavioral and developmental functions. We previously demonstrated that membrane cholesterol is necessary for ligand binding, and G-protein coupling of serotonin1A receptors. Interestingly, recently reported crystal ...
Slide ()
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
Nervous Systems
... Chemicals released from vesicles by exocytosis into synaptic cleft Diffuse across synapse Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells Types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of ...
... Chemicals released from vesicles by exocytosis into synaptic cleft Diffuse across synapse Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells Types of neurotransmitters: Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... there is a sudden change in the voltage across the wall of the axon, caused by the movement of ions in and out of the neuron The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neuron. The fastest travel at about 250 mph Neurons that need to transmit electrical signals quickly are sh ...
... there is a sudden change in the voltage across the wall of the axon, caused by the movement of ions in and out of the neuron The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neuron. The fastest travel at about 250 mph Neurons that need to transmit electrical signals quickly are sh ...
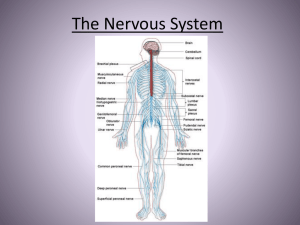
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Study Guide Chapter 10 in Fox
... Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are called ____________ Different forms of sensations are often called__________ ...
... Most sensory receptors are either ______________ or _______________ These receptors receive some form of ___________ and convert it into action potentials. Because they convert energy from one form to another, receptors are called ____________ Different forms of sensations are often called__________ ...
Nervous_System - Ms. Kingery`s Class
... --a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy ...
... --a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy ...
Part 1: True/False
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
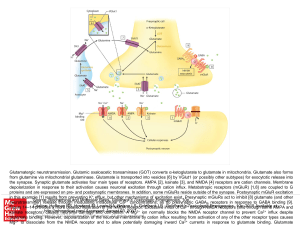
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Exam 4
... -Describe sensations and the classification of sensory receptors (Describe the different ways to classify sensory receptors). -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensor ...
... -Describe sensations and the classification of sensory receptors (Describe the different ways to classify sensory receptors). -Describe the locations and functions of receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations, and for proprioception (Describe the location and function of the somatic sensor ...
Slide ()
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
Test 5 Study Guide
... o The brain waves produced by normal adults while resting with their eyes closed are alpha waves. o In deep sleep the EEG pattern is characterized as "slow wave."\Hallucinogenic drugs, such as LSD, function by stimulating serotonin receptors. Neurotransmitters influence brain chemistry and behavior ...
... o The brain waves produced by normal adults while resting with their eyes closed are alpha waves. o In deep sleep the EEG pattern is characterized as "slow wave."\Hallucinogenic drugs, such as LSD, function by stimulating serotonin receptors. Neurotransmitters influence brain chemistry and behavior ...
Q24 Describe the mechanism of action of the
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
CONCLUSIONS 133
... A2A/D2 heterodimers have been detected in living cells where the stimulation of both receptors doesn’t modify neither the number nor the distance within the heteromer. Heterodimers between A2AR and D2R might be responsible, at least in part, for the strong functional antagonistic interactions betwee ...
... A2A/D2 heterodimers have been detected in living cells where the stimulation of both receptors doesn’t modify neither the number nor the distance within the heteromer. Heterodimers between A2AR and D2R might be responsible, at least in part, for the strong functional antagonistic interactions betwee ...
Part 1: True/False
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
MARIJUANA - ctclearinghouse.org
... actively investigating anandamide’s function in the brain. This research will not only help in gaining a greater understanding of how marijuana acts in the brain and why it is abused, but it will also provide new clues about how the healthy brain works. ...
... actively investigating anandamide’s function in the brain. This research will not only help in gaining a greater understanding of how marijuana acts in the brain and why it is abused, but it will also provide new clues about how the healthy brain works. ...
Receptors and Neurotransmitters
... Most of the postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system secrete the neurotransmitter Dopamine . In the CNS, this neurotransmitter creates a sense of feeling good, but in low doses it can cause feelings of depression. Depending on the receptor located in the PNS, ...
... Most of the postganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system secrete the neurotransmitter Dopamine . In the CNS, this neurotransmitter creates a sense of feeling good, but in low doses it can cause feelings of depression. Depending on the receptor located in the PNS, ...
Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
How specific is ligand
... Nitric oxide is a second messenger more neat things about receptors and their signaling pathways • Do the things that you have learned about affect homeostasis? • **If you are on the U. Windsor Women’s Hockey Team, please see me after class.** ...
... Nitric oxide is a second messenger more neat things about receptors and their signaling pathways • Do the things that you have learned about affect homeostasis? • **If you are on the U. Windsor Women’s Hockey Team, please see me after class.** ...
Slide ()
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
... transcriptional modulators vorinostat (targeting histone deacetylase), azacytidine derivatives (targeting DNA methyltransferase), or retinoid receptor Source: PRINCIPLES OF CANCER TREATMENT, Harrison's Hematology and Oncology, 2e modulators all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) or bexarotene. Cytokine rece ...
Slide ()
... interrupted by lapatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, and imatinib, acting at the ATP binding site; or by cetuximab, trastuzumab, or panitumumab acting at the receptor. Tyrosine kinases (TKs) that are not directly stimulated by growth factors such as p210 bcr-abl or src can be inhibited by imatinib, dasat ...
... interrupted by lapatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, and imatinib, acting at the ATP binding site; or by cetuximab, trastuzumab, or panitumumab acting at the receptor. Tyrosine kinases (TKs) that are not directly stimulated by growth factors such as p210 bcr-abl or src can be inhibited by imatinib, dasat ...