11- neurotransmitters and receptors
... phenylalanine. No whole protein; source of all aa’s minus this one. At least through to adulthood, while nervous ...
... phenylalanine. No whole protein; source of all aa’s minus this one. At least through to adulthood, while nervous ...
Lipid rafts
... – regulation of adipocyte differentiation – regulation of lipid anabolism: in the adipose tissue, they regulate the expression of LPL, FATP… PPARγ are targeted by anti-diabetic substances of the thiazolidinedione class (glitazones, e.g. rosiglitazone) that enhance the tissue sensitivity to insulin a ...
... – regulation of adipocyte differentiation – regulation of lipid anabolism: in the adipose tissue, they regulate the expression of LPL, FATP… PPARγ are targeted by anti-diabetic substances of the thiazolidinedione class (glitazones, e.g. rosiglitazone) that enhance the tissue sensitivity to insulin a ...
Gustation - West Virginia University
... cAMP holds K⁺ ions open – so intracellular K⁺ concentration ↑ ...
... cAMP holds K⁺ ions open – so intracellular K⁺ concentration ↑ ...
G-Protein Coupled Receptor
... signals from receptors target molecules Protein kinase: enzyme that phosphorylates and activates proteins at next level Phosphorylation cascade: enhance and amplify signal ...
... signals from receptors target molecules Protein kinase: enzyme that phosphorylates and activates proteins at next level Phosphorylation cascade: enhance and amplify signal ...
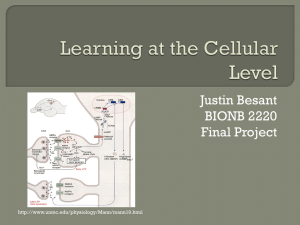
Learning at the Cellular Level
... learning can occur at the cellular level? How this be modeled and simulated quickly using the Izhikevich model? ...
... learning can occur at the cellular level? How this be modeled and simulated quickly using the Izhikevich model? ...
6_4_PeptideTransmMetaboReceptor_HalaszO
... (anterogradly) to the axon terminal. Before being “ready for use”, they go through maturation processes which involve the cleavage of the precursor, resulting in multple neuropeptides. (The cleavage might even happen outside the cell, a bit later.) After exocytosis, they bind to the metabotropic rec ...
... (anterogradly) to the axon terminal. Before being “ready for use”, they go through maturation processes which involve the cleavage of the precursor, resulting in multple neuropeptides. (The cleavage might even happen outside the cell, a bit later.) After exocytosis, they bind to the metabotropic rec ...
Diapositive 1
... neurotransmitter in the brain is converted into the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. -The synaptic actions of the amino acid neurotransmitters are terminated by selective uptake into the presynaptic terminals and glia via specific Na+ -dependent ...
... neurotransmitter in the brain is converted into the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. -The synaptic actions of the amino acid neurotransmitters are terminated by selective uptake into the presynaptic terminals and glia via specific Na+ -dependent ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
Slide 1
... •Cell bodies – midbrain and brain stem raphe nuclei Ascending pathways - fore brain regions (hippocampus, striatum, amygdalae, hypothalamus and cerebral cortex) o5- HT has a modulatory role in aspects of behaviour including mood, emotion, sleep , wakefulness and regulation of circadian functions , ...
... •Cell bodies – midbrain and brain stem raphe nuclei Ascending pathways - fore brain regions (hippocampus, striatum, amygdalae, hypothalamus and cerebral cortex) o5- HT has a modulatory role in aspects of behaviour including mood, emotion, sleep , wakefulness and regulation of circadian functions , ...
Autonomic Nervous System ANS - Anderson School District One
... αlpha & βeta Receptors • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
... αlpha & βeta Receptors • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... receptors… – Air flows in carrying organic molecules – Organic molecules dissolve in mucus lining – Organic molecules bind to receptors – Impulse sent through Olfactory Nerve ...
... receptors… – Air flows in carrying organic molecules – Organic molecules dissolve in mucus lining – Organic molecules bind to receptors – Impulse sent through Olfactory Nerve ...
Chapter 6
... Three types of receptors (nociceptors) - mechanical, thermal, polymodal. All are naked nerve endings and do not adapt. All can be sensitized by prostaglandins (increase pain). Prostaglandins derived from lipid bilayer of membrane released from damaged tissues Mechanical (crushing, cutting, pinching) ...
... Three types of receptors (nociceptors) - mechanical, thermal, polymodal. All are naked nerve endings and do not adapt. All can be sensitized by prostaglandins (increase pain). Prostaglandins derived from lipid bilayer of membrane released from damaged tissues Mechanical (crushing, cutting, pinching) ...
Chapter 4 lec 2
... Released from all parts of the terminal button, not just from active zone (only portion released into synaptic cleft Others act on receptors belonging to neighboring cells Most serve as neuromodulators; but some act as neurotransmitters Once released, they are destroyed by enzymes (no reuptake or re ...
... Released from all parts of the terminal button, not just from active zone (only portion released into synaptic cleft Others act on receptors belonging to neighboring cells Most serve as neuromodulators; but some act as neurotransmitters Once released, they are destroyed by enzymes (no reuptake or re ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter split by a specific enzyme fragments re-absorbed by presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... neurotransmitter split by a specific enzyme fragments re-absorbed by presynaptic neuron used to synthesize more neurotransmitter ex: acetylcholine (Ach) split by enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Physiology2 - Sheet#8 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul - Done By: Mais
... Physiology2 - Sheet#8 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul - Done By: Mais Al-Reem Al-Housani In the brain, NO acts as a neuromodulator to control behavioral activity, influence memory formation, and intensify responses to painful stimuli May be responsible for glutamate induced neurotoxicity: *neurons that work thro ...
... Physiology2 - Sheet#8 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul - Done By: Mais Al-Reem Al-Housani In the brain, NO acts as a neuromodulator to control behavioral activity, influence memory formation, and intensify responses to painful stimuli May be responsible for glutamate induced neurotoxicity: *neurons that work thro ...
Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which relay, amplify, and modulate signals between a neuron and another cell. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles that cluster beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they ...
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which relay, amplify, and modulate signals between a neuron and another cell. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles that cluster beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they ...
Neurotox I
... being expressed as a variety of alterations in development. The effects of toxicant exposure will be markedly affected not only by dose/concentration, but also by timing. Insults by the same dose/concentration at different times during development may result in markedly different sequelae. Extrapola ...
... being expressed as a variety of alterations in development. The effects of toxicant exposure will be markedly affected not only by dose/concentration, but also by timing. Insults by the same dose/concentration at different times during development may result in markedly different sequelae. Extrapola ...
Types of Receptors
... joints and visceral organs. • Touch and pressure employ 3 kinds of receptors • 1) Free nerve endings in between epithelial cells • 2) Meissner’s Corpuscles – most common in hairless portions of the skin. Most responsive to light touch. • 3) Pacinian’s Corpuscles – Found in the subcutaneous layers of ...
... joints and visceral organs. • Touch and pressure employ 3 kinds of receptors • 1) Free nerve endings in between epithelial cells • 2) Meissner’s Corpuscles – most common in hairless portions of the skin. Most responsive to light touch. • 3) Pacinian’s Corpuscles – Found in the subcutaneous layers of ...
Limbic system
... Neurons: specialized nerve cells that make up the nervous system and release transmitters ...
... Neurons: specialized nerve cells that make up the nervous system and release transmitters ...