Signal Transduction pt 1
... subcellular proteins and a cellular response to insulin Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship ...
... subcellular proteins and a cellular response to insulin Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals or proteins, in a specific one-to-one relationship ...
ACh - Perkins Science
... • Electrical synapses occur in smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, between some neurons of the brain, and between glial cells. • Stimulation causes phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of connexin proteins to open or close the channels ...
... • Electrical synapses occur in smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, between some neurons of the brain, and between glial cells. • Stimulation causes phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of connexin proteins to open or close the channels ...
Name
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
Synthesis and degradation of neurotransmitters
... • Appr. 50 known • Mainly in the hypothalamic-pituitary system • Synthesis: prepropeptid → ER, signal sequence cleavage → propeptid in vesicles → further processing → peptide neurotransmitter (1 or more) • Removal from synaptic cleft: Degradation, but not re-uptake ...
... • Appr. 50 known • Mainly in the hypothalamic-pituitary system • Synthesis: prepropeptid → ER, signal sequence cleavage → propeptid in vesicles → further processing → peptide neurotransmitter (1 or more) • Removal from synaptic cleft: Degradation, but not re-uptake ...
fleming_Oct
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
Synaptic Transmission - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements ...
... • Plays a dual role in sleep: day – excites the brain, night – slows down the brain. • Huntington’s disease involves loss of neurons in striatum that utilize GABA – Symptoms: • jerky involuntary movements ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... System (continued) • Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and carried by the blood to all the organs and tissues of the body. • Hormones affect selected tissues that are designed to receive the information. • Hormones may be highly selective or very general with regard to the cells or organs ...
... System (continued) • Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and carried by the blood to all the organs and tissues of the body. • Hormones affect selected tissues that are designed to receive the information. • Hormones may be highly selective or very general with regard to the cells or organs ...
Cell Signaling Mechanisms
... The intracellular domain then interacts with other intracellular signaling proteins These intracellular signaling proteins further relay the message to one or more effector proteins Effector proteins mediate the appropriate response ...
... The intracellular domain then interacts with other intracellular signaling proteins These intracellular signaling proteins further relay the message to one or more effector proteins Effector proteins mediate the appropriate response ...
Document
... • Perception: the conscious interpretation of those stimuli Sensory Integration • Input comes from exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors • Input is relayed toward the head, but is processed along the way Sensory Integration • Levels of neural integration in sensory systems: 1. Receptor le ...
... • Perception: the conscious interpretation of those stimuli Sensory Integration • Input comes from exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors • Input is relayed toward the head, but is processed along the way Sensory Integration • Levels of neural integration in sensory systems: 1. Receptor le ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms ...
Biological Basis for Understanding Psychotropic Drugs
... Link between thought and emotion and internal organs Regulation of sleep-wake cycle Conscious mental activity ...
... Link between thought and emotion and internal organs Regulation of sleep-wake cycle Conscious mental activity ...
11 Signal Transduction
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
... • Each TK adds a phosphate from an ATP to a tyrosine on the tail of the other polypeptide • The receptor is fully activated as a result ...
Slide ()
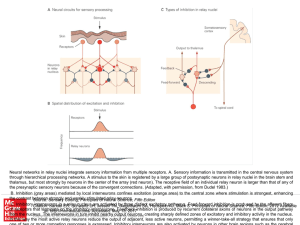
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
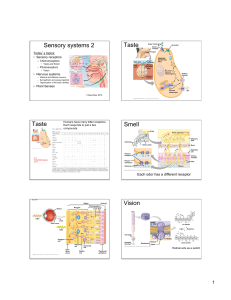
Chemical Senses
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
Biochemistry of Nerve Transmission - I-GaP
... Neurotransmitter Receptors Once the molecules of neurotransmitter are released from a cell as the result of the firing of an action potential, they bind to specific receptors on the surface of the postsynaptic cell. In all cases in which these receptors have been cloned and characterized in detail, ...
... Neurotransmitter Receptors Once the molecules of neurotransmitter are released from a cell as the result of the firing of an action potential, they bind to specific receptors on the surface of the postsynaptic cell. In all cases in which these receptors have been cloned and characterized in detail, ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
CNS Introduction
... -Role in nociception, schizophrenia, depression, eating disorders, temp. regulation ...
... -Role in nociception, schizophrenia, depression, eating disorders, temp. regulation ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • Receives information • Responds to information • Maintains homeostasis ...
... • Receives information • Responds to information • Maintains homeostasis ...
Neuronal signaling and synapses
... -four main types of changes can occur with the activation of metabotropic receptors -opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell member – e.g. opening of a potassium channel (prolonged opening) -activation of cAMP or cGMP in the neuron can activate metabolic processes that result in ...
... -four main types of changes can occur with the activation of metabotropic receptors -opening specific ion channels through the postsynaptic cell member – e.g. opening of a potassium channel (prolonged opening) -activation of cAMP or cGMP in the neuron can activate metabolic processes that result in ...