Abstract
... hyperglycaemia of other major modulators of glucose homeostasis the incretins, glucosedependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). The overall aim of this study was to investigate the role of receptors for incretins and other glucose-regulating hormones in sepsis-i ...
... hyperglycaemia of other major modulators of glucose homeostasis the incretins, glucosedependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). The overall aim of this study was to investigate the role of receptors for incretins and other glucose-regulating hormones in sepsis-i ...
Slide ()
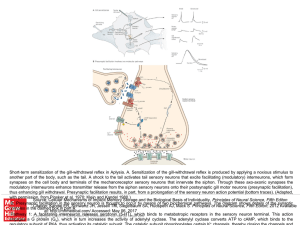
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Chapter 34-4B: Second Messengers
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
... are not transmembrane proteins. Steroid hormones can pass freely through cell membrane, and bind the specific receptor protein in cytosol. The receptor activated by the steroid hormone moves into the nucleus. The active receptor binds a specific region of DNA and activates or inactivates the replica ...
Origin of Long- Term Memory - Neuromarketing Business Association
... The Transcription Factors increases the production of a variety of proteins - some include APMA receptors, which are inserted into he postsynaptic cell membrane at the synapse - others increase the Growth Factor, involved in the formation of new synapses, which is the basis of synaptic plasticity, a ...
... The Transcription Factors increases the production of a variety of proteins - some include APMA receptors, which are inserted into he postsynaptic cell membrane at the synapse - others increase the Growth Factor, involved in the formation of new synapses, which is the basis of synaptic plasticity, a ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... the PNS is the _____that contains motor neurons that direct the movement of skeletal muscles; it is a voluntary system ...
... the PNS is the _____that contains motor neurons that direct the movement of skeletal muscles; it is a voluntary system ...
sensory2
... 16 October 2009 Chapter 7 Sensory Physiology Quiz on Cranial Nerves: Wednesday Lab next week: Sensory Physiology and the Auditory System ...
... 16 October 2009 Chapter 7 Sensory Physiology Quiz on Cranial Nerves: Wednesday Lab next week: Sensory Physiology and the Auditory System ...
Electrical Signaling-2
... the activity of adenylyl cyclase – 2 adenosine receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity – 2 adenosine receptors increase adenylyl cyclase activity ...
... the activity of adenylyl cyclase – 2 adenosine receptors inhibit adenylyl cyclase activity – 2 adenosine receptors increase adenylyl cyclase activity ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... (2nd messenger). -2nd messengers activate a range of cellular proteins, including ion channels, protein kinases and transcription factors. -Glutamate&GABA activate both ionotropic& metabotropic receptors. -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These ...
... (2nd messenger). -2nd messengers activate a range of cellular proteins, including ion channels, protein kinases and transcription factors. -Glutamate&GABA activate both ionotropic& metabotropic receptors. -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These ...
WARM UP 3/4 - KENYON'S CLASS
... •Slowed down messages from the brain to muscle impair our reflexes, reduce reaction time and impair our coordination, and our ability to drive is impaired. •Slurring of speech, stumbling when you walk, loss of ...
... •Slowed down messages from the brain to muscle impair our reflexes, reduce reaction time and impair our coordination, and our ability to drive is impaired. •Slurring of speech, stumbling when you walk, loss of ...
receptor proteins
... Growth factors and their trans‐membrane receptor tyrosine kinases play important roles in cell proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation. One group of growth factors, comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)‐like proteins and neuregulins, stimulates cells ...
... Growth factors and their trans‐membrane receptor tyrosine kinases play important roles in cell proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation. One group of growth factors, comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)‐like proteins and neuregulins, stimulates cells ...
Chapter 15 Anatomy & Physiology
... olfactory organ together with the basal (these are stem cells) and supporting cells. • Exception to the rule that neuronal cells do not replicate, the basal cells regenerate olfactory cells every two months. • The olfactory cell’s dendrites ends are embedded in the mucus layer excreted from olfactor ...
... olfactory organ together with the basal (these are stem cells) and supporting cells. • Exception to the rule that neuronal cells do not replicate, the basal cells regenerate olfactory cells every two months. • The olfactory cell’s dendrites ends are embedded in the mucus layer excreted from olfactor ...
RetinaCircuts
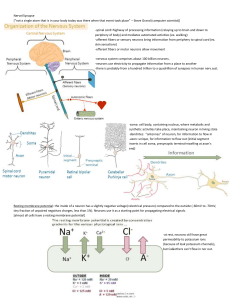
... • Signals from bipolar cells cause effect – Receptors stimulated by dark areas inhibit the response of neighboring cells receiving input from white area – The lateral inhibition causes a reduced response which leads to the perception of gray ...
... • Signals from bipolar cells cause effect – Receptors stimulated by dark areas inhibit the response of neighboring cells receiving input from white area – The lateral inhibition causes a reduced response which leads to the perception of gray ...
Sensory Systems
... the physical stress of temperatures either above or below the animal’s normal body temperature. It is unclear whether these receptors are more like mechanoreceptors, or operate by some other mechanism. ...
... the physical stress of temperatures either above or below the animal’s normal body temperature. It is unclear whether these receptors are more like mechanoreceptors, or operate by some other mechanism. ...
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
... • pain from internal organs often seems to come from unrelated locations e.g., heart to arm; stomach to back • may be caused by neurons converging on same 2° neuron (more nerve fibers in periphery than in lateral spinothalamic tract) • dermatomes = ANALGESIA: • endogenous analgesic neurotransmitters ...
... • pain from internal organs often seems to come from unrelated locations e.g., heart to arm; stomach to back • may be caused by neurons converging on same 2° neuron (more nerve fibers in periphery than in lateral spinothalamic tract) • dermatomes = ANALGESIA: • endogenous analgesic neurotransmitters ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Neuron immediately begins to repolarize. K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
... Neuron immediately begins to repolarize. K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
Synaptic Transmission - Interactive Physiology
... • A second type of mACh receptor is found in the central nervous system, and in the heart. • Acetylcholine acts indirectly at these receptors, producing a slow inhibition of the postsynaptic cells. • In the heart, this effect decreases the heart rate. • Acetylcholine is inhibitory at these muscarini ...
... • A second type of mACh receptor is found in the central nervous system, and in the heart. • Acetylcholine acts indirectly at these receptors, producing a slow inhibition of the postsynaptic cells. • In the heart, this effect decreases the heart rate. • Acetylcholine is inhibitory at these muscarini ...
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the
... • Axons of labeled line carry info about 1 type of stimulus (modality) • Sensory coding = translation of complex sensory info into meaningful patterns of AP ...
... • Axons of labeled line carry info about 1 type of stimulus (modality) • Sensory coding = translation of complex sensory info into meaningful patterns of AP ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... -68• One type of cholinergic muscarinic receptor, or mACh is found in the central nervous system and on most effector organs of the parasympathetic branch of the nervous system. • Acetylcholine acts indirectly at these mACh receptors producing a slow excitatory postsynaptic potential. • Acetylcholi ...
... -68• One type of cholinergic muscarinic receptor, or mACh is found in the central nervous system and on most effector organs of the parasympathetic branch of the nervous system. • Acetylcholine acts indirectly at these mACh receptors producing a slow excitatory postsynaptic potential. • Acetylcholi ...
big
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
here
... sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with ...
... sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with ...
Topic 6
... Purified molecule of interest is injected into an animal to provoke an immune response (keep in mind these are protein-based molecules, or if smaller, they are coupled to larger proteins). The antibodies that the host animal produces can be collected, purified and tagged with a marker (radioactive, ...
... Purified molecule of interest is injected into an animal to provoke an immune response (keep in mind these are protein-based molecules, or if smaller, they are coupled to larger proteins). The antibodies that the host animal produces can be collected, purified and tagged with a marker (radioactive, ...
Review for Quiz 2 Fixed Action Pattern Types of neurons Anatomy of
... Worm Grunting Facial Fusiform Sulcus Hippocampal functions ...
... Worm Grunting Facial Fusiform Sulcus Hippocampal functions ...