FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can
... stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to ganglion cells in the somatosensory, auditory, and visual systems. Receptors are specialized structure ...
... stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to ganglion cells in the somatosensory, auditory, and visual systems. Receptors are specialized structure ...
receptors and ion channels - The Company of Biologists
... action (see chapters by Beltz & Kravitz and by Evans & Myers). In addition, a single neurotransmitter may interact in the nervous system with a number of pharmacologically distinct receptor subtypes each with its own specific mode of action (see chapters by Schwartz, Arrang, Garbarg & Korner and by ...
... action (see chapters by Beltz & Kravitz and by Evans & Myers). In addition, a single neurotransmitter may interact in the nervous system with a number of pharmacologically distinct receptor subtypes each with its own specific mode of action (see chapters by Schwartz, Arrang, Garbarg & Korner and by ...
solutions - Berkeley MCB
... photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. lateral displacement of the ganglion cells from the retina c. all of the photoreceptors here ...
... photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. lateral displacement of the ganglion cells from the retina c. all of the photoreceptors here ...
Overview of the Day
... when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bind to receptor cites on dendrites of next neuron: receptor cites are specific to each type of neurotransmitter ...
... when action potential reaches knob-like terminals at axon's end, it triggers release of neurotransmitter they cross synaptic cleft and bind to receptor cites on dendrites of next neuron: receptor cites are specific to each type of neurotransmitter ...
Bio 201, Fall 2010 Test 3 Study Guide Questions to be able to
... 11. Where are gap junctions found, and why is it important that calcium and cAMP are small enough to pass through gap junctions? 12. What is the purpose of chemical communication between cells? 13. What are the steps in signal transduction? 14. What things make receptors bind to specific ligands? 15 ...
... 11. Where are gap junctions found, and why is it important that calcium and cAMP are small enough to pass through gap junctions? 12. What is the purpose of chemical communication between cells? 13. What are the steps in signal transduction? 14. What things make receptors bind to specific ligands? 15 ...
Androgen Receptor Localization in the Haplochromis burtoni
... antibody has a greater (more selective) binding affinity than the serum primary Ab that we have been using thus far. Let’s keep our fingers crossed…… ...
... antibody has a greater (more selective) binding affinity than the serum primary Ab that we have been using thus far. Let’s keep our fingers crossed…… ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
... The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) _____________________ connect differen ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
Case Studies in a Physiology Course on the Autonomic Nervous
... contrast, are negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase (AC) with their activation, therefore, leading to a decrease of cAMP. Moreover, alpha2-receptors are mainly auto-receptors that are ...
... contrast, are negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase (AC) with their activation, therefore, leading to a decrease of cAMP. Moreover, alpha2-receptors are mainly auto-receptors that are ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... 3. The fact that opioid drugs have little effect on the initial sharp pain of a pinprick implies that opioid drugs do not inhibit firing of sensory pain fibers along rapidly conducting myelinated axons. Instead, opioid drugs inactivate the slower conducting unmyelinated axons that synapse in the spi ...
... 3. The fact that opioid drugs have little effect on the initial sharp pain of a pinprick implies that opioid drugs do not inhibit firing of sensory pain fibers along rapidly conducting myelinated axons. Instead, opioid drugs inactivate the slower conducting unmyelinated axons that synapse in the spi ...
Senses
... • These fibers synapse with neurons located in the enlargements of the olfactory bulbs • Within the olfactory bulbs the sensory impulses are analyzed and additional impulses travel along the olfactory tracts to portions of the limbic system ...
... • These fibers synapse with neurons located in the enlargements of the olfactory bulbs • Within the olfactory bulbs the sensory impulses are analyzed and additional impulses travel along the olfactory tracts to portions of the limbic system ...
Recitation Worksheet 11
... taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, uses population based coding where one olfactory neurons expresses only one kind of receptor, but eac ...
... taste – for example, sweet is detected by taste cells that respond only to sweet, and each sweet taste cell is innervated only by neurons that carry sweet information. The olfactory system, however, uses population based coding where one olfactory neurons expresses only one kind of receptor, but eac ...
Psychology 312: Essay Questions Test 1 G9 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
... Following is a list of essay questions. The essay questions on Test 1 will be taken from this list. You should prepare for the essay part of that test by being able to answer all of them. Your answer must consist of complete sentences. Outline answers will lose points. ------------------------------ ...
... Following is a list of essay questions. The essay questions on Test 1 will be taken from this list. You should prepare for the essay part of that test by being able to answer all of them. Your answer must consist of complete sentences. Outline answers will lose points. ------------------------------ ...
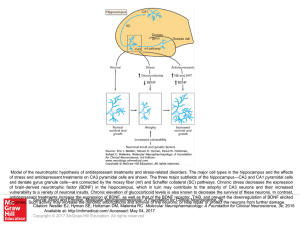
Slide ()
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... – It is not released by calcium-dependent exocytosis (it diffuses) – Its inactivation is passive (there is no active process that terminates its action) • It decays spontaneously – It does not interact with receptors on target cells • Its sphere of action depends on the extent to which it diffuses, ...
... – It is not released by calcium-dependent exocytosis (it diffuses) – Its inactivation is passive (there is no active process that terminates its action) • It decays spontaneously – It does not interact with receptors on target cells • Its sphere of action depends on the extent to which it diffuses, ...
PID *****2515 1.Why is it difficult to understand olfactory neural
... Binding of an odorant to an odorant receptor is loose compared to other GPCRs (p50). The looseness of ORodorant binding is consistent with the finding that odorant dwell times are extremely short (<1ms). Unlike phototransduction amplification, the Cl influx provides the major amplification ste ...
... Binding of an odorant to an odorant receptor is loose compared to other GPCRs (p50). The looseness of ORodorant binding is consistent with the finding that odorant dwell times are extremely short (<1ms). Unlike phototransduction amplification, the Cl influx provides the major amplification ste ...
Inotropes - GEOCITIES.ws
... • Most frequently used inotropic agent in ICU • All act on adrenergic receptors ...
... • Most frequently used inotropic agent in ICU • All act on adrenergic receptors ...
The Reflex Arc
... that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
... that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...