THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
Stress and Brain Development
... While the stress response is vital for our survival, too much stress has deleterious effects on many aspects of our physiology, including immune responses, the cardiovascular system, and our reproductive abilities. It is less well appreciated that excessive stress also compromises the nervous system ...
... While the stress response is vital for our survival, too much stress has deleterious effects on many aspects of our physiology, including immune responses, the cardiovascular system, and our reproductive abilities. It is less well appreciated that excessive stress also compromises the nervous system ...
Chapter 2
... adrenal gland transplants electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
... adrenal gland transplants electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
... Nerve cells or ______________ are highly specialized body cells that convey impulses from one part of the body to the CNS or vice versa. Neurons have important properties like ______________ or the ability to respond to stimuli and ________________ or the ability to transmit a signal. A neuron consi ...
Powerpoint slides
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
... Is located below thalamus It synthesizes & secretes certain hormones which in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones It controls body temperature, hunger, thirst ...
In Pursuit of Ecstasy - Heartland Community College
... • Automatic movements in response to stimuli • In simplest reflex arcs, sensory neurons synapse directly on motor neurons • Most reflexes involve an interneuron ...
... • Automatic movements in response to stimuli • In simplest reflex arcs, sensory neurons synapse directly on motor neurons • Most reflexes involve an interneuron ...
21st_Biology_B6_Revision_Powerpoint
... If neural pathways are not used then they are destroyed. If a new skill, such as language, has not been learned by a particular stage in development, an animal or child may not be able to learn it in the same way. Feral children are children who have been isolated in some way so don’t go through nor ...
... If neural pathways are not used then they are destroyed. If a new skill, such as language, has not been learned by a particular stage in development, an animal or child may not be able to learn it in the same way. Feral children are children who have been isolated in some way so don’t go through nor ...
Name - IB Bio Y2
... brain stem have irreversibly lost all neurological function”. The pupil reflex, along with other tests, is useful because it is a cranial reflex rather than a spinal reflex. Some spinal reflexes, such as the knee jerk reflex, may still be active during brain death because they do not rely on brain a ...
... brain stem have irreversibly lost all neurological function”. The pupil reflex, along with other tests, is useful because it is a cranial reflex rather than a spinal reflex. Some spinal reflexes, such as the knee jerk reflex, may still be active during brain death because they do not rely on brain a ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... Once released, dopamine travels across a synapse, and binds to a receptor on a postsynaptic neurone. This sends a signal to that Cocaine interferes nerve cell, which produces a with a chemical good feeling. Under normal messenger in the conditions, once the dopamine brain called sends that signa ...
... Once released, dopamine travels across a synapse, and binds to a receptor on a postsynaptic neurone. This sends a signal to that Cocaine interferes nerve cell, which produces a with a chemical good feeling. Under normal messenger in the conditions, once the dopamine brain called sends that signa ...
the limbic system
... Different classes of postsynaptic glutamate receptors transduce the glutamate signal into electrical & biochemical events in the postsynaptic neuron. The -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptor opens {unconditionally} in response to glutamate binding and me ...
... Different classes of postsynaptic glutamate receptors transduce the glutamate signal into electrical & biochemical events in the postsynaptic neuron. The -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptor opens {unconditionally} in response to glutamate binding and me ...
Slide
... 2. The NMDA receptors now respond actively to glutamate and admit large amount of Ca2+ through their channels 3. After induction of LTP, transmission at non-NMDA receptors is facilitated (entry of Na+) ...
... 2. The NMDA receptors now respond actively to glutamate and admit large amount of Ca2+ through their channels 3. After induction of LTP, transmission at non-NMDA receptors is facilitated (entry of Na+) ...
Gene Section CMKOR1 (chemokine orphan receptor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Orphan receptor, but its endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. The protein is also a coreceptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV). RDC1 belongs to a family of G-protein coupled receptors, which includes hormone, neurotransmitter and light receptors, all of which transduce extracellul ...
... Orphan receptor, but its endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. The protein is also a coreceptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV). RDC1 belongs to a family of G-protein coupled receptors, which includes hormone, neurotransmitter and light receptors, all of which transduce extracellul ...
2222222222222222222 System • Responsible for coordinating the
... _________ neurons- sends information from the CNS to the muscle cells or the glands __________ Neurons- Nerve cells transmits information about the internal and external environment changes to the CNS ...
... _________ neurons- sends information from the CNS to the muscle cells or the glands __________ Neurons- Nerve cells transmits information about the internal and external environment changes to the CNS ...
Ecstasy
... plays an important role in mood regulation, appetite and your senses. 2. There are 10 serotonin receptors on the receiving neuron that receive the serotonin signal. 3. There are 5 recycling receptors on the synapse of the sending neuron that pick the serotonin back up after it does its job. 4. Serot ...
... plays an important role in mood regulation, appetite and your senses. 2. There are 10 serotonin receptors on the receiving neuron that receive the serotonin signal. 3. There are 5 recycling receptors on the synapse of the sending neuron that pick the serotonin back up after it does its job. 4. Serot ...
Abstract
... sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has not been completely understood so far, while it appears to be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. Orexin, also called hypocretin is a neuropeptide recently identified as a natural liga ...
... sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has not been completely understood so far, while it appears to be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. Orexin, also called hypocretin is a neuropeptide recently identified as a natural liga ...
Slide 1 - King Edward Medical University
... G Protein-Linked Receptors Subunit of G protein separates and activates an effector molecule (causing a functional change). Epinephrine effects different cells differently (heart muscle contracts, intestinal vascular smooth muscle relaxes more nutrients absorbed (Adnl C inhibition). ...
... G Protein-Linked Receptors Subunit of G protein separates and activates an effector molecule (causing a functional change). Epinephrine effects different cells differently (heart muscle contracts, intestinal vascular smooth muscle relaxes more nutrients absorbed (Adnl C inhibition). ...
Powerpoint - Center Grove Community School
... substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
... substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
Claudia G. Almeida, Group leader CG Almeida graduated in
... Having in mind that a better knowledge of cell biology was in need to tackle the mechanism whereby Aβ causes AD, she joined the laboratory of Prof. Louvard at the Curie Institute in Paris in 2007, to work with Dr. Coudrier an expert on regulation of intracellular traffic by the actin cytoskeleton. D ...
... Having in mind that a better knowledge of cell biology was in need to tackle the mechanism whereby Aβ causes AD, she joined the laboratory of Prof. Louvard at the Curie Institute in Paris in 2007, to work with Dr. Coudrier an expert on regulation of intracellular traffic by the actin cytoskeleton. D ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
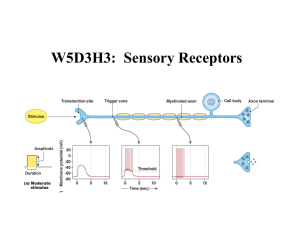
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... for many people and because changes in how stimuli are detected and integrated can be used to identify more serious conditions, it is essential to understand this process. This material also integrates physiology, HFF, and clinical topics by explaining how nerve damage from diabetes can alter neuron ...
... for many people and because changes in how stimuli are detected and integrated can be used to identify more serious conditions, it is essential to understand this process. This material also integrates physiology, HFF, and clinical topics by explaining how nerve damage from diabetes can alter neuron ...
lesson 6
... • Nerve signals are transmitted by action potentials that are abrupt, pulse-like changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of ...
... • Nerve signals are transmitted by action potentials that are abrupt, pulse-like changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of ...
Document
... Produces a continuous postsynaptic effect Blocks reception of additional “messages” Must be removed from its receptor ...
... Produces a continuous postsynaptic effect Blocks reception of additional “messages” Must be removed from its receptor ...