File - Mr. Greenwood Science
... The interneuron then sends an impulse to a motor neuron. The motor neuron then signals its muscle to act. This whole pathway is called an Arc Reflex ...
... The interneuron then sends an impulse to a motor neuron. The motor neuron then signals its muscle to act. This whole pathway is called an Arc Reflex ...
Pre- or postsynaptic distribution of distinct endocannabinoid
... synapses (Katona & Freund, 2008). Upon excess presynaptic activity, it is released from the postsynaptic neuron, passes the synaptic cleft and activates presynaptic CB1 receptors, leading to the reduction of further neurotransmitter release from the axon terminals (Wilson & Nicoll, 2002). Variations ...
... synapses (Katona & Freund, 2008). Upon excess presynaptic activity, it is released from the postsynaptic neuron, passes the synaptic cleft and activates presynaptic CB1 receptors, leading to the reduction of further neurotransmitter release from the axon terminals (Wilson & Nicoll, 2002). Variations ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
Role of Neurotransmitters on Memory and Learning
... go about their job of processing and prioritizing information. Thus peptides filter the input of our senses, significantly altering our perception of reality and selecting which stimuli will be allowed in. “Emotions and bodily sensations”, says Pert, “are thus intricately interwined, in a bidirectio ...
... go about their job of processing and prioritizing information. Thus peptides filter the input of our senses, significantly altering our perception of reality and selecting which stimuli will be allowed in. “Emotions and bodily sensations”, says Pert, “are thus intricately interwined, in a bidirectio ...
proposal2000a.doc
... the deprived barrels. This effect was observed in both neonatally and adult deprived rats, and was still present even after allowing the rats to grow their whiskers for ten additional weeks after the trimming period. Thus, these overall decreases after deprivation were suggested as a downregulating ...
... the deprived barrels. This effect was observed in both neonatally and adult deprived rats, and was still present even after allowing the rats to grow their whiskers for ten additional weeks after the trimming period. Thus, these overall decreases after deprivation were suggested as a downregulating ...
Autonomic nervous system
... voluntary movements, thus it complements the function of the pyramidal system. The “basal ganglia” constitute an essential part of this system. Degenerative changes in the pathway running from the “substantia nigra” to the “corpus striatum” (or nigrostriatal pathway) may cause tremors and muscle rig ...
... voluntary movements, thus it complements the function of the pyramidal system. The “basal ganglia” constitute an essential part of this system. Degenerative changes in the pathway running from the “substantia nigra” to the “corpus striatum” (or nigrostriatal pathway) may cause tremors and muscle rig ...
* Certain neurons in the brain have receptors (opioid receptors) for
... Tolerance – to a drug occurs when increasing the dosage of the drug is required to achieve the effects that initially occurred in response to a smaller dose. Two theories below : 1) Based on previous drug use; the presence of the drug stimulates the synthesis of the enzymes that degrade the drug in ...
... Tolerance – to a drug occurs when increasing the dosage of the drug is required to achieve the effects that initially occurred in response to a smaller dose. Two theories below : 1) Based on previous drug use; the presence of the drug stimulates the synthesis of the enzymes that degrade the drug in ...
here - STAO
... Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two examples. Instead of exciting neurons, it inhibits inhibitory neurons. This causes the same end result of stimulation of the nervous system. Barbiturates and Valium mimic GABA, and increase its inhibitory effe ...
... Caffeine is also a stimulant, but its actions are a little different from the previous two examples. Instead of exciting neurons, it inhibits inhibitory neurons. This causes the same end result of stimulation of the nervous system. Barbiturates and Valium mimic GABA, and increase its inhibitory effe ...
Kinase clamping
... demonstrate a way of creating ‘designer’ receptors that are specifically activated by a ligand with no other biological activity in the cell. G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) are an important class of membrane proteins that orchestrate a wide variety of cellular responses by binding environmental ...
... demonstrate a way of creating ‘designer’ receptors that are specifically activated by a ligand with no other biological activity in the cell. G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) are an important class of membrane proteins that orchestrate a wide variety of cellular responses by binding environmental ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Outline
... Found in the brain, inhibitory in nature Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with schizophrenia o Schizophrenia Symptoms: delusions ...
... Found in the brain, inhibitory in nature Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with schizophrenia o Schizophrenia Symptoms: delusions ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
Chapter 41
... Thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect internal changes in temperature and initiates homeostatic mechanisms to maintain constant body temperature. ...
... Thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect internal changes in temperature and initiates homeostatic mechanisms to maintain constant body temperature. ...
Central adrenergic receptor changes in the
... Adrenergic receptor binding characteristics were analyzed in the mutant mouse tottering (tg/tg), a single gene locus autosomal recessive mutation causing hyperinnervation by locus coeruleus neurons of their target regions, which results in epilepsy. Instead of the expected down-regulation of recepto ...
... Adrenergic receptor binding characteristics were analyzed in the mutant mouse tottering (tg/tg), a single gene locus autosomal recessive mutation causing hyperinnervation by locus coeruleus neurons of their target regions, which results in epilepsy. Instead of the expected down-regulation of recepto ...
83 - VCU
... Finally, before answering the following questions, read and analyze them carefully to identify the information being requested. When you have done this, write your response, using the same organizational format as the question. Be sure to address each point raised in the question, but you are strong ...
... Finally, before answering the following questions, read and analyze them carefully to identify the information being requested. When you have done this, write your response, using the same organizational format as the question. Be sure to address each point raised in the question, but you are strong ...
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2
... binding, ionotropic, and selective for Na+ and K+. NMDA also has a Ca2+ current. AMPA receptor produces a fast, short-duration EPSP. (AMPA receptors are NOT voltage-dependent) NMDA has a voltage-dependent current and does not produce much of an EPSP current at a Vm of –65 mV because Mg2+ blocks the ...
... binding, ionotropic, and selective for Na+ and K+. NMDA also has a Ca2+ current. AMPA receptor produces a fast, short-duration EPSP. (AMPA receptors are NOT voltage-dependent) NMDA has a voltage-dependent current and does not produce much of an EPSP current at a Vm of –65 mV because Mg2+ blocks the ...
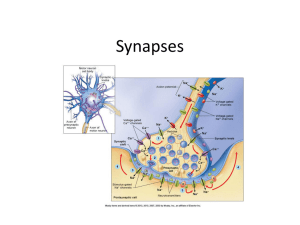
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... • 1. synaptic knob—bulge at end of one axon terminal of presynaptic neuron • 2. synaptic cleft-tiny (25 nm) gap between two neurons • 3. plasma membrane of post synaptic neuron– usually at the dendrite or cell body- contains protein receptors ...
... • 1. synaptic knob—bulge at end of one axon terminal of presynaptic neuron • 2. synaptic cleft-tiny (25 nm) gap between two neurons • 3. plasma membrane of post synaptic neuron– usually at the dendrite or cell body- contains protein receptors ...
How Opioid Drugs Bind to Receptors
... These crystal structures2–5 of inactive ORs receptor (Fig. 1), forming interactions mostly another GPCR — the β1-adrenergic recep- will contribute crucial information to a broad with those helices, but also with TM7. Accord- tor — different conformations of TM1 (and range of therapeutic areas, incl ...
... These crystal structures2–5 of inactive ORs receptor (Fig. 1), forming interactions mostly another GPCR — the β1-adrenergic recep- will contribute crucial information to a broad with those helices, but also with TM7. Accord- tor — different conformations of TM1 (and range of therapeutic areas, incl ...
see p. A4b - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... TRANSMITTERS OF MOTOR SYSTEM..................................................................................................... 20 TRANSMITTERS OF AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – see p. A34 NEUROTRANSMITTER – endogenous chemical agent that relays information from one neuron to another through synapse; ...
... TRANSMITTERS OF MOTOR SYSTEM..................................................................................................... 20 TRANSMITTERS OF AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM – see p. A34 NEUROTRANSMITTER – endogenous chemical agent that relays information from one neuron to another through synapse; ...
Additional Nervous System Notes
... 1. nicotine – causes release of adrenaline from the adrenal glands, increases blood pressure and heart beat – affects mood, acts like a stimulant and causes feeling of euphoria 2. caffeine – increases heart rate and urine production – causes some mood elevation and increases alertness 3. cocaine – r ...
... 1. nicotine – causes release of adrenaline from the adrenal glands, increases blood pressure and heart beat – affects mood, acts like a stimulant and causes feeling of euphoria 2. caffeine – increases heart rate and urine production – causes some mood elevation and increases alertness 3. cocaine – r ...
Cell Signalling
... Responses induced by the activation of a nuclear hormone receptor. (A) Early primary response and (B) delayed secondary response. The figure shows the responses to a steroid hormone, but the same principles apply for all ligands that activate this family of receptor proteins. Some of the primary-re ...
... Responses induced by the activation of a nuclear hormone receptor. (A) Early primary response and (B) delayed secondary response. The figure shows the responses to a steroid hormone, but the same principles apply for all ligands that activate this family of receptor proteins. Some of the primary-re ...
File
... Regulation of pain: A person becomes aware of pain when impulses reach the _______________ in the brain, but the _________ cortex judges the intensity and location of the pain. Other areas of the brain regulate the flow of pain impulses from the spinal cord and can trigger the release of Chemicals c ...
... Regulation of pain: A person becomes aware of pain when impulses reach the _______________ in the brain, but the _________ cortex judges the intensity and location of the pain. Other areas of the brain regulate the flow of pain impulses from the spinal cord and can trigger the release of Chemicals c ...