Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... of different elements are different. 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of 2 or more elements combine w/ each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, but not atoms are destroyed or created. “ ...
... of different elements are different. 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of 2 or more elements combine w/ each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, but not atoms are destroyed or created. “ ...
Chapter 22- Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Chapter 22- Properties of Atoms and the Periodic
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... iv. ______________________________ is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. v. Average atomic mass is closest to its most a_______________ isotope. The Periodic Table a. Elements are organized in the _________________ by increasing atomic number. i. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... 11. Which of these types of nuclear radiation has the greatest penetrating power? (1) alpha (3) neutron (2) beta (4) gamma 12. Alpha particles and beta particles differ in (1) mass, only (2) charge, only (3) both mass and charge (4) neither mass nor charge 13. Which equation represents a fusion reac ...
... 11. Which of these types of nuclear radiation has the greatest penetrating power? (1) alpha (3) neutron (2) beta (4) gamma 12. Alpha particles and beta particles differ in (1) mass, only (2) charge, only (3) both mass and charge (4) neither mass nor charge 13. Which equation represents a fusion reac ...
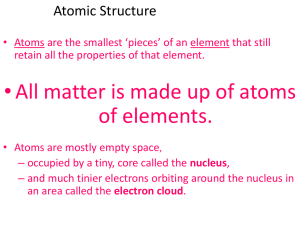
What is Matter? Anything that can be smelled, tasted, touched… Has
... Smallest part or piece of matter that still has the properties of matter Proton: Positively charged particle; largest of three particles; symbol is P+ Neutron: Neutrally charged particle; has both positive and negative charges; slightly smaller than proton; symbol is N= Electron: Negatively charge p ...
... Smallest part or piece of matter that still has the properties of matter Proton: Positively charged particle; largest of three particles; symbol is P+ Neutron: Neutrally charged particle; has both positive and negative charges; slightly smaller than proton; symbol is N= Electron: Negatively charge p ...
Subatomic Particles
... • The ____________ (Z) of an element never changes. However, the number of _______ can vary from one atom of the element to the next. • Examples: 1. ordinary hydrogen= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° 2. deuterium= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° 3. tritium= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° • All three forms of hydr ...
... • The ____________ (Z) of an element never changes. However, the number of _______ can vary from one atom of the element to the next. • Examples: 1. ordinary hydrogen= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° 2. deuterium= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° 3. tritium= ___ p+, ___ e-, and ___ n° • All three forms of hydr ...
HONORS EARTH SCIENCE HOMEWORK, Ch2, Sec 1 Atoms and
... composed of small particles. He called these particles ________. 2. Three basic particles make up an atom: ____________, __________, and ___________. 3. __________ are particles that have a positive electric charge. 4. _________ have no electric charge. 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ...
... composed of small particles. He called these particles ________. 2. Three basic particles make up an atom: ____________, __________, and ___________. 3. __________ are particles that have a positive electric charge. 4. _________ have no electric charge. 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ...
Bill Nye Atoms and Molecules
... If a nucleus were the size of a baseball, how far away would the electrons be? ...
... If a nucleus were the size of a baseball, how far away would the electrons be? ...
Atoms of an element can lose or gain electrons and still
... (pg. 36, P2) 2. Three basic particles make up an atom: ____________, __________, and ___________. (pg 36, P3) 3. __________ are particles that have a positive electric charge. (pg. 36, P3) 4. _________ have no electric charge. (pg. 36, P3) 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ________ and ...
... (pg. 36, P2) 2. Three basic particles make up an atom: ____________, __________, and ___________. (pg 36, P3) 3. __________ are particles that have a positive electric charge. (pg. 36, P3) 4. _________ have no electric charge. (pg. 36, P3) 5. Particles with a negative charge are called ________ and ...
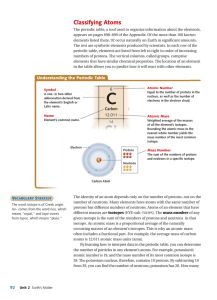
Classifying Atoms
... The identity of an atom depends only on the number of protons, not on the number of neutrons. Many elements have atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of an element that have different masses are isotopes (EYE-suh-TOHPS). The mass number of any given isotope ...
... The identity of an atom depends only on the number of protons, not on the number of neutrons. Many elements have atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms of an element that have different masses are isotopes (EYE-suh-TOHPS). The mass number of any given isotope ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. ...
... • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. ...
atoms - Trinity Regional School
... chemically combined homogeneous Mixture – 2 or more elements, compounds, or both physically combined. homogenous or heterogeneous ...
... chemically combined homogeneous Mixture – 2 or more elements, compounds, or both physically combined. homogenous or heterogeneous ...
What is Matter
... Atom Smallest part or piece of matter that still has the properties of matter Proton: Positively charged particle; largest of three particles; symbol is P+ Neutron: Neutrally charged particle; has both positive and negative charges; slightly smaller than proton; symbol is N= Electron: Negatively ch ...
... Atom Smallest part or piece of matter that still has the properties of matter Proton: Positively charged particle; largest of three particles; symbol is P+ Neutron: Neutrally charged particle; has both positive and negative charges; slightly smaller than proton; symbol is N= Electron: Negatively ch ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Moves around the nucleus at such speeds that they cannot be seen. ...
... Moves around the nucleus at such speeds that they cannot be seen. ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... 38. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent which orbital (s)? 39. How many orbital shapes are in the first energy level? Second? Third? Fourth? What are they? 40. Both copper (atomic number 29) and chromium (atomic number 24) appear to break the pattern in the ...
... 38. A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best represent which orbital (s)? 39. How many orbital shapes are in the first energy level? Second? Third? Fourth? What are they? 40. Both copper (atomic number 29) and chromium (atomic number 24) appear to break the pattern in the ...
The Nature of Molecules
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... Energy Levels of Electrons ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or ...
... Energy Levels of Electrons ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or ...
Chapter 18
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
Atom through Periodic Table Study Guide
... ____7. Determined the charge then calculated the mass of an electron in his oil drop experiment. ____8. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____9. Believed that the world was made of mat ...
... ____7. Determined the charge then calculated the mass of an electron in his oil drop experiment. ____8. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____9. Believed that the world was made of mat ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... • Classification systems are methods of grouping things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their prope ...
... • Classification systems are methods of grouping things together in a way that makes sense, so that like are with like – makes it easier to find things if you know where to look. • The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, as a way of classifying elements according to their prope ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Guided Notes: The Atom
... Millikan-oil drop experiment; found quantity of charge on an _________: carries exactly _____________ of charge, and mass is 1/1840 the mass of a proton Rutherford-1910; __________________ experiment; model of the atom- discovered nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space ...
... Millikan-oil drop experiment; found quantity of charge on an _________: carries exactly _____________ of charge, and mass is 1/1840 the mass of a proton Rutherford-1910; __________________ experiment; model of the atom- discovered nucleus and that the atom is mostly empty space ...