History of the Atom
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike o Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
... In 1803, proposed an Atomic Theory which states: o All substances are made of atoms; atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. o Atoms of the same element are exactly alike o Atoms join with other atoms to make new substances ...
Preview Sample 1
... Structure of the Atom Use the structure of atoms to describe how the composition of atoms can differ. Understand the experiments used to determine the structure of the atom. Compare the properties of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons f ...
... Structure of the Atom Use the structure of atoms to describe how the composition of atoms can differ. Understand the experiments used to determine the structure of the atom. Compare the properties of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons f ...
The History of the Atom Carousel Who-What-When
... Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ the term oxygen as the emitted gas. Lavoisier published the first text on Chemistry, giving the first names to many ...
... Antoine Lavoisier in France and explained what he had done. Lavoisier was a noted scientist who used better methodology and measurements in his work. For Priestly’s ‘air’ he ‘invented’ the term oxygen as the emitted gas. Lavoisier published the first text on Chemistry, giving the first names to many ...
TEST II Study Guide-Atomic Theory Honors Chemistry
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
... 6. ______ What type of bombarding particle was used in Rutherford's "gold foil" experiment? A) alpha; B) beta; C) gamma; D) neutron; E) neutrino; F) X rays. 7. ______ This color-blind English schoolteacher studied the findings of many of his contemporaries, and put forth the first comprehensive atom ...
Ch. 4 Sec. 1 Introduction to Atoms
... 1. All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. 3. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot ...
... 1. All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. 3. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot ...
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE chapter three
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
Element Blocks Project
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
... Your assignment is to produce an element block that will have six sides, each having different information about your element. Elements will be assigned randomly. Your teacher will show you how to make the block after you have researched and obtained all the information that will go onto you block. ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
... • In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of the proton with his nowfamous gold-foil experiment • He shot α-particles at the foil…most passed through, but some were reflected back at the fluorescent ...
Atom Building blocks of matter Proton Sub
... Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties ...
... Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... and protons have a mass of 1 dalton (same as atomic mass unit) Atomic number – number of protons ...
... and protons have a mass of 1 dalton (same as atomic mass unit) Atomic number – number of protons ...
Atomic Structure
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms ...
... Different atoms have different ____________ and ____________ The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape, and movement of ____________ Changes in matter result from changes in the ____________ of atoms and not the atoms ...
The Atom
... Mass can vary from 10 to 14 Average is mass of 12- all others are isotopes Can get mass with decimal – but can’t get a partial proton or neutron! Sample Problems An elements has 35 protons and 47 neutrons; a second element has 34 protons and 47 neutrons. Are they isotopes or different elements? Diff ...
... Mass can vary from 10 to 14 Average is mass of 12- all others are isotopes Can get mass with decimal – but can’t get a partial proton or neutron! Sample Problems An elements has 35 protons and 47 neutrons; a second element has 34 protons and 47 neutrons. Are they isotopes or different elements? Diff ...
Structure of the Atom
... 4. What structural characteristics do all hydrogen atoms have in common? ...
... 4. What structural characteristics do all hydrogen atoms have in common? ...
Scientists timeline
... How did Dalton create his theory? • Studied the way elements combined in chemical reactions and the ratio in which they combined • Ex: Liquid mercury • All drops have the same properties • All drops are made of the same atoms ...
... How did Dalton create his theory? • Studied the way elements combined in chemical reactions and the ratio in which they combined • Ex: Liquid mercury • All drops have the same properties • All drops are made of the same atoms ...
Chapter 5 - Geocities
... Alkali metals: Group 1 of the Periodic Table Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ ...
... Alkali metals: Group 1 of the Periodic Table Alkaline-earth metals: Group 2 Transition elements: d-block elements with typical metallic properties Main-Group elements: p-block elements and s-block elements Halogens: Group 17 Section 3: Electron Configuration and Periodic Properties Atomic radius: ½ ...
Atomic Theory: the beginning
... opposite direction. He called these canal rays and That they had a positive charge. We now call them protons. Their mass is 1840 times an electron ...
... opposite direction. He called these canal rays and That they had a positive charge. We now call them protons. Their mass is 1840 times an electron ...
Physical Science Notes–Ch. 17-Glencoe
... So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of __________uniquely different ...
... So far, scientists have confirmed the existence of __________uniquely different ...
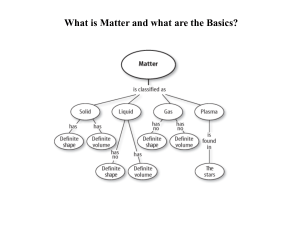
Matter and the Periodic Table
... The Periodic Table In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev (18341907) succeeded in organizing the 62 elements known at that time into a system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar propert ...
... The Periodic Table In 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev (18341907) succeeded in organizing the 62 elements known at that time into a system of rows and columns on the basis of increasing mass and similar chemical and physical properties. Since the organization exhibited a periodic repetition of similar propert ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... All light, whether radiowaves or visible light, travels as the same speed, 3 *108 meters/sec As a result, since the length of each wave decreases from left to right, the frequency of the peaks an troughs of the waves shown above must increase from left to right Referring to light as a particle, know ...
... All light, whether radiowaves or visible light, travels as the same speed, 3 *108 meters/sec As a result, since the length of each wave decreases from left to right, the frequency of the peaks an troughs of the waves shown above must increase from left to right Referring to light as a particle, know ...