Midterm Practice Test Answers
... Modern atom has electron clouds, whereas Bohr’s model had specific rings (energy levels). That is because we only know the probability of where an electron is. ...
... Modern atom has electron clouds, whereas Bohr’s model had specific rings (energy levels). That is because we only know the probability of where an electron is. ...
Structure of Atoms/Periodic Table Review 1. Shade in location of the
... 2. How is the modern periodic table organized? 3. Who created the first periodic table? 4. What can you predict about an element based on where it is on the periodic table? ...
... 2. How is the modern periodic table organized? 3. Who created the first periodic table? 4. What can you predict about an element based on where it is on the periodic table? ...
Atomic Structure Test Review Answer Key - Unit 1
... f. Isotope- two atoms of same element that have differing number of neutrons. g. Nucleus- Center of atom. Contains the protons and neutrons. h. mass number- sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. i. atomic number- indicates the number of protons in an atom. j. atomic mass- weighted average of a ...
... f. Isotope- two atoms of same element that have differing number of neutrons. g. Nucleus- Center of atom. Contains the protons and neutrons. h. mass number- sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. i. atomic number- indicates the number of protons in an atom. j. atomic mass- weighted average of a ...
Atomic History notes
... law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of ...
... law of multiple proportions-In all cases, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of another element will form simple, wholenumber rations. From the evidence of the above 3 laws, in 1803 Dalton proposed an atomic theory of matter. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Theory(1766-1844) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix ...
... - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Theory(1766-1844) 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix ...
Chemistry10AtomicTheory
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes th ...
Atoms and Elements
... Electrons circle the nucleus in a paths called orbits or energy levels. Low-energy = orbit close to nucleus High-energy = orbit father away. Most of an atoms mass is in the nucleus; protons and neutrons have the same mass; electrons as about 1/2000 of a proton ...
... Electrons circle the nucleus in a paths called orbits or energy levels. Low-energy = orbit close to nucleus High-energy = orbit father away. Most of an atoms mass is in the nucleus; protons and neutrons have the same mass; electrons as about 1/2000 of a proton ...
3.1 Classifying Chemical Compounds
... to decide whether the bond between two atoms is ionic or covalent. The symbol Δ EN stands for the difference between two electronegativity values. When calculating the Δ EN, the smaller EN is always subtracted from the larger EN, so that the Δ EN is always positive. ...
... to decide whether the bond between two atoms is ionic or covalent. The symbol Δ EN stands for the difference between two electronegativity values. When calculating the Δ EN, the smaller EN is always subtracted from the larger EN, so that the Δ EN is always positive. ...
ReviewCat1 - greenslime.info
... Conductivity - ability to transfer heat and/or electricity Density - measure of a materials mass per unit volume (m/v) Luster - describes how a material reflect light Malleability - materials flexibility without breaking Metals - good conductors of heat/electricity Metalloids - have properties of bo ...
... Conductivity - ability to transfer heat and/or electricity Density - measure of a materials mass per unit volume (m/v) Luster - describes how a material reflect light Malleability - materials flexibility without breaking Metals - good conductors of heat/electricity Metalloids - have properties of bo ...
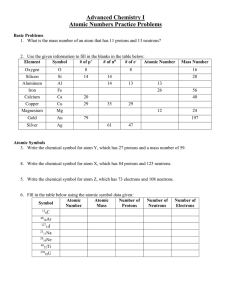
Atomic Numbers Practice Problems
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). ...
... atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). ...
Quantumatom
... do you find the atomic number on the periodic table? What is the atomic number of Oxygen? Where do you find the mass number on the periodic table? What is the mass number of Oxygen? ...
... do you find the atomic number on the periodic table? What is the atomic number of Oxygen? Where do you find the mass number on the periodic table? What is the mass number of Oxygen? ...
Atomic Structure
... ________ The Alkali Earth with the smallest atomic radius. ________ Element number 14 (element with atomic number 14). ________ The second period noble gas. ________ The first metal in group 1. ________ An element that reacts like chlorine, but has a smaller atomic radius. ________ A third period el ...
... ________ The Alkali Earth with the smallest atomic radius. ________ Element number 14 (element with atomic number 14). ________ The second period noble gas. ________ The first metal in group 1. ________ An element that reacts like chlorine, but has a smaller atomic radius. ________ A third period el ...
Unit 10: Chemical Periodicity
... 12. ____________ Chlorine has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p7. 13. ____________ The element in Group 14, period 3, is gallium. 14. ____________ There is a relationship between the electron configuration of elements and their chemical and physical properties. Part C Matching 15. _______ pe ...
... 12. ____________ Chlorine has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p7. 13. ____________ The element in Group 14, period 3, is gallium. 14. ____________ There is a relationship between the electron configuration of elements and their chemical and physical properties. Part C Matching 15. _______ pe ...
ISOTOPES 3 SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Proton Located inside the
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
... Located outside of the nucleus in an “electron cloud” Involved in chemical bonding Negative charge Equal to the # of protons in a neutral atom How many electrons does Potassium have? How many electrons does Nitrogen have? o Neutron Located inside the nucleus of an atom No charge # ...
Element: a pure, simple substance that can`t be broken down into
... What is the smallest unit of matter that we can find everywhere, even in tuna fish? What charge do electrons have? What are elements? Who organized the atomic elements? What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of p ...
... What is the smallest unit of matter that we can find everywhere, even in tuna fish? What charge do electrons have? What are elements? Who organized the atomic elements? What do we call a horizontal row on the periodic table? What do we call the vertical columns on the periodic table? The number of p ...
CHM 1032C: Vocabulary Chapter 3
... Main group element - An element in one of the two groups on the left or the six groups on the right of the periodic table. Mass number (A) - The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Neutrons - An electrically neutral subatomic particle. Noble gas - An element in group 8A of the periodic ...
... Main group element - An element in one of the two groups on the left or the six groups on the right of the periodic table. Mass number (A) - The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Neutrons - An electrically neutral subatomic particle. Noble gas - An element in group 8A of the periodic ...
levels of organization and the atom
... the levels of organization that life shows. You must use and underline at least four (regular) or six (honor) key words. Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. Name Charge Mass L ...
... the levels of organization that life shows. You must use and underline at least four (regular) or six (honor) key words. Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. Name Charge Mass L ...
Atomic Theory Outline
... 3. Mass of 1 amu each (same as neutron) ii. Neutrons 1. Neutral (no/0) charge 2. Made of 3 quarks 3. Mass of 1 amu (same as proton) b. Electrons i. Negative charge (1-) ii. In a cloud around the nucleus – moving quickly so we imagine it to be blurry like the blades of a fan. Cloud makes up most of t ...
... 3. Mass of 1 amu each (same as neutron) ii. Neutrons 1. Neutral (no/0) charge 2. Made of 3 quarks 3. Mass of 1 amu (same as proton) b. Electrons i. Negative charge (1-) ii. In a cloud around the nucleus – moving quickly so we imagine it to be blurry like the blades of a fan. Cloud makes up most of t ...
Bill Nye Atoms Workseet
... With hydrogen in H2O on side and oxygen on the other, the model looks kind of like ____________________ One plus one doesn’t always ____________________________ ___________________________ There are lots of _______________ _________________ in the rubbing alcohol where water molecules can fit. The m ...
... With hydrogen in H2O on side and oxygen on the other, the model looks kind of like ____________________ One plus one doesn’t always ____________________________ ___________________________ There are lots of _______________ _________________ in the rubbing alcohol where water molecules can fit. The m ...
Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Atomic Theory of Matter
... Parts of an atom o Nucleus—dense central core composed of protons and neutrons o Electrons surround the nucleus o Protons and neutrons are made up of small particles called quarks o Protons have positive charge and electrons have a negative charge ...
... Parts of an atom o Nucleus—dense central core composed of protons and neutrons o Electrons surround the nucleus o Protons and neutrons are made up of small particles called quarks o Protons have positive charge and electrons have a negative charge ...