Timeline of Atomic Theory--pdf
... Sir Ernest Rutherford's great contribution to modern science was to show what happens to an element during radioactive decay. This enabled him to construct the first nuclear model of the atom, a cornerstone of present-day ...
... Sir Ernest Rutherford's great contribution to modern science was to show what happens to an element during radioactive decay. This enabled him to construct the first nuclear model of the atom, a cornerstone of present-day ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
... become more stable by emitting radiation. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This radiation can be emitted in the form of a positively charged alpha particle, a negatively charged ...
Atomic Theory Notes Page
... measure its position. He found that the electron's position and momentum did indeed obey the uncertainty relation he had derived mathematically Conclusions: Electrons are located in clouds, not neat orbits; tells you where the electron is most likely to be found (a matter of probability). o Chadwi ...
... measure its position. He found that the electron's position and momentum did indeed obey the uncertainty relation he had derived mathematically Conclusions: Electrons are located in clouds, not neat orbits; tells you where the electron is most likely to be found (a matter of probability). o Chadwi ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
Magic Square and isotope worksheet
... 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment 9. Current explanation of where electrons might be found in the atom 10. Used by scientists to explain something we can not see or understand 11. The smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element 12. The number of neu ...
... 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment 9. Current explanation of where electrons might be found in the atom 10. Used by scientists to explain something we can not see or understand 11. The smallest particle of an element that has the properties of that element 12. The number of neu ...
Document
... Rutherford expected alpha particle to travel almost straight through a target of gold foil. The results of his gold foil experiment did not support a. Millikan’s oil drop experiment b. Thomson’s plum pudding theory c. the cathode ray phenomenon d. Bohr’s atomic model ...
... Rutherford expected alpha particle to travel almost straight through a target of gold foil. The results of his gold foil experiment did not support a. Millikan’s oil drop experiment b. Thomson’s plum pudding theory c. the cathode ray phenomenon d. Bohr’s atomic model ...
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
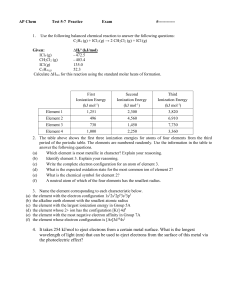
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
What is an atom?
... given element were alike • Believed different atoms could join together to form compounds • His theories are considered the foundation for modern atomic theory ...
... given element were alike • Believed different atoms could join together to form compounds • His theories are considered the foundation for modern atomic theory ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger.__________________________ 14. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____________ ...
... 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger.__________________________ 14. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____________ ...
Review for Periodic - Mr-Durands
... 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the periodic table? 7. How many groups are there? 8. What is a period on the periodic table? 9. How many periods ...
... 3. What is the number of neutrons for Cesium (Cs)? 4. What is the difference between atomic mass and number? 5. How do isotopes affect the atomic mass of an element? 6. What is a group on the periodic table? 7. How many groups are there? 8. What is a period on the periodic table? 9. How many periods ...
Atomic Structure
... • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a marble. ...
... • If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a marble. ...
atomic theory quiz II review
... Review Sheet We will have a quiz over the information you have learned about the atomic theory. Please actively study (sing, dance, act, draw, write) the following info: ...
... Review Sheet We will have a quiz over the information you have learned about the atomic theory. Please actively study (sing, dance, act, draw, write) the following info: ...
PP 04 Atoms_ molecules_ ions
... Atomic Theory: Elements composed of atoms. Atoms can’t be changed. Compounds comtain multiples of atoms. John Dalton The Law of Conservation of Mass: In ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be neither created nor destroyed. The Law of Constant Composition: Compounds always have the same proportio ...
... Atomic Theory: Elements composed of atoms. Atoms can’t be changed. Compounds comtain multiples of atoms. John Dalton The Law of Conservation of Mass: In ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be neither created nor destroyed. The Law of Constant Composition: Compounds always have the same proportio ...
Identify which of the three subatomic particles (p+, n, e–): is the
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
key - Greenslime.info
... The elements in group 17, including fluorine, bromine, chlorine and iodine, are called the halogens. Describe the reactivity of the halogens, and why they have this reactivity. The halogens are very reactive, because they each have seven valence electrons, and only need to gain one valence electron ...
... The elements in group 17, including fluorine, bromine, chlorine and iodine, are called the halogens. Describe the reactivity of the halogens, and why they have this reactivity. The halogens are very reactive, because they each have seven valence electrons, and only need to gain one valence electron ...
Unit 3 Review Worksheet
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
College Chemistry – Atomic Structure / Periodic Table Test Study
... Know how to read the periodic table -- element symbols, element name, atomic number, atomic mass, properties, group #'s, period #'s Know how to determine the number of protons, neutrons, or electrons for an element Know where metals, metalloids, nonmetals, and noble gases are on the periodic table K ...
... Know how to read the periodic table -- element symbols, element name, atomic number, atomic mass, properties, group #'s, period #'s Know how to determine the number of protons, neutrons, or electrons for an element Know where metals, metalloids, nonmetals, and noble gases are on the periodic table K ...
Chapter 4.1 Notes
... Theory 2. John Dalton – - English school teacher, 1808 - atoms could not be divided - all atoms of a given element were exactly alike - atoms of different elements could join to form compounds - developed the law of definite proportions – a chemical compound always contains the same elements in exac ...
... Theory 2. John Dalton – - English school teacher, 1808 - atoms could not be divided - all atoms of a given element were exactly alike - atoms of different elements could join to form compounds - developed the law of definite proportions – a chemical compound always contains the same elements in exac ...
Worksheet - Models of the Atom - Teacher
... models and important discoveries that led to each. (See Changing Atomic Models Notes.) 8. Draw pictures representing the models of Thomson and Rutherford. ...
... models and important discoveries that led to each. (See Changing Atomic Models Notes.) 8. Draw pictures representing the models of Thomson and Rutherford. ...
Atom Study Guide
... Democritus – first person to use the word ATOM John Dalton – experiments led to everybody agreeing that there are atoms. Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. (not true because there are smaller parts within the ...
... Democritus – first person to use the word ATOM John Dalton – experiments led to everybody agreeing that there are atoms. Came up with Dalton’s Atomic Theory. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. (not true because there are smaller parts within the ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
Periodic Table Test Chemistry 1 1. What is the horizontal row in the
... 9. What is the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound? 10.What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom? 11.What elements are in the same period as phosphorus? 12. What does each period in the periodic table corresponds to 13.The modern periodic table ...
... 9. What is the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound? 10.What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom? 11.What elements are in the same period as phosphorus? 12. What does each period in the periodic table corresponds to 13.The modern periodic table ...
(null): 096.AtomReview
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
Periodic Table Fill in Table 1
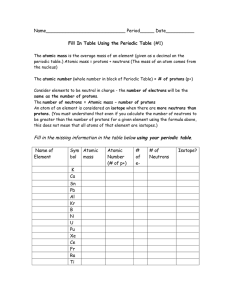
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element (given as a decimal on the periodic table.) Atomic mass = protons + neutrons (The mass of an atom comes from the nucleus) The atomic number (whole number in block of Periodic Table) = # of protons (p+) Consider elements to be neutral in charge - the ...