Document
... Elements are organized in the periodic table by increasing atomic number. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. In 1913, Henry G. J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
... Elements are organized in the periodic table by increasing atomic number. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. In 1913, Henry G. J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
Unit 5 Notes
... the d block. ITM’s are the f block. If given an element, you should be able to tell me the block that it is in. 3. We can use this information, group numbers, and period numbers to help us get our configs much faster. 4. Practice with Ag, Pd, Nb, Ca, S, and I. Note that exceptions to the Aufbau Prin ...
... the d block. ITM’s are the f block. If given an element, you should be able to tell me the block that it is in. 3. We can use this information, group numbers, and period numbers to help us get our configs much faster. 4. Practice with Ag, Pd, Nb, Ca, S, and I. Note that exceptions to the Aufbau Prin ...
for the quiz on 6 mar
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
BillNyeAtoms
... Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘light’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Whic ...
... Which particles in an atom are ‘heavy’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Which particles in an atom are ‘light’ particles? ____________________________ Where are they found? ______________________________________________ Whic ...
Name Chemistry Midterm Review Chapter # 2
... 3. Which of the following are symbols of the representative elements? Na, Mg, Fe, Ni, Cl 4. Which noble gas does not have 8 electrons in its outermost valence shell? _________ 5. Write the electron configuration of these elements: a. The noble gas in period 3 ________________________________________ ...
... 3. Which of the following are symbols of the representative elements? Na, Mg, Fe, Ni, Cl 4. Which noble gas does not have 8 electrons in its outermost valence shell? _________ 5. Write the electron configuration of these elements: a. The noble gas in period 3 ________________________________________ ...
A Brief History of the Atomic Theory
... 1911: Ernest Rutherford British physicist Proved that atoms are mostly empty space Discovered the nucleus, which contains positively charged particles First to propose electrons circle nucleus ...
... 1911: Ernest Rutherford British physicist Proved that atoms are mostly empty space Discovered the nucleus, which contains positively charged particles First to propose electrons circle nucleus ...
Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Every element consists of
... o _________________—dense central core composed of protons and neutrons o _____________ surround the nucleus o Protons and neutrons are made up of small particles called ______________ o Protons have ____________ charge and electrons have a _____________ charge ...
... o _________________—dense central core composed of protons and neutrons o _____________ surround the nucleus o Protons and neutrons are made up of small particles called ______________ o Protons have ____________ charge and electrons have a _____________ charge ...
Chemical Bonding
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
Basic structure of atoms
... – Always a whole number – Determines which type of element an atom is ...
... – Always a whole number – Determines which type of element an atom is ...
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
... Recognize that an element always contains the same number of protons. Describe the location, mass, and charge of protons, electrons, and neutrons Calculate the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in neutral atoms Define and use atomic number, mass number, isotope, valence electrons, a ...
... Recognize that an element always contains the same number of protons. Describe the location, mass, and charge of protons, electrons, and neutrons Calculate the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in neutral atoms Define and use atomic number, mass number, isotope, valence electrons, a ...
Atomic Theory
... Discovered electron clouds (s, p, d, f) Explains that electrons move like waves and not in a ...
... Discovered electron clouds (s, p, d, f) Explains that electrons move like waves and not in a ...
CHEM1101 2010-J-5 June 2010 • Describe the nature of an ionic
... electron density between the two atoms. As the electronegativity difference increases, the bonding orbital has a greater contribution from the more electronegative element. As a result the electron density is larger at the more electronegative element and the electron density between the two atoms i ...
... electron density between the two atoms. As the electronegativity difference increases, the bonding orbital has a greater contribution from the more electronegative element. As a result the electron density is larger at the more electronegative element and the electron density between the two atoms i ...
The Dalton Thompson 1889 Rutherford Niels Bohr Moseley
... The famous ‘gold foil experiment’ by Rutherford proved the ‘Plum Pudding’ model wrong as not all alpha particles passed through the gold atoms, some were deflected. The positively charged alpha particle hit a positive substance which caused it to be deflected, therefore atoms must have a nucleus whe ...
... The famous ‘gold foil experiment’ by Rutherford proved the ‘Plum Pudding’ model wrong as not all alpha particles passed through the gold atoms, some were deflected. The positively charged alpha particle hit a positive substance which caused it to be deflected, therefore atoms must have a nucleus whe ...
The Periodic Table
... • The difference between atom and element is atoms are submicroscopic particles that make up elements and element refers to the microscopic and ...
... • The difference between atom and element is atoms are submicroscopic particles that make up elements and element refers to the microscopic and ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
The atom - WordPress.com
... In 1910 JJ Thomson discovered that even atoms from the same element varied in mass. He called atoms from the same element with varying masses isotopes. The average of all the known isotopes of an element give the element its average atomic mass. Elements on the periodic table have decimals in their ...
... In 1910 JJ Thomson discovered that even atoms from the same element varied in mass. He called atoms from the same element with varying masses isotopes. The average of all the known isotopes of an element give the element its average atomic mass. Elements on the periodic table have decimals in their ...
Understanding Atomic Structure of an Element
... • Electron Shells/Orbitals – An electron has only 1/1837th the mass of an proton or neutron – Electrons move around on specific patterns outside of the nucleus (the majority of the empty space in an atom) ...
... • Electron Shells/Orbitals – An electron has only 1/1837th the mass of an proton or neutron – Electrons move around on specific patterns outside of the nucleus (the majority of the empty space in an atom) ...
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford
... -Element – matter made of atoms of only one kind (periodic table of elements) ...
... -Element – matter made of atoms of only one kind (periodic table of elements) ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
chapter_four
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
... found outside the nucleus in regions called orbitals Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus of an atom with neutrons, which have no charge There are even smaller particles but we do not study ...
pg156
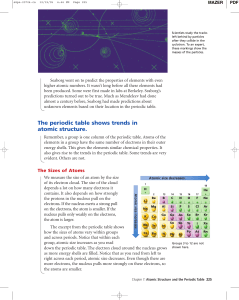
... a. How do the first ionization energies of main-group elements vary across a period and down a group? ...
... a. How do the first ionization energies of main-group elements vary across a period and down a group? ...