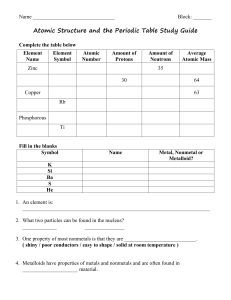
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
... Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum ...
ch2_objectives
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
... 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this model simplifies our understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic num ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 9. Why do elements in the same vertical column in the periodic table belong to the same family? _________________________________________________________________ ...
... 9. Why do elements in the same vertical column in the periodic table belong to the same family? _________________________________________________________________ ...
Reading the Periodic Table - Science
... • Electrons are added one at a time moving from left to right across a period • The electrons of the outermost shell have increasingly strong nuclear attraction, so the electrons become closer to the nucleus • Ionization energy increases • Electronegativity increases ...
... • Electrons are added one at a time moving from left to right across a period • The electrons of the outermost shell have increasingly strong nuclear attraction, so the electrons become closer to the nucleus • Ionization energy increases • Electronegativity increases ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
... Discovered e-, experiment, predictable shells, indivisible All matter made of plum pudding discovered p+, Bohr model 1st to think atoms model Atoms mostly about matter Matter cannot be empty space, dense and its’ makecreated or center up of atoms destroyed Atoms of same element look the same Chem re ...
Thursday, October 31, 2013 D-day
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
... • Radioactive Elements- no naturally occurring stable isotope (what is an isotope?). – These elements loose neutrons and protons and emit them as particles. – All manmade elements are radioactive. ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
Atomic Structure
... • Atomic Number – how many protons and electrons there are in an atom • Mass Number – total number of protons and neutrons. • Atomic Mass Units – atomic mass does appear on the periodic table and is measured in u. – Not measured on a balance, it is how they are relative to each other – A proton is a ...
... • Atomic Number – how many protons and electrons there are in an atom • Mass Number – total number of protons and neutrons. • Atomic Mass Units – atomic mass does appear on the periodic table and is measured in u. – Not measured on a balance, it is how they are relative to each other – A proton is a ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinat ...
... 3. How are ions formed from atoms? History 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinat ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
... So, what’s up with all these isotopes anyway? In nature elements are not made up of atoms that are all exactly the same! Some will be heavier than others, even though they are still the same type of atom. C-12 and C-14 are both Carbon, with all the usual Carbon properties, but the C-14 has two more ...
File
... and the momentum of a particle at the same time; “cloud” model aka quantum mechanical model ...
... and the momentum of a particle at the same time; “cloud” model aka quantum mechanical model ...
Science Review Sheet: Periodic Table Test Name: ______ Study
... List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag line. Metals Non ...
... List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag line. Metals Non ...
Periodic Table Vocab page 7
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. This number identifies the atom. Mass number: the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass number = protons + neutrons Valence #: The number of outermost electrons in an atom. Periodic Table: An arrangement of elem ...
The Chemical Basis of Life Chapter 4
... How is Matter Organized? •Divided into pure substances or mixtures based on composition. –Pure substance •Uniform composition with same properties throughout •Can be classified as either an element or a compound ...
... How is Matter Organized? •Divided into pure substances or mixtures based on composition. –Pure substance •Uniform composition with same properties throughout •Can be classified as either an element or a compound ...
Isotopes and Ions - Wando High School
... Ions IONS are charged atoms (or groups of atoms) that have a ...
... Ions IONS are charged atoms (or groups of atoms) that have a ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
... Law of Definite Proportions Nearly discovered the Law of multiple proportions, but his data used percentages instead of weights. ...
... Law of Definite Proportions Nearly discovered the Law of multiple proportions, but his data used percentages instead of weights. ...
answers
... d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
... d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
Regents Chemistry Review
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...
... together in the 12 o’clock position, continue placing electrons in the remaining positions (3, 6 & 9 o’clock), one at a time, until you have two in each; the max is an OCTET. ...
PS 2.2
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...
... the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table. Since it is an average, it is usually not a whole number. ...
File - Fern Creek Chemistry
... The number of neutrons PLUS the number of protons EQUALS an atom’s atomic mass. ...
... The number of neutrons PLUS the number of protons EQUALS an atom’s atomic mass. ...