atomic structure - IGCSE STUDY BANK
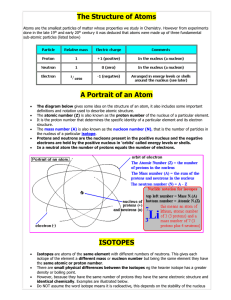
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This gives each isotope of the element a different mass or nucleon number but being the same element they have the same atomic or proton number. There are small physical differences between the isotopes eg the heavier isotope ...
Elements Unit Test
... fire, water, earth and stone earth, wind, fire and wood earth, air, water and fire stone, liquid, air and flame ...
... fire, water, earth and stone earth, wind, fire and wood earth, air, water and fire stone, liquid, air and flame ...
Chapter 4 notes outline
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
... number of neutrons Elements can have several isotopes 4.3 Modern Atomic Theory Bohr’s Model of the Atom Better description of electrons Electrons orbit around nucleus in energy levels like planets 1st Level = holds up to 2 electrons 2nd Level = holds up to 8 electrons Electrons can move to d ...
SNC1D0 Atomic History
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of isotopes were also discovered ...
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of isotopes were also discovered ...
Worksheet 2: 1-19-17 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
Date Period - Swift Classroom
... He put the elements in order by _______________________ He found that other properties such as _________________________, _______________________, and the ability to ______________________ with other elements seemed to ____________________ over and over. This repeating pattern is called ______ ...
... He put the elements in order by _______________________ He found that other properties such as _________________________, _______________________, and the ability to ______________________ with other elements seemed to ____________________ over and over. This repeating pattern is called ______ ...
Define the following: Electronegativity
... 21. How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic table? decreases 22. What element in the first period has the largest atomic radius? Hydrogen 23. What is the charge of a cation? + Anion? 24. What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value? Cesium 25. ...
... 21. How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic table? decreases 22. What element in the first period has the largest atomic radius? Hydrogen 23. What is the charge of a cation? + Anion? 24. What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value? Cesium 25. ...
Elements and the Periodic Table Section One
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu): a unit used to measure the mass of particles in atoms; a proton or neutron has a mass of 1 amu (pg. 79) Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (pg. 79) Chemical Symbol: a one- or two- letter representation of an element (pg. 82) Family: elements in the ...
... Atomic Mass Unit (amu): a unit used to measure the mass of particles in atoms; a proton or neutron has a mass of 1 amu (pg. 79) Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (pg. 79) Chemical Symbol: a one- or two- letter representation of an element (pg. 82) Family: elements in the ...
File
... Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Vary in mass, but are all atoms of the same element because they have the same number of protons When it is important to distinguish one isotope from another, the mass number will follow the element name o Ex.: Carbon-12 ...
... Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons Vary in mass, but are all atoms of the same element because they have the same number of protons When it is important to distinguish one isotope from another, the mass number will follow the element name o Ex.: Carbon-12 ...
SOL Review Station: Equipment, Accuracy, Precision and Lab Safety
... 1. What is formed if you change the following in an atom? a. Protons ...
... 1. What is formed if you change the following in an atom? a. Protons ...
8th Grade Science Notes Chapter 2
... Protons & Neutrons have the same relative mass Niels Bohr - proposed an atomic model that placed electrons in circular orbits called energy levels. Electron Cloud - the modern atomic model. Electrons move in an area represented as a cloud around the nucleus. Quarks - smaller particles that make up p ...
... Protons & Neutrons have the same relative mass Niels Bohr - proposed an atomic model that placed electrons in circular orbits called energy levels. Electron Cloud - the modern atomic model. Electrons move in an area represented as a cloud around the nucleus. Quarks - smaller particles that make up p ...
CHEM 101 Dual Enrollment HW4 Question 1 of 12 Dalton`s
... updated or changed due to new discoveries. Which of the following statements were parts of Dalton's original atomic theory? Select all that apply. Atoms of the same element have the same size, mass, and structure. Different elements have atoms of different masses and properties. Matter is comprised ...
... updated or changed due to new discoveries. Which of the following statements were parts of Dalton's original atomic theory? Select all that apply. Atoms of the same element have the same size, mass, and structure. Different elements have atoms of different masses and properties. Matter is comprised ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
... ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) ...
File
... d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical orbits ...
... d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical orbits ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (II) Explain how Demitri Mendeleev organized the periodic table. In your answer clearly describe why the table is referred to as “The PERIODIC Table” and give at least one example of a periodic trend and one example of a non-periodic trend. (see pages 126-131) ...
... (II) Explain how Demitri Mendeleev organized the periodic table. In your answer clearly describe why the table is referred to as “The PERIODIC Table” and give at least one example of a periodic trend and one example of a non-periodic trend. (see pages 126-131) ...
Keypoints of Basic Atomic Structure
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
... Atomic Number Atomic Radius Electrons Element Isotope Neutrons Periodic Table Protons Subatomic Particles Concepts 1. Be able to describe how protons, neutrons and electrons are arranged in an atom. 2. Be able to list the charges on the subatomic particles that make up and atom, and giv ...
1.2 Atomic Theory
... The average atomic mass for magnesium found on the periodic table is a weighted average of the three isotopes: 24.31 g of Mg Radioactivity: spontaneous decay of nuclei, releasing energy and subatomic particles Radioisotopes: an unstable isotope of an element, which undergoes radioactive decay ...
... The average atomic mass for magnesium found on the periodic table is a weighted average of the three isotopes: 24.31 g of Mg Radioactivity: spontaneous decay of nuclei, releasing energy and subatomic particles Radioisotopes: an unstable isotope of an element, which undergoes radioactive decay ...
Structure of an Atom structure_of_atom
... Bohr model of Nitrogen: • Check your periodic table for Nitrogen ...
... Bohr model of Nitrogen: • Check your periodic table for Nitrogen ...
Structure of Atom and Periodic Table
... (5) Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: (A) describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the el ...
... (5) Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: (A) describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the el ...
General Chemistry Mr. MacGillivray Quiz #7: Development of Atomic
... General Chemistry Mr. MacGillivray Quiz #7: Development of Atomic Theory ...
... General Chemistry Mr. MacGillivray Quiz #7: Development of Atomic Theory ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
Atomic Structure Power Point
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...
... is a form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass on the periodic table reflects the average mass of all of the known isotopes of an element. Each isotope may have different characteristics. ...