HtoN
... can be used with other procedures to select cells and their DNA May be of interest to a researcher ...
... can be used with other procedures to select cells and their DNA May be of interest to a researcher ...
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
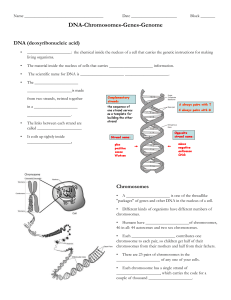
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Molecular Diagnostics
... How Do We Help Our Patients? Bone Marrow Transplants: Molecular diagnostics plays a large role in stem cell transplants by determining whose cells are populating the bone marrow post transplant (donor or recipient?) This difference helps the treatment team determine the next steps for a successful t ...
... How Do We Help Our Patients? Bone Marrow Transplants: Molecular diagnostics plays a large role in stem cell transplants by determining whose cells are populating the bone marrow post transplant (donor or recipient?) This difference helps the treatment team determine the next steps for a successful t ...
Name - EdWeb
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _______________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be ______________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene cause what disorder? __________________________________ What is a Chromosome? 12. ...
... 9. Blood cells use a protein called _______________________ to capture and carry oxygen. 10. When a gene is changed, it is said to be ______________________________________________ 11. A mutation in the hemoglobin gene cause what disorder? __________________________________ What is a Chromosome? 12. ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome or gene. 21. ____________________ ...
... 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome or gene. 21. ____________________ ...
Biotechnology - Valhalla High School
... the action of microorganism in their creation. • Bread and alcohol use yeast, while yogurt use bacteria. • Cheese is made using an enzyme called Rennin. Some cheese also contains molds. ...
... the action of microorganism in their creation. • Bread and alcohol use yeast, while yogurt use bacteria. • Cheese is made using an enzyme called Rennin. Some cheese also contains molds. ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
What is the NUTRIENT needed for growth and repair
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
Genetic Engineering and The Human Genome
... • An ongoing effort to analyze the human DNA sequence **Important because it could be used to ...
... • An ongoing effort to analyze the human DNA sequence **Important because it could be used to ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
Cloning Using Plasmid Vectors
... Selectable Genes Unique restriction sites May have additional features such as mob sites, RNA polymerase promoters, etc. ...
... Selectable Genes Unique restriction sites May have additional features such as mob sites, RNA polymerase promoters, etc. ...
Cloning Power Point
... multiple copies of that gene using bacterial plasmids, selfreplicating extra-chromosomal circular DNA molecules, that are distinctly different from the normal bacterial genome. Genes and other chromosomes are copied to make enough samples for further study. In order to clone a gene, a fragment of DN ...
... multiple copies of that gene using bacterial plasmids, selfreplicating extra-chromosomal circular DNA molecules, that are distinctly different from the normal bacterial genome. Genes and other chromosomes are copied to make enough samples for further study. In order to clone a gene, a fragment of DN ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? ...
... 5. Why did most scientists think the protein was the genetic material prior to the research of Griffith, Avery, and Hershey/Chase? 6. Understand Hershey and Chase’s experiment. 7. What information led to the discovery of the structure of the DNA molecule? 8. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to the discovery of DNA? 13) Why is the work of Rosalind Franklin overlooked in the discovery of DNA? 14) List the pieces of information about DNA structure that Rosalind Franklin discovered through her x-ray diffraction research. 15) What ...
... 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to the discovery of DNA? 13) Why is the work of Rosalind Franklin overlooked in the discovery of DNA? 14) List the pieces of information about DNA structure that Rosalind Franklin discovered through her x-ray diffraction research. 15) What ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Protein Synthesis
... _______________________________________________________________________________ Name the part of a double stranded chromosome to which spindle fibres attach during cell division _______________________________________________________________________________ Outline the process of DNA replication ...
... _______________________________________________________________________________ Name the part of a double stranded chromosome to which spindle fibres attach during cell division _______________________________________________________________________________ Outline the process of DNA replication ...
DNA: Technology: Stem Cells
... Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome Gene cloning involves using bacteria to make multiple copies of a gene For ...
... Most methods for cloning pieces of DNA in the laboratory share general features, such as the use of bacteria and their plasmids Plasmids are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome Gene cloning involves using bacteria to make multiple copies of a gene For ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 7. What is genetic engineering used for? 8. Some genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are due to ___________. 9. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a _______. 10. What is a phenotype? 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a _____. 12. The d ...
... 7. What is genetic engineering used for? 8. Some genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, are due to ___________. 9. Nucleotides are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a _______. 10. What is a phenotype? 11. A string of nucleotides that has instructions for a certain trait is a _____. 12. The d ...
Genetics Webquest Name: What is DNA? http://learn.genetics.utah
... 6) A DNA strand is made of _________ which make up __________ which make up sentences. 7) These "sentences" are called ________________. What is a Gene? ( just look at the navigation bar and you'll see What is a Gene? ) 8) What is a gene? 9) Blood cells use a protein called ___________ to capture an ...
... 6) A DNA strand is made of _________ which make up __________ which make up sentences. 7) These "sentences" are called ________________. What is a Gene? ( just look at the navigation bar and you'll see What is a Gene? ) 8) What is a gene? 9) Blood cells use a protein called ___________ to capture an ...
DNA extraction activity
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
DNA technology notes
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.