Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... about 3 billion base pairs one base pair is 0.00000000034 meters ...
... about 3 billion base pairs one base pair is 0.00000000034 meters ...
I`m the prokaryotic cell
... From the biggest to the least My simplest form Is in everyday yeast ...
... From the biggest to the least My simplest form Is in everyday yeast ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
What is Cloning?
... By fragmenting DNA of any origin (human, animal, or plant) and inserting it in the DNA of rapidly reproducing foreign cells, billions of copies of a single gene or DNA segment can be produced in a very short time. DNA to be cloned is inserted into a plasmid (a small, self-replicating circular mol ...
... By fragmenting DNA of any origin (human, animal, or plant) and inserting it in the DNA of rapidly reproducing foreign cells, billions of copies of a single gene or DNA segment can be produced in a very short time. DNA to be cloned is inserted into a plasmid (a small, self-replicating circular mol ...
3-3-16 Biology Bell Work: Where does DNA replication take place
... Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be ____________. The process of copying DNA is called ___________. Before a DNA can be replicated it needs to ___________. The DNA ___________ joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA. DNA polymerase also ______-reads each new DNA strand f ...
... Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be ____________. The process of copying DNA is called ___________. Before a DNA can be replicated it needs to ___________. The DNA ___________ joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA. DNA polymerase also ______-reads each new DNA strand f ...
The Chemistry of Life
... information) to RNA (messenger-RNA), in turn provide the genetic code for protein/enzyme production, and thus establishes the hierarchy of the cell. ...
... information) to RNA (messenger-RNA), in turn provide the genetic code for protein/enzyme production, and thus establishes the hierarchy of the cell. ...
Reproduction
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and bonucIeic acid (ANA) are two of the cell’s most Important molecules. These nucleic acids have a complex three-dimensional structure that enab les them to direct protein synthesis in the cell. • Study the structure of the DNA and RNA molecules shown below. Fill in the ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... • Gene Markers make it easier to identify vectors that have taken up the recombinant DNA. • the common ones are CFP Green fluorescent protein which is a gene found in jellyfish which makes them glow green. • Antibiotic resistance. ...
... • Gene Markers make it easier to identify vectors that have taken up the recombinant DNA. • the common ones are CFP Green fluorescent protein which is a gene found in jellyfish which makes them glow green. • Antibiotic resistance. ...
What is DNA?
... process of Mitosis. • Replication is the process by which DNA duplicate in order to form two identical cells • Cells need to reproduce to create new cells for growth, repair of tissue, (healing) and to produce other things our body needs. • Why do the body cells have to be identical? ...
... process of Mitosis. • Replication is the process by which DNA duplicate in order to form two identical cells • Cells need to reproduce to create new cells for growth, repair of tissue, (healing) and to produce other things our body needs. • Why do the body cells have to be identical? ...
Genetics
... • Adenine and thymine make a lovely pair • Cytosine without guanine would seem very bare • Oh, de-ox-y-ri-bo-nu-cleic acid • RNA is ri-bo-nu-cleic acid ...
... • Adenine and thymine make a lovely pair • Cytosine without guanine would seem very bare • Oh, de-ox-y-ri-bo-nu-cleic acid • RNA is ri-bo-nu-cleic acid ...
Changes in DNA can produce variation
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
... • There is a large number of DNA bases in any organism that need to be copied • Errors can occur when DNA is copied or affected by environment – UV radiation – X-rays – Toxins ...
Applied Genetics
... Cloning • A clone is an organism that has the exact same genes as the organism from which it was produced. • African violet • Sheep • Pigs ...
... Cloning • A clone is an organism that has the exact same genes as the organism from which it was produced. • African violet • Sheep • Pigs ...
Notes
... • Human genome project (HGP) • Completed in 2003 • Goal was to determine the sequence of the approximately three billion nucleotides that make up human DNA and to identify all of the human genes • How done? • Each of the 46 chromosomes was cleaved • Several restriction enzymes were used to ...
... • Human genome project (HGP) • Completed in 2003 • Goal was to determine the sequence of the approximately three billion nucleotides that make up human DNA and to identify all of the human genes • How done? • Each of the 46 chromosomes was cleaved • Several restriction enzymes were used to ...
deoxyribonucleic acid contained in the chromosomes humans have
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one ...
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one ...
DNA Replication Graphic Organizer
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
... REVIEW: Explain the TWO things an enzyme does in chemical reactions in the body… ...
Gene Cloning
... bacterial cells on agar containing antibiotic and X-gal any colonies that grow and are white contain our recombinant DNA with our gene of interest. ...
... bacterial cells on agar containing antibiotic and X-gal any colonies that grow and are white contain our recombinant DNA with our gene of interest. ...
WEEK 1 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 1
... substrate metabolite (small molecule) W is converted into a final product metabolite Z through a sequence of three steps catalyzed by the enzymes- A, B, and C. Each of the enzymes is the product of a different gene. Which metabolites would be expected to be missing, and which present in excess, in c ...
... substrate metabolite (small molecule) W is converted into a final product metabolite Z through a sequence of three steps catalyzed by the enzymes- A, B, and C. Each of the enzymes is the product of a different gene. Which metabolites would be expected to be missing, and which present in excess, in c ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering
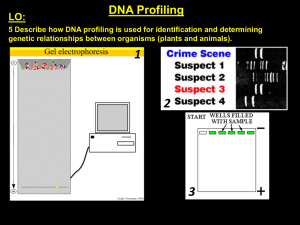
... DNA Extraction – taking DNA out of the cell Restriction enzymes: are special enzymes that cut DNA in specific locations by recognizing certain base sequences ...small pieces are easier to work with, study and identify now, let's organize: Gel electrophoresis: separates DNA fragments through a gel us ...
... DNA Extraction – taking DNA out of the cell Restriction enzymes: are special enzymes that cut DNA in specific locations by recognizing certain base sequences ...small pieces are easier to work with, study and identify now, let's organize: Gel electrophoresis: separates DNA fragments through a gel us ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.