PowerPoint
... material in an organism is the genome. • 2. Locating and recording the site of specific genes within the chromosomes is gene mapping. Selected portions of DNA containing the desired gene are cut with a restriction enzyme. ...
... material in an organism is the genome. • 2. Locating and recording the site of specific genes within the chromosomes is gene mapping. Selected portions of DNA containing the desired gene are cut with a restriction enzyme. ...
Biological ideas relating to genetic modification
... and genotypes ratios of offspring by showing how the alleles combine ...
... and genotypes ratios of offspring by showing how the alleles combine ...
BiotechnologySimple
... • composed of four different nucleotides in different combinations • each cell in the human body contains more than 3 BILLION letters ...
... • composed of four different nucleotides in different combinations • each cell in the human body contains more than 3 BILLION letters ...
Gene Technology
... extracted from the pancreases of slaughtered cows and pigs and then purified. Today, the human insulin gene is cloned ...
... extracted from the pancreases of slaughtered cows and pigs and then purified. Today, the human insulin gene is cloned ...
Slide 1
... Polymerase chain reactions, etc. • Gel electrophoresis employs electricity to separate strands of DNA based on their size • Bands of DNA can be identified using Southern blotting – a small sequence is radioactively tagged, then put with DNA and every where it pairs up with complementary bases it ca ...
... Polymerase chain reactions, etc. • Gel electrophoresis employs electricity to separate strands of DNA based on their size • Bands of DNA can be identified using Southern blotting – a small sequence is radioactively tagged, then put with DNA and every where it pairs up with complementary bases it ca ...
Viruses
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
Genetic Engineering - Woodstown-Pilesgrove Regional School
... What is gene therapy? Changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. A faulty or absent gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. List several diseases being treated with Gene therapy Cystic fibrosis, SCID (severe combined immune disorder) ...
... What is gene therapy? Changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. A faulty or absent gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. List several diseases being treated with Gene therapy Cystic fibrosis, SCID (severe combined immune disorder) ...
Genetic engineering
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... be introduced into the bacteria o Transformation o The process of transformation in the lab is similar to transformation in nature o However, we usually have to use tricks to get the bacteria to take up the DNA o Electroporation and biolistics are other methods We can use other tricks to find the ...
... be introduced into the bacteria o Transformation o The process of transformation in the lab is similar to transformation in nature o However, we usually have to use tricks to get the bacteria to take up the DNA o Electroporation and biolistics are other methods We can use other tricks to find the ...
amp R - Fort Bend ISD
... A. Selective breeding-choosing only animals with desired traits and mating or crossing them; this has been done with all domesticated animals and many food crops and flowers and trees 1. hybridization-crossing dissimilar individuals to hopefully get the best of both buffalo and a cow to get a beefa ...
... A. Selective breeding-choosing only animals with desired traits and mating or crossing them; this has been done with all domesticated animals and many food crops and flowers and trees 1. hybridization-crossing dissimilar individuals to hopefully get the best of both buffalo and a cow to get a beefa ...
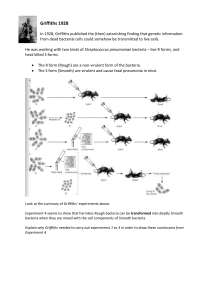
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology can be used to transform cells by inserting new DNA or genes into th ...
... molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology can be used to transform cells by inserting new DNA or genes into th ...
Study Guide for LS
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
Test Study Guide
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
... 15. What is the center of the chromosome called? 16. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 17. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replication? 18. What enzyme attempts to “fix” this problem? How? ...
Chapter 21
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
Journey Into dna
... Go to the following website: www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/genome/dna.html# Click on the flash version of the graphic and wait for it to load. Read each paragraph about a different aspect of DNA. Complete the worksheet section for that slide. When you have finished reading and have answered the question(s), ...
... Go to the following website: www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/genome/dna.html# Click on the flash version of the graphic and wait for it to load. Read each paragraph about a different aspect of DNA. Complete the worksheet section for that slide. When you have finished reading and have answered the question(s), ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology & Genomics
... Insert cloned gene into the fertilized egg implant into surrogate mother Traits inserted increase nutritional value of animal ...
... Insert cloned gene into the fertilized egg implant into surrogate mother Traits inserted increase nutritional value of animal ...
DNA Notes - Firelands Local Schools
... SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
... SYNTHESIS. – DNA IS A SELF-REPLICATING MOLECULE WHICH GETS PASSED ON FROM ONE GENERATION TO THE NEXT. ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.