Genetic engineering – stepping stones
... New gene is inserted and ligase enzymes rejoin the DNA. Gene begins to be expressed in transgenic organism. Transgenic organism is cloned. ...
... New gene is inserted and ligase enzymes rejoin the DNA. Gene begins to be expressed in transgenic organism. Transgenic organism is cloned. ...
Biotechnology
... Use a modified Ti plasmid which does not produce tumour or The Ti plasmid contains a region T-DNA that integrates into plant genome ...
... Use a modified Ti plasmid which does not produce tumour or The Ti plasmid contains a region T-DNA that integrates into plant genome ...
DNA WebQuest - Pearland ISD
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
DNA Study guide
... DNA (section 8.2 and 8.3) 1. Know the parts of a nucleotide and how they combine in a finished DNA molecule. 2. Be sure to know the four types of nucleotides and how they pair together. 3. Know the importance of Franklin, Watson, and Crick. 4. Be able to diagram DNA replication until two identical s ...
... DNA (section 8.2 and 8.3) 1. Know the parts of a nucleotide and how they combine in a finished DNA molecule. 2. Be sure to know the four types of nucleotides and how they pair together. 3. Know the importance of Franklin, Watson, and Crick. 4. Be able to diagram DNA replication until two identical s ...
A. Restriction Enzymes
... Recombinant DNA is DNA combined from different sources. The genetic code is universalcells in different species read genes and use this information to make a proteins in the same way. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8rXizmLjegI&feature=related ...
... Recombinant DNA is DNA combined from different sources. The genetic code is universalcells in different species read genes and use this information to make a proteins in the same way. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8rXizmLjegI&feature=related ...
Agrobacterium
... Various kinds of information were used to make these maps. Chromosome 6 contains about 1500 genes. You can see more of them if you zoom in on the right-most map. ...
... Various kinds of information were used to make these maps. Chromosome 6 contains about 1500 genes. You can see more of them if you zoom in on the right-most map. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 8. Following transcription, what would be the complementary mRNA sequence to this strand of DNA? a. DNA: AGC TCC GAT GCA TAC TTG CCA ...
... 8. Following transcription, what would be the complementary mRNA sequence to this strand of DNA? a. DNA: AGC TCC GAT GCA TAC TTG CCA ...
Exploratorium Presentation
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
... What is bacterial transformation? Transformation is the alteration of cells by the incorporation of foreign DNA into the cell ...
DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
Unit 2 Review: Molecular Genetics
... -double helix is wrapped around histones to form nucleosomes, which are coiled into chromatin fibres, which are then supercoiled -individuals have microsatellites (random repeats, non-coding) that make them unique -some can cause diseases (Huntington’s) -also for protection during division, degradat ...
... -double helix is wrapped around histones to form nucleosomes, which are coiled into chromatin fibres, which are then supercoiled -individuals have microsatellites (random repeats, non-coding) that make them unique -some can cause diseases (Huntington’s) -also for protection during division, degradat ...
Figure 20.2 Overview of gene cloning with a bacterial
... Figure 12.3 Cloning a gene in a bacterial plasmid Human cell ...
... Figure 12.3 Cloning a gene in a bacterial plasmid Human cell ...
Document
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
NOTES: 12.2 – 12.3 – DNA Structure
... -# of chromosomes varies widely from species to species DNA molecules are long…how does DNA fit in the nucleus? ● It forms ...
... -# of chromosomes varies widely from species to species DNA molecules are long…how does DNA fit in the nucleus? ● It forms ...
Genetic Technology
... Genetic Engineering • Under the genetic engineering flap write the following definitions and examples • Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragments into a host organism of the same or different species. • Scientist use Ecoli bacteria to make expensive Die for blue Jeans ...
... Genetic Engineering • Under the genetic engineering flap write the following definitions and examples • Method of cutting DNA from one organism and inserting the DNA fragments into a host organism of the same or different species. • Scientist use Ecoli bacteria to make expensive Die for blue Jeans ...
Name
... For 31- 38, Choose DNA Replication, Tanscription, Translation, Both Replication and Transcription, or Both Transcription and Translation: 31. Occurs in the nucleus 32. The two stages of protein synthesis 33. Process where mRNA is “decoded” into a chain of amino acids 34. Process where DNA is copied ...
... For 31- 38, Choose DNA Replication, Tanscription, Translation, Both Replication and Transcription, or Both Transcription and Translation: 31. Occurs in the nucleus 32. The two stages of protein synthesis 33. Process where mRNA is “decoded” into a chain of amino acids 34. Process where DNA is copied ...
DNA – The Building Blocks of Life
... responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from your parents. An example is the brown-eyed gene. This is a specific protein that’s made using the instructions from DNA. If this protein doesn’t get made (because you don’t have the brown eyed gene), you have no or little pigment and you hav ...
... responsible for some of the traits you can inherit from your parents. An example is the brown-eyed gene. This is a specific protein that’s made using the instructions from DNA. If this protein doesn’t get made (because you don’t have the brown eyed gene), you have no or little pigment and you hav ...
Cell Cycle
... 17. How does the DNA molecule repair itself? 18. What are the three different roles of DNA polymerase in DNA replication? 19. Explain how DNA synthesis can proceed in both directions from a replication origin, even though DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA only in one direction. ...
... 17. How does the DNA molecule repair itself? 18. What are the three different roles of DNA polymerase in DNA replication? 19. Explain how DNA synthesis can proceed in both directions from a replication origin, even though DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA only in one direction. ...
Hfr cells
... promoters, operators, effectors, inducers, repressors and co-repressors in your answer. Discuss the levels of bacterial control of gene expression, paying particular attention to post-translational and transcriptional control, as discussed in lecture. What is quorum sensing? How does it relate to ge ...
... promoters, operators, effectors, inducers, repressors and co-repressors in your answer. Discuss the levels of bacterial control of gene expression, paying particular attention to post-translational and transcriptional control, as discussed in lecture. What is quorum sensing? How does it relate to ge ...
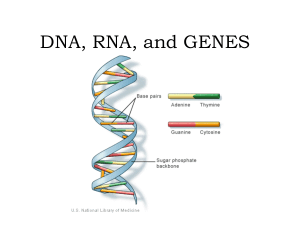
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
Some Products Made Using Biotechnology
... manipulate DNA • The procedures are often referred to as genetic engineering ...
... manipulate DNA • The procedures are often referred to as genetic engineering ...
assignment DNA - UniMAP Portal
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
... 4. Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms? ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.