Biology Test Topics Chapters 11-12 Slideshows
... What is the basic process by which eukaryotic DNA replicates itself? Be sure to mention the action of enzymes. What is a telomere? How can telomeres be related to cancerous growth? Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication Be able to label any of the diagrams in our DNA packet. Gel electro ...
... What is the basic process by which eukaryotic DNA replicates itself? Be sure to mention the action of enzymes. What is a telomere? How can telomeres be related to cancerous growth? Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication Be able to label any of the diagrams in our DNA packet. Gel electro ...
Cloning and selection
... 3.Selective marker (usually antibiotic resistance gene) to select for bacteria containing plasmid. 4.Polycloning site (unique restriction target sites useful for inserting donor fragments 5.Many plasmids allow for blue/white selection for distinguishing between recombinant vs nonrecombinant plasmids ...
... 3.Selective marker (usually antibiotic resistance gene) to select for bacteria containing plasmid. 4.Polycloning site (unique restriction target sites useful for inserting donor fragments 5.Many plasmids allow for blue/white selection for distinguishing between recombinant vs nonrecombinant plasmids ...
DNA Replication
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the nuclear area. Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the nuclear area. Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
PP-WEEK-12-CLASS
... Using DNA to our Advantage Genetic Modification Introduction of new DNA sequences into an organism to alter the genetic makeup – Introduces very specific characteristics – Use enzymes to manipulate DNA – Recombinant DNA - new form of DNA that is introduced – Gene cloning – splicing genes from a var ...
... Using DNA to our Advantage Genetic Modification Introduction of new DNA sequences into an organism to alter the genetic makeup – Introduces very specific characteristics – Use enzymes to manipulate DNA – Recombinant DNA - new form of DNA that is introduced – Gene cloning – splicing genes from a var ...
Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 4. During the process of carried by mRNA is used to produce proteins. ...
... 4. During the process of carried by mRNA is used to produce proteins. ...
History of Genetics
... base sequence), occur constantly in all cells and organisms. Offspring rarely get a perfect copy of the DNA from its parents. • but mutations are rare: about 1 DNA base change per 109 bases each cell generation. (Humans have about 3 x 109 bases and E. coli bacteria have about 4 x 106 ...
... base sequence), occur constantly in all cells and organisms. Offspring rarely get a perfect copy of the DNA from its parents. • but mutations are rare: about 1 DNA base change per 109 bases each cell generation. (Humans have about 3 x 109 bases and E. coli bacteria have about 4 x 106 ...
PowerPoint
... Imagine you are a breeder, and want to find a mate for your organism. You have a desired trait, and you want to ensure that all offspring will have that trait. How do you ensure that the mate will always have offspring that have the trait? Homozygous recessive is easy to determine because it is ...
... Imagine you are a breeder, and want to find a mate for your organism. You have a desired trait, and you want to ensure that all offspring will have that trait. How do you ensure that the mate will always have offspring that have the trait? Homozygous recessive is easy to determine because it is ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosome Quiz
... 24.) DNA is converted into RNA during the process of DNA _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ****Bonus***** 1.) What is the 3 letter sequence that codes for an amino acid called? ...
... 24.) DNA is converted into RNA during the process of DNA _____________________________________. This process occurs in the __________________________________. ****Bonus***** 1.) What is the 3 letter sequence that codes for an amino acid called? ...
Bill Nye the Science Guy Worksheet-A
... The reproductive cell that a father donates to his child is called the ______ ...
... The reproductive cell that a father donates to his child is called the ______ ...
A8xb1e3x8x1 (2)
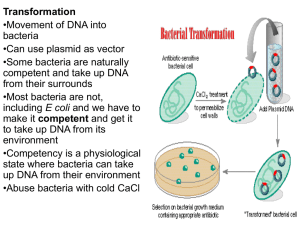
... Small circular DNA molecules in bacteria Add DNA to plasmid and then the bacteria it is located in will duplicate itself and the added DNA. ...
... Small circular DNA molecules in bacteria Add DNA to plasmid and then the bacteria it is located in will duplicate itself and the added DNA. ...
15.2_Recombinant_DNA
... Small circular DNA molecules in bacteria Add DNA to plasmid and then the bacteria it is located in will duplicate itself and the added DNA. ...
... Small circular DNA molecules in bacteria Add DNA to plasmid and then the bacteria it is located in will duplicate itself and the added DNA. ...
Homeostasis
... BIOLOGY FIRST SEMESTER STUDY GUIDE: Don’t wait until the last minute to study all the information below. It’s a good idea to buddy up with someone. ...
... BIOLOGY FIRST SEMESTER STUDY GUIDE: Don’t wait until the last minute to study all the information below. It’s a good idea to buddy up with someone. ...
Chapter 13
... Odds are 1/100,000,000,000 that any two people will have the same genetic fingerprint!!! ...
... Odds are 1/100,000,000,000 that any two people will have the same genetic fingerprint!!! ...
03 Biotechnology Note
... least 2 different sources – scientists use this DNA to mess with (manipulate) genes and proteins ...
... least 2 different sources – scientists use this DNA to mess with (manipulate) genes and proteins ...
Biology Summary Sheet
... which codes for different amino acids. The type of protein made is determined by the sequence of bases on the DNA, as this determines the order of the amino acids. The order of amino acids then determines which proteins are formed. There is no way for DNA (containing the information to make proteins ...
... which codes for different amino acids. The type of protein made is determined by the sequence of bases on the DNA, as this determines the order of the amino acids. The order of amino acids then determines which proteins are formed. There is no way for DNA (containing the information to make proteins ...
PCR - Polymerase Chain Reaction
... • DNA can be processed by RFLP either directly (if you can get enough DNA from an environment) or from PCR product • T-RFLP (terminal-RFLP) is in most respects identical except for a marker on the end of the enzyme • Works as fingerprinting technique because different organisms with different DNA se ...
... • DNA can be processed by RFLP either directly (if you can get enough DNA from an environment) or from PCR product • T-RFLP (terminal-RFLP) is in most respects identical except for a marker on the end of the enzyme • Works as fingerprinting technique because different organisms with different DNA se ...
Ch 20 Lecture
... • “Knocks out” or “knocks in” gene of interest at particular chromosomal locus, where it trades places with an existing gene. • By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behavior or condition, researchers can infer its probable function ...
... • “Knocks out” or “knocks in” gene of interest at particular chromosomal locus, where it trades places with an existing gene. • By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behavior or condition, researchers can infer its probable function ...
What is Genetic Engineering?
... Steps of Genetic Engineering: 3)This gene is then “spliced” to the DNA of another organism. 4)Once in the new organism, the transferred genes direct the new organism’s cells to make the same protein as the original organism. ...
... Steps of Genetic Engineering: 3)This gene is then “spliced” to the DNA of another organism. 4)Once in the new organism, the transferred genes direct the new organism’s cells to make the same protein as the original organism. ...
restriction enzymes
... •Bacteriophage lambda: insert = 25 kb; recombinant DNA packaged into phage particles used to infect E. coli ...
... •Bacteriophage lambda: insert = 25 kb; recombinant DNA packaged into phage particles used to infect E. coli ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.