Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... 12. Transcribe the following DNA sequence CCCGAGTAACAT. (p. 206) 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUC ...
... 12. Transcribe the following DNA sequence CCCGAGTAACAT. (p. 206) 13. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUC ...
talk given by Brian Powling on 20 th January 2017
... Brian introduced the analogy of Waddington’s Tree rather than a landscape because he thought it would be easier to visualise what was going on. As cells become more differentiated, they progress from being in the trunk as stem cells, to the branch and then the twig with the fully differentiated cell ...
... Brian introduced the analogy of Waddington’s Tree rather than a landscape because he thought it would be easier to visualise what was going on. As cells become more differentiated, they progress from being in the trunk as stem cells, to the branch and then the twig with the fully differentiated cell ...
Genes and Evolution - Mad River Local Schools
... ◦ Those that fit best are more likely to reproduce and survive (natural selection) ...
... ◦ Those that fit best are more likely to reproduce and survive (natural selection) ...
DNA and the genetic code
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... 3. Compare and contrast DNA replication and transcription. 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a ...
... 3. Compare and contrast DNA replication and transcription. 4. Name three types of RNA (one is from DNA replication, two from protein synthesis) described and explain the function of each. 5. How many different DNA triplets are possible? 6. The DNA triplet “CGA” is transcribed into which RNA codon? a ...
review-genetics-final-exam-2016
... 50. What are restriction enzymes used for? 51. What process is used to separate the DNA fragments after restriction enzymes have been used? 52. If an electrophoresis gel was used to separate DNA fragments and it ran from bottom to top, where would the longer fragments be located? 53. What charge doe ...
... 50. What are restriction enzymes used for? 51. What process is used to separate the DNA fragments after restriction enzymes have been used? 52. If an electrophoresis gel was used to separate DNA fragments and it ran from bottom to top, where would the longer fragments be located? 53. What charge doe ...
Genetic Information
... A new amino acid (base pair) is inserted into an entire codon All other codons shifted out of place THE DOG BIT THE CAT THE DOB ITT HEC AT ...
... A new amino acid (base pair) is inserted into an entire codon All other codons shifted out of place THE DOG BIT THE CAT THE DOB ITT HEC AT ...
9.1 Manipulating DNA
... • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
... • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
9.1 Manipulating DNA KEY CONCEPT Biotechnology relies on cutting DNA at specific places.
... • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
... • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
Chapter 19
... Ch 20 Gel Electrophoresis A solution of DNA pieces (which were cut by restriction ...
... Ch 20 Gel Electrophoresis A solution of DNA pieces (which were cut by restriction ...
Match each macromolecule (Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids
... These molecules are primarily used for structural and mediator components of the cell, are grouped by chemical properties of their R side chains. __________________________________ Identify which chemical group each of the following R side chains belongs to: ...
... These molecules are primarily used for structural and mediator components of the cell, are grouped by chemical properties of their R side chains. __________________________________ Identify which chemical group each of the following R side chains belongs to: ...
DNA notes
... http://www.tamu.edu/classes/plan/magill/gene603/Lecture%20outlines/Molecular/DNA_notes.html ...
... http://www.tamu.edu/classes/plan/magill/gene603/Lecture%20outlines/Molecular/DNA_notes.html ...
Gene mutation and sickle cell
... As a result, they get shorter each time. • When they get too short, essential parts of DNA can be destroyed. ...
... As a result, they get shorter each time. • When they get too short, essential parts of DNA can be destroyed. ...
Things to Cover for Exam 1
... information from each parent. Each parent contributes one of the two homologous chromosomes. What type of cells result from Meiosis? Sex cells or somatic (body) cells? Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically identical or genetically different? If the chromosome number of a diploid c ...
... information from each parent. Each parent contributes one of the two homologous chromosomes. What type of cells result from Meiosis? Sex cells or somatic (body) cells? Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically identical or genetically different? If the chromosome number of a diploid c ...
our leaflet: Autism families study
... for the differences among us. Yet these DNA base sequence variations influence most of our physical differences and many of our other characteristics, as well. Sequence variations occur in our genes, and the resulting different forms of the same gene are called alleles. People can have two identical ...
... for the differences among us. Yet these DNA base sequence variations influence most of our physical differences and many of our other characteristics, as well. Sequence variations occur in our genes, and the resulting different forms of the same gene are called alleles. People can have two identical ...
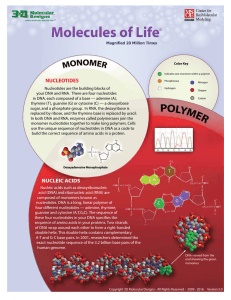
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Bell work Objectives: DNA replication DNA Replication
... As we discussed in class, the DNA molecules consists of nitrogen base pairs. The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ___________________ or ____________________ ...
... As we discussed in class, the DNA molecules consists of nitrogen base pairs. The order of the pairs determines the genetic code, which controls protein synthesis or the production of proteins. 6. What do we call a set of three nitrogen bases? ___________________ or ____________________ ...
Recitation Section 17 Answer Key Recombinant DNA and Cloning
... Recombinant DNA is a set of tools that allows scientists to move between genetics, biochemistry and molecular biology – allowing us to determine how the parts of a cell or organism work. 1. What does it mean to clone a gene? Cloning DNA means to isolate a gene or fragment of DNA away from the other ...
... Recombinant DNA is a set of tools that allows scientists to move between genetics, biochemistry and molecular biology – allowing us to determine how the parts of a cell or organism work. 1. What does it mean to clone a gene? Cloning DNA means to isolate a gene or fragment of DNA away from the other ...
Teacher Resource 8: Genetic engineering
... Each group then uses various art/craft resources such as Plasticine, wool, pipe-cleaners, straws, card etc. to model the process. Digital cameras/video recorders can be used to take snapshots of each stage of the process. Learners can either use one image for each statement to make a storyboard/cart ...
... Each group then uses various art/craft resources such as Plasticine, wool, pipe-cleaners, straws, card etc. to model the process. Digital cameras/video recorders can be used to take snapshots of each stage of the process. Learners can either use one image for each statement to make a storyboard/cart ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.