Chapters 19-21 review
... 23. A scientist recovers a bit of tissue from a 400 year old Dodo bird and would like to compare it against samples from living birds. What technology would be most useful in increasing the amount of DNA for testing? a. bacterial transformation ...
... 23. A scientist recovers a bit of tissue from a 400 year old Dodo bird and would like to compare it against samples from living birds. What technology would be most useful in increasing the amount of DNA for testing? a. bacterial transformation ...
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
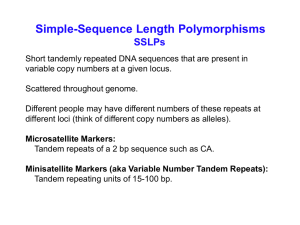
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
SNC2D Genes - Malvern Science
... of testing individuals to determine whether they have the gene or genes associated with certain genetic disorders (i.e. cancer, cystic fibrosis, and spina bifida) Two ways: 1. amniocentesis – fluid is taken from the amniotic sac that surrounds the growing fetus e.g. test for PKU ...
... of testing individuals to determine whether they have the gene or genes associated with certain genetic disorders (i.e. cancer, cystic fibrosis, and spina bifida) Two ways: 1. amniocentesis – fluid is taken from the amniotic sac that surrounds the growing fetus e.g. test for PKU ...
Does your DNA define you Ans
... allows DNA to be packaged into the nucleus of cells. Histones have a tail section ...
... allows DNA to be packaged into the nucleus of cells. Histones have a tail section ...
Transcription Factors
... – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...
... – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...
20-DNA-technology
... of eukaryotic organisms • in laboratory, it results from reverse transcription • in certain gene: cDNA < DNA • It is quantified by qPCR - marker of gene expression ...
... of eukaryotic organisms • in laboratory, it results from reverse transcription • in certain gene: cDNA < DNA • It is quantified by qPCR - marker of gene expression ...
Fluorescent dye, SYBR Green, is incorporated into PCR reaction
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
... – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
DNA stucture - worldofbiology09
... DNA replicates with the help of enzymes (DNA helicase, DNA polymerase and DNA ligase). After DNA unwinds and unzips, DNA polymerase adds free nucleotides to each strand (base pair rule). One strand is created continuously while the other needs to be created in segments due to the 5΄ and 3΄ polarity ...
... DNA replicates with the help of enzymes (DNA helicase, DNA polymerase and DNA ligase). After DNA unwinds and unzips, DNA polymerase adds free nucleotides to each strand (base pair rule). One strand is created continuously while the other needs to be created in segments due to the 5΄ and 3΄ polarity ...
Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA Technology
... Introducing the normal gene into humans with disease We can make the genes through rDNA, but how do we get them inside to every cell? Ex vivo gene therapy uses modified viruses to get the new gene inside cells SCID, familial hypercholesterolemia In vivo gene therapy uses direct injection o ...
... Introducing the normal gene into humans with disease We can make the genes through rDNA, but how do we get them inside to every cell? Ex vivo gene therapy uses modified viruses to get the new gene inside cells SCID, familial hypercholesterolemia In vivo gene therapy uses direct injection o ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... Science is often advanced by the careful repetition, with modification, of the experiments of others. ...
... Science is often advanced by the careful repetition, with modification, of the experiments of others. ...
Discovery of DNA structure
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Double-stranded helical molecule found in the nucleus of the cell Replicates itself before the cell divides, ensuring genetic continuity Provides instructions for protein synthesis ...
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Double-stranded helical molecule found in the nucleus of the cell Replicates itself before the cell divides, ensuring genetic continuity Provides instructions for protein synthesis ...
Genetic Technology - Solon City Schools
... • 2. bacteria that live on the roots of corn plants have been given the gene that produces insect toxin. The toxin protects the roots from insects. • 3. Possibly engineer bacteria that live in soil to make more nitrogen (natural fertilizer) so farmers can cut back costs on fertilizers. ...
... • 2. bacteria that live on the roots of corn plants have been given the gene that produces insect toxin. The toxin protects the roots from insects. • 3. Possibly engineer bacteria that live in soil to make more nitrogen (natural fertilizer) so farmers can cut back costs on fertilizers. ...
Chapter 1 - Ohio University
... with a particular genetic defect are transformed with the plasmids containing normal DNA. The cells which contain the target gene will then function normally and will grow on a minimal medium. 9. A cDNA library is a collection of cDNA clones that were generated in vitro from the mRNA sequences of a ...
... with a particular genetic defect are transformed with the plasmids containing normal DNA. The cells which contain the target gene will then function normally and will grow on a minimal medium. 9. A cDNA library is a collection of cDNA clones that were generated in vitro from the mRNA sequences of a ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
DNA Notes How was the DNA Model Formed? 1) In the 1950`s a
... How DNA makes a copy of itself One of the unique characteristics of DNA is that it can copy itself using one of the strands as a template. DNA can replicate and match base pairs to make complementary strands EX: Strand 1: A T C C G T A G C Strand 2 ...
... How DNA makes a copy of itself One of the unique characteristics of DNA is that it can copy itself using one of the strands as a template. DNA can replicate and match base pairs to make complementary strands EX: Strand 1: A T C C G T A G C Strand 2 ...
File
... group of genetically related organisms that make up a single step in the line of descent (passing of traits) ...
... group of genetically related organisms that make up a single step in the line of descent (passing of traits) ...
Microbial Genetics
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
Gel Electrophoresis DNA Fingerprinting
... • In this hypothetical case, DNA was extracted from samples obtained from the five possible suspects, and the crime scene sample • You will cleave the DNA with a restriction enzyme and simulated a “mock” DNA fingerprint analysis using Southern Blotting ...
... • In this hypothetical case, DNA was extracted from samples obtained from the five possible suspects, and the crime scene sample • You will cleave the DNA with a restriction enzyme and simulated a “mock” DNA fingerprint analysis using Southern Blotting ...
DNA Review Cards
... Explain which type of mutation has the potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
... Explain which type of mutation has the potential least effect on the protein. Describe the process of transcription. What is a mutagen? What is the primary enzyme in transcription. Give examples of mutagens. What type of cell must a mutation occur in to be passed on to offspring? ...
DNA Fill in the blank notes.
... gather new nucleotides and assemble new DNA molecules using complimentary bases. Remember: ...
... gather new nucleotides and assemble new DNA molecules using complimentary bases. Remember: ...
1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter
... DNA Replication/Transcription/Translation Quiz 1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only ...
... DNA Replication/Transcription/Translation Quiz 1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter DNA molecule is composed of one original strand and one new strand. B) nucleotides are constantly being recycled as cells make DNA. C) the cell can proofread its newly synthesized DNA only ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.