Week 2 Lecture Summarys copy
... - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst) and the rapidly dividing cells form a ball of about 100 cells - implantation comes next (embedding itself in the cell wall-hormones prepare the uterus to receive the cell mass) at ...
... - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst) and the rapidly dividing cells form a ball of about 100 cells - implantation comes next (embedding itself in the cell wall-hormones prepare the uterus to receive the cell mass) at ...
MAIN IDEAS
... Phase changes-evaporation, condensation, sublimation Phase change diagram •Basic unit of structure in all living things ...
... Phase changes-evaporation, condensation, sublimation Phase change diagram •Basic unit of structure in all living things ...
1.2 From Cells to Organisms
... the plant. The flesh of fruit is another example of plant tissue. It protects the plant’s seeds. B. Plant and animals tissues that come together for a specific purpose form organs a. Examples of plant organs are stems, fruit, onions (store water). b. Examples of animal organs are brains, lungs, hear ...
... the plant. The flesh of fruit is another example of plant tissue. It protects the plant’s seeds. B. Plant and animals tissues that come together for a specific purpose form organs a. Examples of plant organs are stems, fruit, onions (store water). b. Examples of animal organs are brains, lungs, hear ...
The Cell: A Review
... including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its ...
... including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its ...
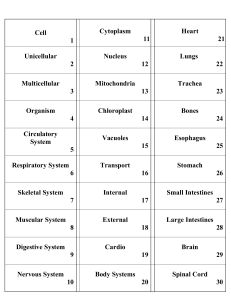
Levels of Organization
... • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
... • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
Cells and Organs
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
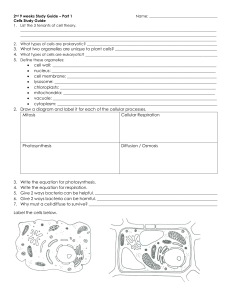
3. What two organelles are unique to plant cells? • cell wall: ______
... ____________________ to give the body its final shape ____________________ makes blood cells and stores minerals ____________________ to change food to a form that the body cells can use ____________________ to move oxygen into the body ____________________ cleans blood and rids body of waste in blo ...
... ____________________ to give the body its final shape ____________________ makes blood cells and stores minerals ____________________ to change food to a form that the body cells can use ____________________ to move oxygen into the body ____________________ cleans blood and rids body of waste in blo ...
Use for Nov. 20,12 Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... 7. Which of the following structures are adapted for supporting a plant? Phloem tissues, root hair cells, stomata, xylem vessels 8. Which describes the structure and function of a red blood cell? ...
... 7. Which of the following structures are adapted for supporting a plant? Phloem tissues, root hair cells, stomata, xylem vessels 8. Which describes the structure and function of a red blood cell? ...
Human Body Progress Check
... I can describe differences between plant cells and animal cells I can explain what is meant by the term ‘specialised cell.’ I can give examples of specialised cells and identify features that make them specialised. I can state that a group of similar cells is called a tissue. I can state that a grou ...
... I can describe differences between plant cells and animal cells I can explain what is meant by the term ‘specialised cell.’ I can give examples of specialised cells and identify features that make them specialised. I can state that a group of similar cells is called a tissue. I can state that a grou ...
Living Systems
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
... • A cell is the basic unit of a living system. • A group of specialized cells that performs a particular function is called a tissue. • An organ is a group of tissues that works together to carry out a set of functions. • A group of organs that works together to perform a set of functions is called ...
Cell Processes Overview
... 5. Cell membranes are “selectively permeable”. What does that mean? ____________________________________________________________________ 6. Osmosis – In osmosis, cell membranes let through __________. If we put pure water on one side the membrane and a chemical solution on the other, the water will ...
... 5. Cell membranes are “selectively permeable”. What does that mean? ____________________________________________________________________ 6. Osmosis – In osmosis, cell membranes let through __________. If we put pure water on one side the membrane and a chemical solution on the other, the water will ...
levels of organization directed reading
... system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissues is made up of various kinds of cells. ...
... system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissues is made up of various kinds of cells. ...
File
... 10. an enzyme that starts the chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy 11. carbon 12. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 13. CHO, carbs are sugars; are simple sugars = monosaccharides, two sugars = disaccharides, many sugars = polysaccharides; examples are glucose, fructose 1 ...
... 10. an enzyme that starts the chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy 11. carbon 12. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 13. CHO, carbs are sugars; are simple sugars = monosaccharides, two sugars = disaccharides, many sugars = polysaccharides; examples are glucose, fructose 1 ...
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Chapter review p 83-84 Model answers Cell Function Organelles
... 19. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of folded membranes within a cell where many proteins, lipids, and other materials are made in the cell. The smooth ER also helps break down toxic materials. The ER is the part of the internal delivery system in a cell. The Golgi complex modifies, packa ...
... 19. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of folded membranes within a cell where many proteins, lipids, and other materials are made in the cell. The smooth ER also helps break down toxic materials. The ER is the part of the internal delivery system in a cell. The Golgi complex modifies, packa ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
... working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
Regents Review
... • Antibodies- proteins that either attack the invaders or mark them for killing • Microbes- microscopic organisms • Vaccines- made of weakened or killed pathogens that help build antibodies for immunity • AIDS- an example of a disease caused by an attack on the immune system • Allergy- rapid immune ...
... • Antibodies- proteins that either attack the invaders or mark them for killing • Microbes- microscopic organisms • Vaccines- made of weakened or killed pathogens that help build antibodies for immunity • AIDS- an example of a disease caused by an attack on the immune system • Allergy- rapid immune ...
Overview of Kingdom Animalia
... because sensory organs are highly developed •Good muscular control •Developed from ectoderm, endoderm & mesoderm •Often have fluid-filled spaces inside in which internal organs are suspended. ...
... because sensory organs are highly developed •Good muscular control •Developed from ectoderm, endoderm & mesoderm •Often have fluid-filled spaces inside in which internal organs are suspended. ...
found in all eukaryotes
... • Ribosomes – where proteins are made • Endoplasmic reticulum – path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another • Golgi apparatus – processes and packages substances produced by the cell ...
... • Ribosomes – where proteins are made • Endoplasmic reticulum – path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another • Golgi apparatus – processes and packages substances produced by the cell ...
The Different Jobs of Cells
... • Plants have different type of cells in their leaves, roots, and stems • Root Cells are block shaped and do not contain chloroplasts ...
... • Plants have different type of cells in their leaves, roots, and stems • Root Cells are block shaped and do not contain chloroplasts ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are