what know about protists cells and human body
... • Cytoplasm - a gel-like material inside the cell; it contains water and nutrients for the cell • Nucleus - directs the activity of a cell; it contains chromosomes with the DNA • Nuclear Membrane -separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Mitochondria - break down food and release energy to the cel ...
... • Cytoplasm - a gel-like material inside the cell; it contains water and nutrients for the cell • Nucleus - directs the activity of a cell; it contains chromosomes with the DNA • Nuclear Membrane -separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Mitochondria - break down food and release energy to the cel ...
kakamega south cemtral districts mock examination
... b) Regulate the openings and closing of the stoma;; a) Light - Activates germination hormones; - Raises internal temperatures of the seed; Award for one b) Soaking in water - softens seedcoat; Autotrophs are organisms who utilize simple substances to manufacture complex organic substances; while Het ...
... b) Regulate the openings and closing of the stoma;; a) Light - Activates germination hormones; - Raises internal temperatures of the seed; Award for one b) Soaking in water - softens seedcoat; Autotrophs are organisms who utilize simple substances to manufacture complex organic substances; while Het ...
Summer Review Package: `16-`17 1. Vocabulary
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
Slide 1
... • The advantages and disadvantages associated with the commercial use of cloned plants: – advantage: can be sure of the characteristics of the plant since all plants will be genetically identical; – advantage: it is possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seed; – disadvan ...
... • The advantages and disadvantages associated with the commercial use of cloned plants: – advantage: can be sure of the characteristics of the plant since all plants will be genetically identical; – advantage: it is possible to mass produce plants that may be difficult to grow from seed; – disadvan ...
Summer Review Package: `14 -`15 PART I 1. Vocabulary – Please b
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
What is Biology?
... Biology: Organisms: 1. Organization cells -> ___ ___ ___ specialization 2. Reproduction ...
... Biology: Organisms: 1. Organization cells -> ___ ___ ___ specialization 2. Reproduction ...
of the cell - MrMsciences
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
PP text version
... Ectoderm becomes the nervous system and outer epithelium Mesoderm becomes internal organs (skeletal system, muscles, circulatory system, reproductive system, excretory system, and ...
... Ectoderm becomes the nervous system and outer epithelium Mesoderm becomes internal organs (skeletal system, muscles, circulatory system, reproductive system, excretory system, and ...
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
Unit 03 - fixurscore
... hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface area and it is small to fit in capillaries. 6. Nerve cells: they conduct electrical impulses which travel to & from the brain. They are very long and their chemical reactions cause impulses to travel through their fibers. They also h ...
... hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface area and it is small to fit in capillaries. 6. Nerve cells: they conduct electrical impulses which travel to & from the brain. They are very long and their chemical reactions cause impulses to travel through their fibers. They also h ...
The History of Cell Biology
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
active reading worksheets
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
Biology Final Semester 1 Study Guide
... 71. Where does the calvin cycle take place? 72. Products of calvin cycle 73. sequence of cellular respiration 74. equation for respiration 75. glycolysis—how many ATPs, what does it start with? 76. lactic acid ferm. 77. Alcoholic ferm. 78. Oxygen debt 79. after 90 secs. Of activity how can our bodie ...
... 71. Where does the calvin cycle take place? 72. Products of calvin cycle 73. sequence of cellular respiration 74. equation for respiration 75. glycolysis—how many ATPs, what does it start with? 76. lactic acid ferm. 77. Alcoholic ferm. 78. Oxygen debt 79. after 90 secs. Of activity how can our bodie ...
LIfe processes 2010 living Environment
... • Is the total of all the life processes. When a person states he has high or low metabolism this is what they are talking about. It is the combination of all the life ...
... • Is the total of all the life processes. When a person states he has high or low metabolism this is what they are talking about. It is the combination of all the life ...
active reading worksheets
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
... The discovery of cells was made possible by the development of the microscope in the 17th century. In 1665, the English scientist Robert Hooke used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. Hooke described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes.” These “little boxes” reminded him of the ...
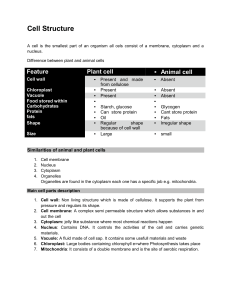
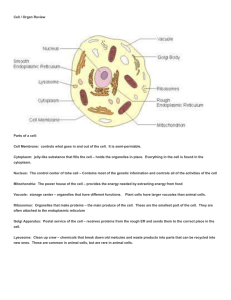
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
231_study guide
... MAIN IDEA: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the Y s ...
... MAIN IDEA: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the Y s ...
3.1 Study Guide
... MAIN IDEA: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the Y s ...
... MAIN IDEA: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the Y s ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Key
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
Asexual Reproduction
... Sexual Reproduction – two parents causes variation among a species Fertilization – when egg and sperm join to make one body cell (zygote) zygote – the first body cell of an organism (a fertilized egg) ...
... Sexual Reproduction – two parents causes variation among a species Fertilization – when egg and sperm join to make one body cell (zygote) zygote – the first body cell of an organism (a fertilized egg) ...
Living Systems PowerPoint Notes
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
... __________________ organisms. Multicellular organisms have _____________ _____________ – (humans have many trillion cells). The cells must remain a part of the organism’s body to _____________. Your body is made up of many _____________ _____________ of cells. You have skin cells, Organisms that are ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are