Science Chapter 1 Unit A
... know plant and animal cells break down sugar to obtain energy, a process resulting in carbon dioxide and water ...
... know plant and animal cells break down sugar to obtain energy, a process resulting in carbon dioxide and water ...
Chapter 30: Comparing Invertebrates
... There is a third cell layer in embryos, called the __________________________, which is located between the endoderm and the ectoderm ...
... There is a third cell layer in embryos, called the __________________________, which is located between the endoderm and the ectoderm ...
62.1E6 INVESTIGATOR Name Thomas M. Jessell and
... Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., Roelink, H., and Jessell, T.M. (1995). Dorsal differentiation of neural plate cells induced by BMP-mediated signals from epidermal ectoderm. Cell 82, 969-979. Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., and Jessell, T.M. (1997). A role for the roof plate and its resident TGFß-related p ...
... Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., Roelink, H., and Jessell, T.M. (1995). Dorsal differentiation of neural plate cells induced by BMP-mediated signals from epidermal ectoderm. Cell 82, 969-979. Liem, Jr., K.F., Tremml, G., and Jessell, T.M. (1997). A role for the roof plate and its resident TGFß-related p ...
Unit V Outline
... contains amniotic fluid which provides a watery environment for the development of the fetus, and protects the fetus from shock. (d) The fourth membrane is the yolk sac which surrounds the yolk. The yolk is the stored food for the embryo. Blood vessels grow into the sack to assist in the transfer of ...
... contains amniotic fluid which provides a watery environment for the development of the fetus, and protects the fetus from shock. (d) The fourth membrane is the yolk sac which surrounds the yolk. The yolk is the stored food for the embryo. Blood vessels grow into the sack to assist in the transfer of ...
Animals as Organisms chapter_2_animals_as_organisms
... Scientific names is based on the taxonomy of an animal species. Each animal has a two part name. (Genus and Species) Common name is the name of everyday conversation. Kingdom animalia share three traits ...
... Scientific names is based on the taxonomy of an animal species. Each animal has a two part name. (Genus and Species) Common name is the name of everyday conversation. Kingdom animalia share three traits ...
22/18 INVESTIGATOR Name Jeremy P. Brockes Address Ludwig
... We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagent,) developed by [Investiga ...
... We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagent,) developed by [Investiga ...
Test Study Guide-cell processes_ homeostasis2
... SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate wastes Know that cells in multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis for the entire organism. SHORT ANSWER: Know the main tran ...
... SHORT ANSWER: Know the four things that cells need to maintain homeostasis: obtain and use energy, make new cells, exchange materials, and eliminate wastes Know that cells in multicellular organisms work together to maintain homeostasis for the entire organism. SHORT ANSWER: Know the main tran ...
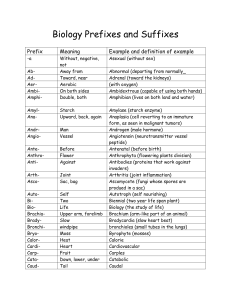
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyperthyroidism (condition resulting from the excessive productio ...
... histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyperthyroidism (condition resulting from the excessive productio ...
Making a wet mount slide Place a very thin piece of specimen, flat
... leo. Members of the same species can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. The 6 Kingdoms Plants, Animals, Protists, Fungi, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria. Organisms are placed into kingdoms depending upon: Cell type, complex or simple; Ability to make food; Number of cells in their body. Vertebrate ...
... leo. Members of the same species can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. The 6 Kingdoms Plants, Animals, Protists, Fungi, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria. Organisms are placed into kingdoms depending upon: Cell type, complex or simple; Ability to make food; Number of cells in their body. Vertebrate ...
Define: Cell, Tissue, organ, and organ system
... organisms. Some organisms, like bacteria and protists, are unicellular (made entirely of one cell). Some organisms, like fungi, plants, and animals, are multicellular (made of many cells). In multicellular organisms, cells exhibit cell specialisation. They take on specific jobs and look differ ...
... organisms. Some organisms, like bacteria and protists, are unicellular (made entirely of one cell). Some organisms, like fungi, plants, and animals, are multicellular (made of many cells). In multicellular organisms, cells exhibit cell specialisation. They take on specific jobs and look differ ...
Scott Foresman Science
... Cells are the most basic unit of living things. They are the smallest living part of an organism. A single cell is so tiny that you need a microscope to see it. Organisms can be made of only one cell. Organisms made of many cells are called multicellular. Cells have the same needs as you do. They ne ...
... Cells are the most basic unit of living things. They are the smallest living part of an organism. A single cell is so tiny that you need a microscope to see it. Organisms can be made of only one cell. Organisms made of many cells are called multicellular. Cells have the same needs as you do. They ne ...
Meiosis
... Asexual Reproduction used by some plant and invertebrate species requires 1 parent offspring are genetically identical to the parent uses body cells ...
... Asexual Reproduction used by some plant and invertebrate species requires 1 parent offspring are genetically identical to the parent uses body cells ...
Document
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
syllabus - srm.cse.section-a
... organisms from the perspective of engineers. In addition, the course is expected to encourage engineering students to think about solving biological problems with engineering tools. INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES 1. To familiarize the students with the basic organization of organisms and subsequent buildi ...
... organisms from the perspective of engineers. In addition, the course is expected to encourage engineering students to think about solving biological problems with engineering tools. INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES 1. To familiarize the students with the basic organization of organisms and subsequent buildi ...
Inhibition of SCLC Survival and Proliferation by Knockdown of the
... Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Louisville, KY 40292. Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (SCLC) is a rapidly progressing cancer of neuroendocrine origin that accounts for about 13% of all diagnosed lung cancers. Left untreated, the median survival rate after diagnosis is 2-4 months. ...
... Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Louisville, KY 40292. Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (SCLC) is a rapidly progressing cancer of neuroendocrine origin that accounts for about 13% of all diagnosed lung cancers. Left untreated, the median survival rate after diagnosis is 2-4 months. ...
COMMUNICATION
... The names of structures a, b, c and d are, respectively a. chloroplast, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion b. mitochondrion, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body c. chloroplast, vacuole, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum d. chloroplast, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body 8) ...
... The names of structures a, b, c and d are, respectively a. chloroplast, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion b. mitochondrion, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body c. chloroplast, vacuole, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum d. chloroplast, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body 8) ...
5.16.05 Development and Aging
... Induction • Induction occurs when embryonic cells influence one another to develop in a particular way. • A molecular concentration gradient may act as a chemical signal to induce germ layer differentiation. • The presumptive (potential) notochord tissue induces the formation of the nervous system ...
... Induction • Induction occurs when embryonic cells influence one another to develop in a particular way. • A molecular concentration gradient may act as a chemical signal to induce germ layer differentiation. • The presumptive (potential) notochord tissue induces the formation of the nervous system ...
Unit 1 From Single Cells
... Tough bands of tissue called tendons attach bones to muscles. 17. ligaments Other bands of tissue called ligaments attach bones to each other. 18. neurons To move, a muscle must receive a signal from the nervous system. Specialized cells called neurons, detect conditions in the body’s environm ...
... Tough bands of tissue called tendons attach bones to muscles. 17. ligaments Other bands of tissue called ligaments attach bones to each other. 18. neurons To move, a muscle must receive a signal from the nervous system. Specialized cells called neurons, detect conditions in the body’s environm ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... Variation exists amongst the members of a species. When a characteristic can be used to divide the species into distinct groups, it is said to show DISCRETE variation. When the characteristic varies in an UNINTERRUPTED way from one extreme to the other, it is said to show CONTINUOUS variation. ...
... Variation exists amongst the members of a species. When a characteristic can be used to divide the species into distinct groups, it is said to show DISCRETE variation. When the characteristic varies in an UNINTERRUPTED way from one extreme to the other, it is said to show CONTINUOUS variation. ...
1 - WordPress.com
... times the bacterium will divide? If there is food, moisture, low radiation (darker conditions), and the right temperature 13. Why are most multicellular organisms unable to reproduce by budding? Budding occurs mostly in organisms that move little and most animals move which makes budding a less prac ...
... times the bacterium will divide? If there is food, moisture, low radiation (darker conditions), and the right temperature 13. Why are most multicellular organisms unable to reproduce by budding? Budding occurs mostly in organisms that move little and most animals move which makes budding a less prac ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are