* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inhibition of SCLC Survival and Proliferation by Knockdown of the
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Somatic evolution in cancer wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of cancer wikipedia , lookup
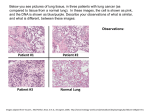
CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Restriction of Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival and Proliferation by Inhibition of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase IV Rachel Cary*, Ben Willcut, and UmaSankar Owensboro Cancer Research Program and James Graham Brown Cancer Center, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Louisville, KY 40292. Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (SCLC) is a rapidly progressing cancer of neuroendocrine origin that accounts for about 13% of all diagnosed lung cancers. Left untreated, the median survival rate after diagnosis is 2-4 months. Our previous findings have shown that Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKIV) levels are highly elevated in SCLCs.CaMKIV is a signaling molecule found in neural, endocrine, and lymphatic cells that is involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Using aGFPlentivirus-mediated shRNA system to create CaMKIV-knockdown SCLCs, we demonstrate the significance of CaMKIV in SCLC growth and survival.