Asexual Reproduction - South Buffalo Charter School
... it can regenerate into an entirely new organism. • Echinoderms and the hydra in molds are examples of organisms that reproduce by regeneration. ...
... it can regenerate into an entirely new organism. • Echinoderms and the hydra in molds are examples of organisms that reproduce by regeneration. ...
Unicellular Organisms what are they? write down some key
... because they have no nucleus, no mitochondria and no ribosomes. Their chromosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. They move through their environments using a flagellum or tail or pili which are hairlike structures. Disease causing bacteria sometimes have a capsule which is a sticky coating that make ...
... because they have no nucleus, no mitochondria and no ribosomes. Their chromosomes float freely in the cytoplasm. They move through their environments using a flagellum or tail or pili which are hairlike structures. Disease causing bacteria sometimes have a capsule which is a sticky coating that make ...
Cillia and flagella
... cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability to reproduce. The ciliated cells that line our respiratory tract sweep debris trapped within mucus back up the throat, which helps keep the lungs clean similarly, ciliated cells move an egg along the oviduct, where it will be fertilized ...
... cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability to reproduce. The ciliated cells that line our respiratory tract sweep debris trapped within mucus back up the throat, which helps keep the lungs clean similarly, ciliated cells move an egg along the oviduct, where it will be fertilized ...
stem cell
... organisms, multicellular organisms are made of many cells that are specialized to perform particular tasks. Multicellular organisms are made up of specialized cells that work together to make tissues, followed by organs, then organ systems, and finally an organism. ...
... organisms, multicellular organisms are made of many cells that are specialized to perform particular tasks. Multicellular organisms are made up of specialized cells that work together to make tissues, followed by organs, then organ systems, and finally an organism. ...
File The Characteristic of Living Things1
... that a plant stems bends toward the light? Plants and other organisms react to changes in their environment. A change in an organism’s environment is called a stimulus. An organism reacts to a stimulus with a response (which is an action or change in behavior). Ex: Has the sound of a car horn ever s ...
... that a plant stems bends toward the light? Plants and other organisms react to changes in their environment. A change in an organism’s environment is called a stimulus. An organism reacts to a stimulus with a response (which is an action or change in behavior). Ex: Has the sound of a car horn ever s ...
Cells - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
02. Organizing principles of human body
... 3. Egg becomes activated and developmental changes begin 4. Sperm and egg nuclei fuse ...
... 3. Egg becomes activated and developmental changes begin 4. Sperm and egg nuclei fuse ...
EOCT Quiz #6
... A biologist has just discovered a new life form. The newly described organism is multicellular, does not carry on photosynthesis, and absorbs nutrients from the environment. It is composed of eukaryotic cells with cell walls made of chitin. In which kingdom would the ...
... A biologist has just discovered a new life form. The newly described organism is multicellular, does not carry on photosynthesis, and absorbs nutrients from the environment. It is composed of eukaryotic cells with cell walls made of chitin. In which kingdom would the ...
Chapter 1 Lesson 1~ Cells cells split or divide to form new cells 1 ½
... Plant & animal kingdoms only contain multicellular organisms Animal kingdom Vertebrates: have backbone Invertebrates: no backbone Plant kingdom Vascular: contains tubes or vessels Nonvascular: no vascular tissue Fungus kingdom Differ from plants (must get food from other organisms) Only ...
... Plant & animal kingdoms only contain multicellular organisms Animal kingdom Vertebrates: have backbone Invertebrates: no backbone Plant kingdom Vascular: contains tubes or vessels Nonvascular: no vascular tissue Fungus kingdom Differ from plants (must get food from other organisms) Only ...
SEVENTH GRADE LIFE SCIENCES THEME: LIFE AROUND US
... a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logical conclusion for the given experimental data. d. Place an object, organism, or event into a classification system. e. Commun ...
... a. Use appropriate tools and technology to perform tests, collect and display data. b. Use a variety of resources to collect information for research. c. Select the most logical conclusion for the given experimental data. d. Place an object, organism, or event into a classification system. e. Commun ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - VZFTITININMZ.ppt [\310\243\310
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice ...
... • Frogs, chicken, fish (zebrafish) – Develop in eggs outside the mother’s body • Mouse – Identifying the gene function using genetically modified mice ...
Specialized Cells Notes
... The human body is made of many specialized cells that perform specific functions. Specialized cells arise from the differentiation of unspecialized cells during embryological development. Unspecialized cells are called STEM cells that have the ability to reproduce and differentiate into a diverse ra ...
... The human body is made of many specialized cells that perform specific functions. Specialized cells arise from the differentiation of unspecialized cells during embryological development. Unspecialized cells are called STEM cells that have the ability to reproduce and differentiate into a diverse ra ...
GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... prokaryotic cells. Explain how the main sub-cellular structures, including the nucleus, cell membranes, mitochondria, cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells and plasmids in bacterial cells are related to their functions Explain how the structure of different types of cell relate to their function ...
... prokaryotic cells. Explain how the main sub-cellular structures, including the nucleus, cell membranes, mitochondria, cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells and plasmids in bacterial cells are related to their functions Explain how the structure of different types of cell relate to their function ...
Year 9 Cells Quick Quiz
... Look at the diagram of a slide being made. The object you want to look at (‘Y’) is called the: ...
... Look at the diagram of a slide being made. The object you want to look at (‘Y’) is called the: ...
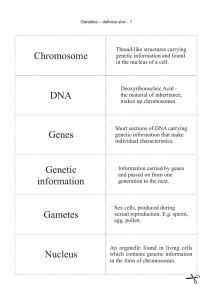
Chromosome DNA Genes Genetic information
... Getting a few cells from a desirable plant to make a big mass of identical cells, each of which can be grown on to produce a tiny identical plant. ...
... Getting a few cells from a desirable plant to make a big mass of identical cells, each of which can be grown on to produce a tiny identical plant. ...
Sexual Reproduction
... reproduction for this type of organism. However, if environmental conditions are changing, variations in the hereditary information are needed…..sexual reproduction provides more of a benefit for that particular species. ...
... reproduction for this type of organism. However, if environmental conditions are changing, variations in the hereditary information are needed…..sexual reproduction provides more of a benefit for that particular species. ...
sexual reproduction
... - a ZYGOTE is first formed when the male a and female sex cells unite - the zygote then divides in two and the divisions repeated during a process called CLEAVAGE -the continued cell divisions result in an EMBRYO being formed -the new organism will show characteristics of both parents ...
... - a ZYGOTE is first formed when the male a and female sex cells unite - the zygote then divides in two and the divisions repeated during a process called CLEAVAGE -the continued cell divisions result in an EMBRYO being formed -the new organism will show characteristics of both parents ...
Class Notes - North Star Academy
... BOTH: mate and lay eggs, when eggs hatch both species are on their own SNAIL: leaves its eggs PYTHON: stays until eggs hatch, lives much longer ...
... BOTH: mate and lay eggs, when eggs hatch both species are on their own SNAIL: leaves its eggs PYTHON: stays until eggs hatch, lives much longer ...
Cell Theory - Teacher Pages
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
Introduction to Animals Crosswords
... 4. Fertilization restores this chromosome number 7. Outer germ layer 8. Hollow ball cell stage of a developing zygote 9. More than 95% of all animals are this 11. Circulatory system in which blood empties into the body cavity to bathe tissues 14. development in which the young animal looks like that ...
... 4. Fertilization restores this chromosome number 7. Outer germ layer 8. Hollow ball cell stage of a developing zygote 9. More than 95% of all animals are this 11. Circulatory system in which blood empties into the body cavity to bathe tissues 14. development in which the young animal looks like that ...
Mitosis Worksheet
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant cell. It is strong and supports the cell – cell wall Activity 2 [Objective 7 1/4a] Discuss the idea with pupils that the cells we have been looking at so far ar ...
... 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant cell. It is strong and supports the cell – cell wall Activity 2 [Objective 7 1/4a] Discuss the idea with pupils that the cells we have been looking at so far ar ...
Document
... bodies too. Plants have organs, which are composed of different tissues that are made up of different types of cells. Plants have underground organs called roots. Plants organs that are above ground make up the shoot system: stems and leaves. Plant roots have an important job. They anchor the plant ...
... bodies too. Plants have organs, which are composed of different tissues that are made up of different types of cells. Plants have underground organs called roots. Plants organs that are above ground make up the shoot system: stems and leaves. Plant roots have an important job. They anchor the plant ...
Job Vacancy: Postdoctoral Research Scientist in Cell Biology
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are