* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download found in all eukaryotes
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
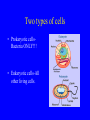
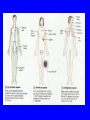
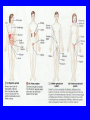
TAKS- Living Systems Cells and organization of living systems Organization of living systems • All matter made of atoms • Atoms organized into molecules • Molecules organized into cells (Living things are made of cells) • Cells organized into tissues • Tissues organized into organs • Organs organized into organ systems • Organ systems organized into organisms Two types of cells • Prokaryotic cellsBacteria ONLY!!! • Eukaryotic cells-All other living cells. Prokaryotic Cells • Lack nucleus and most other organelles (structure within cell – performs specific function) • Include Eubacteria and Archaebacteria • Archaebacteria – ancient bacteria – true • Eubacteria bacteria • Good bacteria and pathogenic bacteria Eukaryotic cells • Have nucleus and other organelles Ex. Nuclear Membrane and Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles. FYI: Mitochondria have their own nuclei and can reproduce like in muscle tissue. Organelles in Eukaryotic cells • Nucleus – contains DNA; command center of cell • Mitochondria – found in all eukaryotes – breaks down food molecules (i.e. – glucose) to release energy (cellular respiration) Equation for cellular respiration: C6 H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP • Ribosomes – where proteins are made • Endoplasmic reticulum – path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another • Golgi apparatus – processes and packages substances produced by the cell • Lysosome – digests molecules, old organelles, and foreign substances • Cilia and flagella – propel cells through the environment; move materials over cell surface • Vacuole – storage of water, waste, and/or enzymes • Microfilaments and microtubules – forms cytoskeleton of cell for support, movement, and division of cells • Chloroplast – found in cells of plants and some protists – use energy in sunlight to make the sugar glucose (photosynthesis). Glucose fuels all life’s processes (plant and animal). • Cell wall – (plants) supports/protects cell Plant and Animal cells-Cell Organelle Game in Student Packet Rules: 1. You will work in teams of 4 and place the organelle cut outs in the appropriate plant and animal cell model. We will begin in 5 minutes. 2. You will place the organelle in the model(s) and quickly write the function to the side of your labels in pencil. 3. Each organelle is worth 5 points. 4. Having finished the race have another team verify you results. 5. Give your total score for each model on your score card. End of Day 1: Turn in your score cards for Cell Review. How cells keep themselves alive • Maintain stable internal environment homeostasis Ways to maintain homeostasis • Passive transport – no ATP used – Diffusion – Osmosis – Facilitated diffusion • Carrier proteins • Ion channels • Active transport – ATP used – Carrier proteins • Cell membrane pumps (sodium-potassium) – Endocytosis – exocytosis Interdependence • In multicellular organisms cells work together in organs and organ systems to help one another maintain homeostasis Organ Systems • Circulatory – transports oxygen and nutrients to cells and carries wastes away from cells • Respiratory – moves oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body • Digestive – breaks down food and absorbs nutrients • Nervous – detects changes outside and inside your body and controls the way your body responds to these changes • Skeletal – movement, protection, shape, support, storage of minerals and produces blood cells • Muscular – movement, posture, and production of heat • Endocrine – produces chemical messengers called hormones; some hormones help to maintain homeostasis while others control development and growth • Integumentary – forms protective barrier around body, prevents water loss, controls body temperature, and gathers information about your surroundings • Immune – protects body from infection • Lymphatic – takes fluid from the spaces between cells and returns it to the circulatory system; filters bacteria and other microorganisms from this fluid • Reproductive – males – sperm production; females – eggs • Excretory – removes wastes from the body and helps maintain homeostasis