End of Course Exam 6th Grade Review Answer Key
... DNA, cells, reproduce, respond to stimuli, use energy, grow and develop 2. Describe the 7 levels of organization going from smallest to largest. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism 3. What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? Pro: single c ...
... DNA, cells, reproduce, respond to stimuli, use energy, grow and develop 2. Describe the 7 levels of organization going from smallest to largest. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism 3. What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? Pro: single c ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 The Answer are under each
... Disease of uncontrolled cell growth 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. What occurred during the osmosis experiment (egg and vinegar) and the diffusion experiment (bag and corn starch) and why? The egg got bigger and increased in mass because there was a higher conce ...
... Disease of uncontrolled cell growth 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. What occurred during the osmosis experiment (egg and vinegar) and the diffusion experiment (bag and corn starch) and why? The egg got bigger and increased in mass because there was a higher conce ...
Taxonomy and Virus Review Answer Key File
... 8. The graphic below gives the taxonomic classifications for four different species. Explain how you know that one organism is an outlier. Corn is the outlier because it does not belong in the same kingdom as the other three organisms. ...
... 8. The graphic below gives the taxonomic classifications for four different species. Explain how you know that one organism is an outlier. Corn is the outlier because it does not belong in the same kingdom as the other three organisms. ...
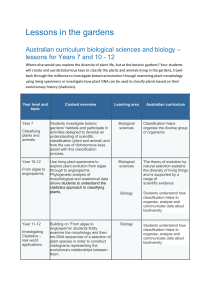
Curriculum information for Biological sciences and Biology
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
... back through the millennia to investigate botanical evolution through examining plant morphology using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
Chapter 1
... Distinguish between homeostasis and metabolism and between growth, development, and reproduction o Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable level of internal conditions even though environmental conditions are constantly changing. While metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that ta ...
... Distinguish between homeostasis and metabolism and between growth, development, and reproduction o Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable level of internal conditions even though environmental conditions are constantly changing. While metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that ta ...
Biology Review Notes
... ADAPT: SURVIVE: REPRODUCE The father of Evolution was Charles Darwin. Natural Selection describes that an organism best adapted to its environment will be most successful (the survival of the fittest) Common Ancestor: If living organisms share similar traits or sequences of DNA, proteins, amino acid ...
... ADAPT: SURVIVE: REPRODUCE The father of Evolution was Charles Darwin. Natural Selection describes that an organism best adapted to its environment will be most successful (the survival of the fittest) Common Ancestor: If living organisms share similar traits or sequences of DNA, proteins, amino acid ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Some organisms are made up of tr ...
... one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Some organisms are made up of tr ...
Evolution - Gonzalez
... reproduce offspring that are also well adapted The least adapted produce fewer offspring and are less likely to survive. ...
... reproduce offspring that are also well adapted The least adapted produce fewer offspring and are less likely to survive. ...
Biology 4974/5974, Evolution
... Why is the genetic code universal? To code for 20 amino acids + stop code, at least 1,070 possibilities using 64 codons. Why this code? Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon associatio ...
... Why is the genetic code universal? To code for 20 amino acids + stop code, at least 1,070 possibilities using 64 codons. Why this code? Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon associatio ...
Chapter 1: What is Biology
... Their experiments disproved abiogenesis Miller and Urey: recreated conditions of early earth in a lab to see if they could produce the believed 1st organic molecules ...
... Their experiments disproved abiogenesis Miller and Urey: recreated conditions of early earth in a lab to see if they could produce the believed 1st organic molecules ...
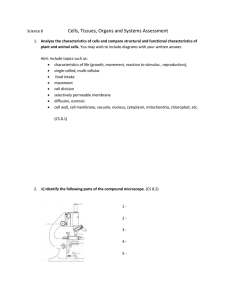
CS 8.1 - 8.4 Assessment Event
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
MAIN IDEAS
... •Cell membrane – a thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell •Nucleus – controls many of the functions of the cell contains DNA •Mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell where food is burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for expor ...
... •Cell membrane – a thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell •Nucleus – controls many of the functions of the cell contains DNA •Mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell where food is burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for expor ...
Name - SchoolNotes
... Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction Sexual reproduction: 2 parents prod ...
... Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction Sexual reproduction: 2 parents prod ...
Introduction to Biology
... constantly to build molecules (synthesis) and cells and to break down (digest) substances (such as breaking down food for nutrition) b. Organisms must transport nutrients to be used in cellular respiration to produce energy. c. An organisms’ chemical reactions are called its metabolism ...
... constantly to build molecules (synthesis) and cells and to break down (digest) substances (such as breaking down food for nutrition) b. Organisms must transport nutrients to be used in cellular respiration to produce energy. c. An organisms’ chemical reactions are called its metabolism ...
Functions and Structures
... You grew from a baby to your present size. What structures inside your body enabled you to grow? Why and how do all living organisms grow to the sizes they do? 5. Wastes: Animals get rid of waste gases like carbon dioxide. They also get rid of other wastes through urine and feces. What structures do ...
... You grew from a baby to your present size. What structures inside your body enabled you to grow? Why and how do all living organisms grow to the sizes they do? 5. Wastes: Animals get rid of waste gases like carbon dioxide. They also get rid of other wastes through urine and feces. What structures do ...
Chapter 2: Intro to Multicellular Organisms
... characteristic that increases the change of an organism’s survival and reproduction. › Getting energy › Shape/structure of body ...
... characteristic that increases the change of an organism’s survival and reproduction. › Getting energy › Shape/structure of body ...
Biology Concepts to Study
... F. ARCHAEBACTERIA: unicellular prokaryotes which can be found living in conditions that are similar to the earliest environments on earth (deep sea thermal vents, hot springs, etc.). This kingdom is genetically quite different from all other bacteria, and is considered to be among the oldest group o ...
... F. ARCHAEBACTERIA: unicellular prokaryotes which can be found living in conditions that are similar to the earliest environments on earth (deep sea thermal vents, hot springs, etc.). This kingdom is genetically quite different from all other bacteria, and is considered to be among the oldest group o ...
CAPT Biology Concepts Study Sheet
... F. ARCHAEBACTERIA: unicellular prokaryotes which can be found living in conditions that are similar to the earliest environments on earth (deep sea thermal vents, hot springs, etc.). This kingdom is genetically quite different from all other bacteria, and is considered to be among the oldest group o ...
... F. ARCHAEBACTERIA: unicellular prokaryotes which can be found living in conditions that are similar to the earliest environments on earth (deep sea thermal vents, hot springs, etc.). This kingdom is genetically quite different from all other bacteria, and is considered to be among the oldest group o ...
Classifying organisms
... A huge variety of organisms live on our planet. Scientists have categorized organisms to make them easier to identify. This is called classification. Organisms can be classified into different species. A species contains individuals with the same physical characteristics and common ancestors. So far ...
... A huge variety of organisms live on our planet. Scientists have categorized organisms to make them easier to identify. This is called classification. Organisms can be classified into different species. A species contains individuals with the same physical characteristics and common ancestors. So far ...
File - Craftsbury Science
... Big Ideas and Enduring Understandings (These are the specific learning targets of the 4 big themes in AP Biology that are discussed in the chapter). These Big Ideas and Enduring Understandings will guide our learning throughout each unit, and allow you to make connections between different units. ...
... Big Ideas and Enduring Understandings (These are the specific learning targets of the 4 big themes in AP Biology that are discussed in the chapter). These Big Ideas and Enduring Understandings will guide our learning throughout each unit, and allow you to make connections between different units. ...
1.10 EVOLUTION CONNECTION
... 1.9 CONNECTION: Biology, technology, and society are connected in important ways Many of today’s global issues relate to biology ...
... 1.9 CONNECTION: Biology, technology, and society are connected in important ways Many of today’s global issues relate to biology ...
Science / Science Pre AP
... (ii) Students learn that all organisms obtain energy, get rid of wastes, grow, and reproduce. During both sexual and asexual reproduction, traits are passed onto the next generation. These traits are contained in genetic material that is found on genes within a chromosome from the parent. Changes in ...
... (ii) Students learn that all organisms obtain energy, get rid of wastes, grow, and reproduce. During both sexual and asexual reproduction, traits are passed onto the next generation. These traits are contained in genetic material that is found on genes within a chromosome from the parent. Changes in ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.