Bacteria and Viruses
... • Likely evolved later since they are dependent on living things. • Why Non-Living? – Cannot reproduce without infecting a host cell – Do not grow and develop – Do not respond to the environment. ...
... • Likely evolved later since they are dependent on living things. • Why Non-Living? – Cannot reproduce without infecting a host cell – Do not grow and develop – Do not respond to the environment. ...
Co-Requisite – Characteristics of Science
... c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. *Give five pieces of evidence to support the theory of evolution: ...
... c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory. *Give five pieces of evidence to support the theory of evolution: ...
honors biology unit one study guide
... Put these classification divisions in order from largest to smallest: Genus kingdom family phylum class species order _____________________________________________________________________________________ Fill in the following chart of the three domains: (also pp. 326-327 ) and (Barron’s book pp. 216 ...
... Put these classification divisions in order from largest to smallest: Genus kingdom family phylum class species order _____________________________________________________________________________________ Fill in the following chart of the three domains: (also pp. 326-327 ) and (Barron’s book pp. 216 ...
levels of organization directed reading
... Level 5 - Organism Organism is the name of the independent living thing. It can carry out the basic functions of life. Organisms can be made of a single cell or of multiple cells. The definition of "living thing" is still debated in scientific circles (a virus, for example, is considered by some to ...
... Level 5 - Organism Organism is the name of the independent living thing. It can carry out the basic functions of life. Organisms can be made of a single cell or of multiple cells. The definition of "living thing" is still debated in scientific circles (a virus, for example, is considered by some to ...
EJU Syllabus for Biology for printing
... The purpose of this examination is to test whether international students have the basic academic ability in science necessary for studying at universities or other such higher educational institutions in Japan. [Classification of Examination] The examination consists of three subjects, i.e. physics ...
... The purpose of this examination is to test whether international students have the basic academic ability in science necessary for studying at universities or other such higher educational institutions in Japan. [Classification of Examination] The examination consists of three subjects, i.e. physics ...
Reproduction Gas exchange Growth Take in energy
... The living things are called _____________ factors and the non-living factors such as wind, air, water, soil, etc. are the _____________ factors. Where an organism lives such as an owl in a tree is its ____________ and the job the organism has in the environment is its ____________. An owl’s niche w ...
... The living things are called _____________ factors and the non-living factors such as wind, air, water, soil, etc. are the _____________ factors. Where an organism lives such as an owl in a tree is its ____________ and the job the organism has in the environment is its ____________. An owl’s niche w ...
What you absolutely must know to pass the regent`s test
... Living things are made up of cells. 2. Living things reproduce. 3. Living things are based on a universal genetic code. 4. Living things grow and develop. 5. Living things use materials and energy. 6. Living things respond to their environment. 7. Living things maintain a stable internal environment ...
... Living things are made up of cells. 2. Living things reproduce. 3. Living things are based on a universal genetic code. 4. Living things grow and develop. 5. Living things use materials and energy. 6. Living things respond to their environment. 7. Living things maintain a stable internal environment ...
Biology EOC Review
... Characteristics of Life All living things exhibit several basic life characteristics: ...
... Characteristics of Life All living things exhibit several basic life characteristics: ...
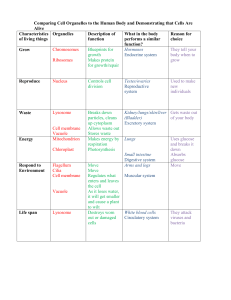
Comparing Cell Organelles to the Human Body and
... Description of What in the body Reason for of living things function performs a similar choice function? Chromosomes Blueprints for Hormones They tell your Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
... Description of What in the body Reason for of living things function performs a similar choice function? Chromosomes Blueprints for Hormones They tell your Grow growth Endocrine system body when to Ribosomes Makes protein grow for growth/repair ...
Unicellular Organisms what are they? write down some key
... successful because they are plentiful and have changed very little over billions of years. Some bacteria, like plants, make their own food while others are parasites. Parasites live by invading the body of a plant or animal. Bacteria are different from animal and plant cells because they have no nuc ...
... successful because they are plentiful and have changed very little over billions of years. Some bacteria, like plants, make their own food while others are parasites. Parasites live by invading the body of a plant or animal. Bacteria are different from animal and plant cells because they have no nuc ...
b2revisioncards
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
Biology 2nd QTR EQT Review To which group does an organism
... d. keeping warm with thick fur Which characteristic is used to place the shark and the moray 15. Study the two animals eel into two different taxonomic classes? below. ...
... d. keeping warm with thick fur Which characteristic is used to place the shark and the moray 15. Study the two animals eel into two different taxonomic classes? below. ...
I. Organization of Living Things TISSUE CELL
... cell. All organisms (living things) are made up of cells. Every cell in an organism has a special job to do. However, the cell may act alone or be part of a team depending on the complexity of the organism. The simplest animals, the sponges, have cells that work independently. The next higher phylum ...
... cell. All organisms (living things) are made up of cells. Every cell in an organism has a special job to do. However, the cell may act alone or be part of a team depending on the complexity of the organism. The simplest animals, the sponges, have cells that work independently. The next higher phylum ...
BIOLOGY END OF COURSE TEST STUDY GUIDE
... ___biome___________. Plants are the only organisms that can convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. Plants are the __autotrophs________ or ____producers_______ and the animals and fungi are the ____heterotrophs_____________________ or _____consumers_______.The process by ...
... ___biome___________. Plants are the only organisms that can convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. Plants are the __autotrophs________ or ____producers_______ and the animals and fungi are the ____heterotrophs_____________________ or _____consumers_______.The process by ...
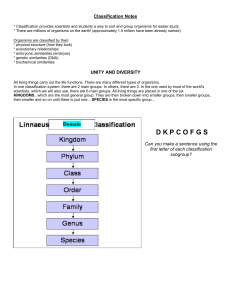
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
... protein coat. They don’t have any organelles or cytoplasm. They can have capsule surrounding protein coat. Some viruses infect bacteria, they are called bacteriophages. Viruses can be classified according to their nucleic acid type. Mostly animal viruses have DNA and plant viruses have RNA. ...
... protein coat. They don’t have any organelles or cytoplasm. They can have capsule surrounding protein coat. Some viruses infect bacteria, they are called bacteriophages. Viruses can be classified according to their nucleic acid type. Mostly animal viruses have DNA and plant viruses have RNA. ...
Internal Systems Digestive System
... Biology as a science is based on the Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the simplest unit that can carry out all life processes. 3. All cells come from other cells, they do not come from non-living matter. ...
... Biology as a science is based on the Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the simplest unit that can carry out all life processes. 3. All cells come from other cells, they do not come from non-living matter. ...
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
eoc powerpoint # 2
... • CHANGE OVER TIME (Charles Darwin) • Found similarities with finches and tortoises ...
... • CHANGE OVER TIME (Charles Darwin) • Found similarities with finches and tortoises ...
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
... DNA provides the blueprints for making proteins, and proteins serve as the tools that actually build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a ...
... DNA provides the blueprints for making proteins, and proteins serve as the tools that actually build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a ...
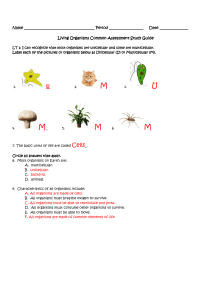
Living Organisms unit test study guide - Answer Key - Parkway C-2
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
... -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cells with cell walls, and must consume other organisms for energy --A plant is made of ...
Bacteria and Viruses Notes Review: Archaebacteria • Are
... Composed of DNA or RNA in a protein coat called a capsid. ...
... Composed of DNA or RNA in a protein coat called a capsid. ...
Vocabulary review
... b. stores energy in its bonds c. compounds made primarily of carbon atoms d. process used to break down a polymer e. building blocks of DNA f. cluster of atoms that influences the characteristics of a molecule g. building blocks of protein h. place where a substrate fits into an enzyme ...
... b. stores energy in its bonds c. compounds made primarily of carbon atoms d. process used to break down a polymer e. building blocks of DNA f. cluster of atoms that influences the characteristics of a molecule g. building blocks of protein h. place where a substrate fits into an enzyme ...
S2 rev pkt 2013(evol - body)
... traveled to the Galapagos Islands and made many observations about the organisms ...
... traveled to the Galapagos Islands and made many observations about the organisms ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.