Fun with Cells with the Amoeba Sisters
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
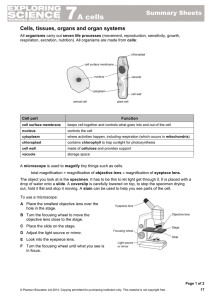
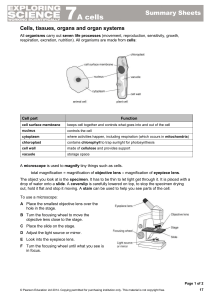
Cells and Organs
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
... combustion of food and they eliminate the carbon dioxide produced. The urinary system disposes of dissolved waste molecules, the intestinal tract removes solid wastes and the skin and lungs rid the body of heat energy. The circulatory system moves all these substances to or from cells where they are ...
CHAPTER 3
... - Contains carbon and hydrogen and are usually associated with living things or things that were once alive; four groups of organic substances make up all living things. 1. Carbohydrates-supply energy for cell processes 2. Lipids- store and release large amounts of energy 3. Proteins- the building b ...
... - Contains carbon and hydrogen and are usually associated with living things or things that were once alive; four groups of organic substances make up all living things. 1. Carbohydrates-supply energy for cell processes 2. Lipids- store and release large amounts of energy 3. Proteins- the building b ...
Bozeman Video Guide - Cell Communication
... 7) How does the macrophage pass information to the helper T cell? 8) What message does the helper T cell pass on to the B cells and the killer T cells? 9) How are messages sent between neurons? 10) What is the benefit of a local regulator vs. communication through cell-to-cell contact communication? ...
... 7) How does the macrophage pass information to the helper T cell? 8) What message does the helper T cell pass on to the B cells and the killer T cells? 9) How are messages sent between neurons? 10) What is the benefit of a local regulator vs. communication through cell-to-cell contact communication? ...
The History of Cell Biology
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
active reading worksheets
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
active reading worksheets
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
... What Hooke had observed were actually the remains of dead plant cells. The first person to observe living cells was a Dutch trader, Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Although van Leeuwenhoek’s microscope was rather simple, in 1673 it was powerful enough to enable him to view the world of microscopic organisms ...
Biology EOCT Study Guide MrsFrank – KEY
... 50. What are the base pairs in DNA? A,T,G,C RNA? A,U,G,C 51. What is a mutation? change in DNA What can cause a mutation? copying error; mutagens 52. Distinguish between chromosomal mutations and gene mutations. Give an example of each. Chromosomal mutations: entire chromosome is duplicated or lost; ...
... 50. What are the base pairs in DNA? A,T,G,C RNA? A,U,G,C 51. What is a mutation? change in DNA What can cause a mutation? copying error; mutagens 52. Distinguish between chromosomal mutations and gene mutations. Give an example of each. Chromosomal mutations: entire chromosome is duplicated or lost; ...
Midterm Exam: 2000-2001
... 20. The dispersal of ammonia fumes throughout a room is an example of A. Diffusion B. Osmosis ...
... 20. The dispersal of ammonia fumes throughout a room is an example of A. Diffusion B. Osmosis ...
Coarse-Graining of Macromolecules
... by chopping up DNA of interest with restriction enzymes and then gluing these fragments into the phage genome and then infecting cells with the modified phage. The phage DNA circularizes within E. coli and is then propagated from one generation of E. coli to the next and carries with it copies of th ...
... by chopping up DNA of interest with restriction enzymes and then gluing these fragments into the phage genome and then infecting cells with the modified phage. The phage DNA circularizes within E. coli and is then propagated from one generation of E. coli to the next and carries with it copies of th ...
Test Review BIOLOGY
... • Basic building block is called nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base) ...
... • Basic building block is called nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base) ...
Biology 11 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Grouping Species The
... Kingdom Plantae § Members of Kingdom Plantae form the base of all terrestrial habitats. § All plants are multicellular and have cell walls composed of cellulose. § Most plants are autotrophs, but some are heterotrophic. ...
... Kingdom Plantae § Members of Kingdom Plantae form the base of all terrestrial habitats. § All plants are multicellular and have cell walls composed of cellulose. § Most plants are autotrophs, but some are heterotrophic. ...
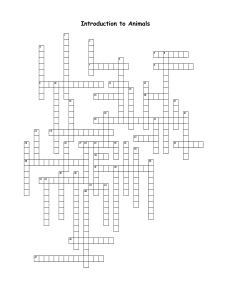
Introduction to Animals Crosswords
... 28. Specialized nerve cells 29. How animals take in food 30. Number of tissue layers in Cnidarians 31. Symmetry where organisms have a right and left side 33. Organisms whose first opening becomes the mouth 36. Outer coverings of an animal 38. Rigid outer covering in all arthropods 39. Series of rap ...
... 28. Specialized nerve cells 29. How animals take in food 30. Number of tissue layers in Cnidarians 31. Symmetry where organisms have a right and left side 33. Organisms whose first opening becomes the mouth 36. Outer coverings of an animal 38. Rigid outer covering in all arthropods 39. Series of rap ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 The Answer are under each
... Disease of uncontrolled cell growth 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. What occurred during the osmosis experiment (egg and vinegar) and the diffusion experiment (bag and corn starch) and why? The egg got bigger and increased in mass because there was a higher conce ...
... Disease of uncontrolled cell growth 24. Be able to complete a one trait cross using a punnet square. 25. What occurred during the osmosis experiment (egg and vinegar) and the diffusion experiment (bag and corn starch) and why? The egg got bigger and increased in mass because there was a higher conce ...
Name - Valhalla High School
... d. integumentary & reproductive 4. _______ Finding shelter, avoiding predators, and obtaining food are most closely related to the ability of an animal to a. increase the rate of cell division c. use structures adapted for movement b. transport carbon dioxide to cells d. excrete waste products to ce ...
... d. integumentary & reproductive 4. _______ Finding shelter, avoiding predators, and obtaining food are most closely related to the ability of an animal to a. increase the rate of cell division c. use structures adapted for movement b. transport carbon dioxide to cells d. excrete waste products to ce ...
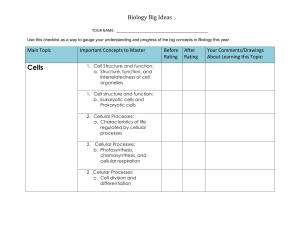
Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
File chemical comp. in cells notes 8a
... found in the cell walls of plants is a type of carbohydrate Lipids – are energy-rich organic compounds made of C, H and O – fats, oils and waxes are all lipids Lipids contain even more energy than carbohydrates! Cells store energy in lipids for late use What do a bird’s feathers, a spider’s web and ...
... found in the cell walls of plants is a type of carbohydrate Lipids – are energy-rich organic compounds made of C, H and O – fats, oils and waxes are all lipids Lipids contain even more energy than carbohydrates! Cells store energy in lipids for late use What do a bird’s feathers, a spider’s web and ...
Name - 7th Grade Life Science and STEM
... Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction Sexual reproduction: 2 parents prod ...
... Grow- increase in size Development- change in form as the organism grows 2. What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Example: body temp and human muscles 3. The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction Sexual reproduction: 2 parents prod ...
Evidence for Evolution
... – in other words, we share a more recent ancestor with them than any other living species. Our genes are 98.2% identical. The humans and chimps last shared an ancestor with the gorillas at an earlier time. Human and chimp DNA is 97.7% identical to a gorilla’s. Human, chimp, and gorilla genes are ...
... – in other words, we share a more recent ancestor with them than any other living species. Our genes are 98.2% identical. The humans and chimps last shared an ancestor with the gorillas at an earlier time. Human and chimp DNA is 97.7% identical to a gorilla’s. Human, chimp, and gorilla genes are ...
Name Answers MOD _____ Living Environment Benchmark Review
... 11. Many cells working together to perform a job is called a tissue. 12. The main purpose of the vascular system in a plant is to … Transport necessary materials (nutrients and water) throughout the plant 13. Which system in an animal is most closely related to the vascular system in a plant? circu ...
... 11. Many cells working together to perform a job is called a tissue. 12. The main purpose of the vascular system in a plant is to … Transport necessary materials (nutrients and water) throughout the plant 13. Which system in an animal is most closely related to the vascular system in a plant? circu ...
Spring Semester Biology Review
... • Meiosis occurs in diploid cells. The chromosomes duplicate once, and through two successive divisions, four haploid cells are produced, each with half the chromosome number of the parental cell. • Meiosis occurs only in sexually reproducing organisms. Depending on the organism, it may produce hapl ...
... • Meiosis occurs in diploid cells. The chromosomes duplicate once, and through two successive divisions, four haploid cells are produced, each with half the chromosome number of the parental cell. • Meiosis occurs only in sexually reproducing organisms. Depending on the organism, it may produce hapl ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.