Job Vacancy: Postdoctoral Research Scientist in Cell Biology
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
Life Science Second Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide Chapters 7
... ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the identity of an organism b. how many animals are birds c. how long a fungus can live d. when a species of organism appeared on Earth ____ 33. How many kingdoms are recognized today? a. four c. six b. five d. ten ...
... ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the identity of an organism b. how many animals are birds c. how long a fungus can live d. when a species of organism appeared on Earth ____ 33. How many kingdoms are recognized today? a. four c. six b. five d. ten ...
OB41 - OB42
... may harm cells if not removed • examples of toxic substances are carbon dioxide and urea www.juniorscience.ie ...
... may harm cells if not removed • examples of toxic substances are carbon dioxide and urea www.juniorscience.ie ...
goal 4 answers
... 4. What is the current seven-level classification system? (DKPCOFGS) Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus & Species (What is binomial nomenclature? A two-name naming system based in Latin to identify a single organism. 6. How do you write a “scientific name?” All in italics or underl ...
... 4. What is the current seven-level classification system? (DKPCOFGS) Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus & Species (What is binomial nomenclature? A two-name naming system based in Latin to identify a single organism. 6. How do you write a “scientific name?” All in italics or underl ...
topic1 RETEST
... 17. Communication between cells is affected if there is decreased ability to produce (1) digestive enzymes and gametes (2) antibodies and chloroplasts (3) hormones and nerve impulses (4) antibiotics and guard cell 18. Organ systems of the human body interact to maintain a balanced internal environme ...
... 17. Communication between cells is affected if there is decreased ability to produce (1) digestive enzymes and gametes (2) antibodies and chloroplasts (3) hormones and nerve impulses (4) antibiotics and guard cell 18. Organ systems of the human body interact to maintain a balanced internal environme ...
File
... • Found in every living part of a living cell • Amino acids – are the small molecular units that make up the very large protein molecules a. 22 different amino acids b. 9 essential amino acids – must be ingested because they cannot be made by the body Enzymes • Specialized protein molecules found in ...
... • Found in every living part of a living cell • Amino acids – are the small molecular units that make up the very large protein molecules a. 22 different amino acids b. 9 essential amino acids – must be ingested because they cannot be made by the body Enzymes • Specialized protein molecules found in ...
chapter2 review
... (d) The smaller cell should be better at absorbing nutrients and removing waste because it has a 2:1 ratio of surface area to volume. It has twice as much surface area as the larger cell, for the same amount of volume. 9. Tissues, organs, and organ systems are required in large multicellular organis ...
... (d) The smaller cell should be better at absorbing nutrients and removing waste because it has a 2:1 ratio of surface area to volume. It has twice as much surface area as the larger cell, for the same amount of volume. 9. Tissues, organs, and organ systems are required in large multicellular organis ...
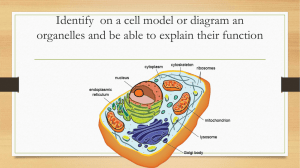
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... contain more hemoglobin and, therefore, carry more oxygen molecules. It also allows the cell to have its distinctive bi-concave shape which aids diffusion. This shape would not be possible if the cell had a nucleus in the ...
... contain more hemoglobin and, therefore, carry more oxygen molecules. It also allows the cell to have its distinctive bi-concave shape which aids diffusion. This shape would not be possible if the cell had a nucleus in the ...
Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems
... Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
... Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
Review of the EOC
... • Scientists theorize that multi-cellular organisms evolved from colonies of eukaryotes cells. • Terrestrial organisms evolved about 450 million years ago. Adaptations for life on land included internal transport systems and methods to conserve water. • The locations of Earth’s continents have chang ...
... • Scientists theorize that multi-cellular organisms evolved from colonies of eukaryotes cells. • Terrestrial organisms evolved about 450 million years ago. Adaptations for life on land included internal transport systems and methods to conserve water. • The locations of Earth’s continents have chang ...
BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW - G. Holmes Braddock High School
... • Scientists theorize that multi-cellular organisms evolved from colonies of eukaryotes cells. • Terrestrial organisms evolved about 450 million years ago. Adaptations for life on land included internal transport systems and methods to conserve water. • The locations of Earth’s continents have chang ...
... • Scientists theorize that multi-cellular organisms evolved from colonies of eukaryotes cells. • Terrestrial organisms evolved about 450 million years ago. Adaptations for life on land included internal transport systems and methods to conserve water. • The locations of Earth’s continents have chang ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Refreshers April 2015
... Prokaryotes are not as complex as eukaryotes and have some major differences. What do these images reference to? ...
... Prokaryotes are not as complex as eukaryotes and have some major differences. What do these images reference to? ...
File
... and other materials would not be able to reach all parts of the cell quickly enough to keep it alive. 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each ce ...
... and other materials would not be able to reach all parts of the cell quickly enough to keep it alive. 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each ce ...
Biology Learning Targets Explained
... recent common ancestor are more closely related than those with an older common ancestor. ...
... recent common ancestor are more closely related than those with an older common ancestor. ...
CG--SCI-answers-NJ.ASK - Grade 8 Learning from the Fossil
... same stage in humans when we are adolescents. We mature into adults, and the flies then grow into adult flies. We then reproduce, and so do the flies. The cycle starts all over again, with babies or eggs. This pattern doesn’t take the same amount of time to occur, but the same stages happen. The org ...
... same stage in humans when we are adolescents. We mature into adults, and the flies then grow into adult flies. We then reproduce, and so do the flies. The cycle starts all over again, with babies or eggs. This pattern doesn’t take the same amount of time to occur, but the same stages happen. The org ...
RELEASED North Carolina READY End-of-Course Assessment
... A freshwater plant is placed in a container of saltwater. What will most likely happen to the cells of the plant? They will swell because water will move into them. ...
... A freshwater plant is placed in a container of saltwater. What will most likely happen to the cells of the plant? They will swell because water will move into them. ...
File
... flagella - a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and functions in locomotion Cell wall - A cell wall is a tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds Plant cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and pr ...
... flagella - a tail-like projection that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and functions in locomotion Cell wall - A cell wall is a tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds Plant cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and pr ...
Sophie Wilson November 2, 2010 Bio, Mr. Miller Investigation 4
... into our previous investigation), carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids (lipids make up the membrane of cells that have barriers, consisting of everything within the cell and prevents compounds from passing in or out of the cell. All organisms are made up of cells, some unicellular and others multicel ...
... into our previous investigation), carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids (lipids make up the membrane of cells that have barriers, consisting of everything within the cell and prevents compounds from passing in or out of the cell. All organisms are made up of cells, some unicellular and others multicel ...
File - PATRIOTS POINT
... There are millions of organisms living on Earth. Biologists have created a method for naming and classifying these organisms based on their similarities. The study of how scientists classify organisms is k ...
... There are millions of organisms living on Earth. Biologists have created a method for naming and classifying these organisms based on their similarities. The study of how scientists classify organisms is k ...
Chapter 2: Living Things Notes
... Objective 1.0: Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth & development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify homeostasis as the process by which an organism responds to its internal or external envir ...
... Objective 1.0: Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth & development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify homeostasis as the process by which an organism responds to its internal or external envir ...
Worcester Public Schools High School Course Syllabus – District
... An understanding of concepts in Biology is essential for living in society today. There are social, ethical and legal issues associated with different aspects of Biology. Many new technologies used in Biology have both positive and negative attributes. Cells have organized structures and systems nec ...
... An understanding of concepts in Biology is essential for living in society today. There are social, ethical and legal issues associated with different aspects of Biology. Many new technologies used in Biology have both positive and negative attributes. Cells have organized structures and systems nec ...
III Bimester Questionnaire
... Lungs take in oxygen. Other parts of the respiratory system transfer it to the blood. Carbon Dioxide is removed from the blood and then exhaled from the body. ...
... Lungs take in oxygen. Other parts of the respiratory system transfer it to the blood. Carbon Dioxide is removed from the blood and then exhaled from the body. ...
Evolution / Classification
... 10. Which kingdoms have the most clear cut division? (The most different from each other?) 457 Plants & Animals 11. What is a dichotomous key and how is it used? 462 It is a way to identify unknown organisms. It is used by answering a series of yes & no questions. Evolution 1. Define the following t ...
... 10. Which kingdoms have the most clear cut division? (The most different from each other?) 457 Plants & Animals 11. What is a dichotomous key and how is it used? 462 It is a way to identify unknown organisms. It is used by answering a series of yes & no questions. Evolution 1. Define the following t ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.