Characteristics of Life- Borton
... Fire can grow. Fire needs fuel and oxygen. But fire is not a form of life, although it shares a few traits with some living things. How can you distinguish between non-living and living things? The Characteristics of Life ...
... Fire can grow. Fire needs fuel and oxygen. But fire is not a form of life, although it shares a few traits with some living things. How can you distinguish between non-living and living things? The Characteristics of Life ...
1.1 Unity and Diversity
... common ancestor, the diversity of the forelimbs having been modified by natural selection operating over millions of generations in different environmental conditions. ...
... common ancestor, the diversity of the forelimbs having been modified by natural selection operating over millions of generations in different environmental conditions. ...
TAKS biology review
... Do vaccines work on viruses? • Vaccines are a piece of protein from the virus coat, or a weaker or empty virus, in a shot that the doctor gives you. • The bits train your immune system to recognize and attack when they see that protein or virus. • But some viruses change proteins too quickly for us ...
... Do vaccines work on viruses? • Vaccines are a piece of protein from the virus coat, or a weaker or empty virus, in a shot that the doctor gives you. • The bits train your immune system to recognize and attack when they see that protein or virus. • But some viruses change proteins too quickly for us ...
Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam
... Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam Chapters 19-22, 26-28, 30-32 1. Be able to recognize the three shapes of bacteria. 2. How are prokaryotic bacteria identified / classified? 3. Bacteria are sometimes called nature’s recyclers because they _______________ nutrients in dead matter. 4. Bacteria tha ...
... Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam Chapters 19-22, 26-28, 30-32 1. Be able to recognize the three shapes of bacteria. 2. How are prokaryotic bacteria identified / classified? 3. Bacteria are sometimes called nature’s recyclers because they _______________ nutrients in dead matter. 4. Bacteria tha ...
BIOLOGY20SOL20REVIEW20SHEET2020131
... #, energy, and biomass as you move through a food chain? Which level has the highest # and which has the lowest #? 48. Define consumer, producer, carnivore, omnivore, herbivore, heterotroph, and autotroph. 49. Diagram the Carbon cycle. 50. What is transpiration? 51. Define mutualism, commensalism, a ...
... #, energy, and biomass as you move through a food chain? Which level has the highest # and which has the lowest #? 48. Define consumer, producer, carnivore, omnivore, herbivore, heterotroph, and autotroph. 49. Diagram the Carbon cycle. 50. What is transpiration? 51. Define mutualism, commensalism, a ...
KeystoneReview Guide Cells
... Bio Review – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: ...
... Bio Review – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: ...
DNA and Proteins
... have been accumulating over recent years. Developments in molecular biology and gene mapping have made it necessary to develop a system where research can be shared easily. Click here to find out how scientists can use bioinformatics in their genetic research ...
... have been accumulating over recent years. Developments in molecular biology and gene mapping have made it necessary to develop a system where research can be shared easily. Click here to find out how scientists can use bioinformatics in their genetic research ...
Abiotic- a non living thing
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
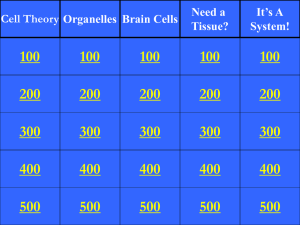
Cell Theory Organelles Brain Cells Need a Tissue?
... 2. Saw the units of life for the first time. 3. Named these units “cells” ...
... 2. Saw the units of life for the first time. 3. Named these units “cells” ...
Organization of Living Things
... cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue contracts, making the heart pump. The nerve tissue brings messages that tell the heart how fast to beat. The blood tissue is carried from the heart to other organs of the body. ...
... cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue contracts, making the heart pump. The nerve tissue brings messages that tell the heart how fast to beat. The blood tissue is carried from the heart to other organs of the body. ...
Biology_Review-1
... What is Biology, you ask? Biology is the study of life. Living things are called organisms. Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. Viruses are not alive – they are not organisms. ...
... What is Biology, you ask? Biology is the study of life. Living things are called organisms. Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. Viruses are not alive – they are not organisms. ...
Review Guide Cells
... BioBoot Camp – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: ...
... BioBoot Camp – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: ...
BioBoot Camp – Cells
... BioBoot Camp – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: Organization and cells – all organisms have cells. May be made of 1 cell (unicellular) or many cells (multicellular). Response to stimuli - the stimulus ...
... BioBoot Camp – Cells BIO.A.1.1.1 Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms All living organisms have: Organization and cells – all organisms have cells. May be made of 1 cell (unicellular) or many cells (multicellular). Response to stimuli - the stimulus ...
Introduction to Animals Worksheet
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
Biology Syllabus
... Quarter 4- Guiding Question(s): How do we all work together? What did we learn? How do we affect the rest of the world? 2 weeks Biology Standard 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments. 2.1.1 Analyze the flow of energy and cycling of Create an Ecosystem matter ( ...
... Quarter 4- Guiding Question(s): How do we all work together? What did we learn? How do we affect the rest of the world? 2 weeks Biology Standard 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments. 2.1.1 Analyze the flow of energy and cycling of Create an Ecosystem matter ( ...
Afterschool Biology EOC Program
... Biology Teachers Katie Sparks **Tiffaney Clark Lauren Edmonds and Susan Waldron Reagan Davis and Erica Flint Callie Kresta Kathleen Farmer ...
... Biology Teachers Katie Sparks **Tiffaney Clark Lauren Edmonds and Susan Waldron Reagan Davis and Erica Flint Callie Kresta Kathleen Farmer ...
Chapters 16-19: Diversity of Life 1. Taxonomic Classification The Classification of Organisms
... don’t ingest food like animals do): • secrete digestive enzymes, absorb food • some are detritus feeders (consume dead matter) some are parasites (prey on living) • decomposition of dead organic matter is extremely important for ecosystems (recycles nutrients) ...
... don’t ingest food like animals do): • secrete digestive enzymes, absorb food • some are detritus feeders (consume dead matter) some are parasites (prey on living) • decomposition of dead organic matter is extremely important for ecosystems (recycles nutrients) ...
HERE
... disorder? Because they only have one X chromosome, they show the trait given by that chromosome Stem Cells What are some benefits of growing stem cells in the laboratory? We can make any type of cell, therefore we can repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of ...
... disorder? Because they only have one X chromosome, they show the trait given by that chromosome Stem Cells What are some benefits of growing stem cells in the laboratory? We can make any type of cell, therefore we can repair cells, organs, and repairing limbs. Discuss the steps in Darwin’s theory of ...
Evolution Worksheet #2
... 2) What is the definition of a Species? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3) An inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in its sp ...
... 2) What is the definition of a Species? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3) An inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in its sp ...
EOC_CUMMULATIVE_REVIEW
... 3. ____________________- to get bigger or gain mass by adding new cells 4. ____________________- change; puberty during adolescence 5. ____________________- either asexually or sexually 6. ____________________- ex. body temperature, metabolism B. Place the following biological terms in order from sm ...
... 3. ____________________- to get bigger or gain mass by adding new cells 4. ____________________- change; puberty during adolescence 5. ____________________- either asexually or sexually 6. ____________________- ex. body temperature, metabolism B. Place the following biological terms in order from sm ...
midterm 16 review
... Homeostasis through small changes that keep the internal environment at a level needed for survival ...
... Homeostasis through small changes that keep the internal environment at a level needed for survival ...
Warm Up Question: - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... Multicellular • Then came the multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell. • Most life is multicellular, as are all animals (except for specialized organisms such as Myxozoa) and land plants. ...
... Multicellular • Then came the multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell. • Most life is multicellular, as are all animals (except for specialized organisms such as Myxozoa) and land plants. ...
Physiology (17%) Sample Test Prep Questions
... -------------------------------------------------------------Which of the following require a host cell because they are not able to make proteins on their own? A blue-green algae B bacteria C protozoans D viruses Answer: D. viruses ...
... -------------------------------------------------------------Which of the following require a host cell because they are not able to make proteins on their own? A blue-green algae B bacteria C protozoans D viruses Answer: D. viruses ...
Chapter 18
... Some are heterotrophs that use organic molecules that they engulf & breakdown Some use aerobic respiration and others use fermentation (anaerobic). These processes produce energy ...
... Some are heterotrophs that use organic molecules that they engulf & breakdown Some use aerobic respiration and others use fermentation (anaerobic). These processes produce energy ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.