File
... Navigate through the virtual investigation titled “DNA, RNA & Gene Expression” on the Holt website. Answer these questions as you proceed. This should serve as a refresher on the scientific method. Remember, for full credit you must use complete sentences. Part 1 of 5 Look at the diagram in this par ...
... Navigate through the virtual investigation titled “DNA, RNA & Gene Expression” on the Holt website. Answer these questions as you proceed. This should serve as a refresher on the scientific method. Remember, for full credit you must use complete sentences. Part 1 of 5 Look at the diagram in this par ...
EOC Review Packet
... 2. Form a Hypothesis – research using many different sources for current findings a. Scientific Journals are the best place to locate current findings on the newest technologies b. Encyclopedias are a good place to find information on extinct species or historical theories c. State/Local agencies ca ...
... 2. Form a Hypothesis – research using many different sources for current findings a. Scientific Journals are the best place to locate current findings on the newest technologies b. Encyclopedias are a good place to find information on extinct species or historical theories c. State/Local agencies ca ...
Nervous System
... Multi cellular organisms have well developed transport systems because all cells of a multicellular organism are not in direct contact with the outside environment for the exchange of substances. The surface cells are in contact with the external environment Energy produced in one cell is transporte ...
... Multi cellular organisms have well developed transport systems because all cells of a multicellular organism are not in direct contact with the outside environment for the exchange of substances. The surface cells are in contact with the external environment Energy produced in one cell is transporte ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
THREE DOMAINS NOTES
... and store free energy for use in biological processes; how cells can meet their energy needs D. Heterotrophs 1. These organisms must "take in" nutrition 2.they capture free energy that is present in carbon compounds produced by other organisms 3. includes all animals, all fungi, and many protists an ...
... and store free energy for use in biological processes; how cells can meet their energy needs D. Heterotrophs 1. These organisms must "take in" nutrition 2.they capture free energy that is present in carbon compounds produced by other organisms 3. includes all animals, all fungi, and many protists an ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
... a place to live, and oxygen. They are made up of cells, the building blocks of living things. They are made up of parts that have specific jobs to help keep them alive. ...
Honors Biology Final Exam Review Mrs. Speirs Directions: In no
... your learning. This review is intended for you to use to support your study sessions. Can you demonstrate proficiency with these concepts? How well can you connect the big ideas with each other? What kind of whiteboard representations come to mind as you review these concepts? Could you write a shor ...
... your learning. This review is intended for you to use to support your study sessions. Can you demonstrate proficiency with these concepts? How well can you connect the big ideas with each other? What kind of whiteboard representations come to mind as you review these concepts? Could you write a shor ...
Worksheet
... air, water, weather, temperature, any organisms in the area, and many other factors. These external environmental factors act as stimuli and can cause a response from living things. Organisms need to respond to the changes in order to stay alive and healthy. For example, if you go outside on a brigh ...
... air, water, weather, temperature, any organisms in the area, and many other factors. These external environmental factors act as stimuli and can cause a response from living things. Organisms need to respond to the changes in order to stay alive and healthy. For example, if you go outside on a brigh ...
WEB . WHRSD . ORG - Whitman-Hanson Regional School District
... interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (car ...
... interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (car ...
Protist and Fungi
... medicines work against them? Vaccines Antibiotics Chlorine in water Antifungal medicines ...
... medicines work against them? Vaccines Antibiotics Chlorine in water Antifungal medicines ...
interactive_textbook reading
... organisms get food in the same way. There are three ways in which organisms can get food. Some organisms, such as plants, are producers. Producers make their own food using energy from their environment. For example, plants, and some bacteria and protists, use the sun’s energy to make food from carb ...
... organisms get food in the same way. There are three ways in which organisms can get food. Some organisms, such as plants, are producers. Producers make their own food using energy from their environment. For example, plants, and some bacteria and protists, use the sun’s energy to make food from carb ...
Bioinformatics
... 66% of drugs are rejected (poor efficacy) • Phase III: positive effect on variety of (300–3,000) patients 75% of drugs are rejected ~8 years, fewer than 6% of compounds get approval $300 million to $1.7 billion and up to 20 years, only 1/10 projects succeeds [1] D Young, Computational drug design, N ...
... 66% of drugs are rejected (poor efficacy) • Phase III: positive effect on variety of (300–3,000) patients 75% of drugs are rejected ~8 years, fewer than 6% of compounds get approval $300 million to $1.7 billion and up to 20 years, only 1/10 projects succeeds [1] D Young, Computational drug design, N ...
Introduction
... What Does the Science of Biology Encompass? Scientific principles underlie all scientific inquiry: 1) All events can be traced to natural causes that can be comprehended 2) Laws of nature (physics) hold in all time and space 3) People perceive natural events in similar ways Scientific method is the ...
... What Does the Science of Biology Encompass? Scientific principles underlie all scientific inquiry: 1) All events can be traced to natural causes that can be comprehended 2) Laws of nature (physics) hold in all time and space 3) People perceive natural events in similar ways Scientific method is the ...
AHSGE Biology Review
... 35. catalyst – substance that lowers the activation energy (energy needed to start a reaction) of a reaction, but is not affected by the reaction 36. cell – smallest unit of life, all living things are made of one or more cells 37. cell membrane – barrier that separates a cell from it’s surrounding ...
... 35. catalyst – substance that lowers the activation energy (energy needed to start a reaction) of a reaction, but is not affected by the reaction 36. cell – smallest unit of life, all living things are made of one or more cells 37. cell membrane – barrier that separates a cell from it’s surrounding ...
WS Chapter 1
... b. Only one variable is tested at a time. c. Scientists always use controlled experiments. d. Controlled experiments cannot be performed on living things. 7. A scientific theory is a. another word for hypothesis. b. a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. c. the same as ...
... b. Only one variable is tested at a time. c. Scientists always use controlled experiments. d. Controlled experiments cannot be performed on living things. 7. A scientific theory is a. another word for hypothesis. b. a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. c. the same as ...
CELLS
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
Characteristics of Life - Glasgow Independent Schools
... Adults don’t always look like the babies of a species. All organisms begin their lives as single cells. Over time, these organisms grow and take on the characteristics of their species. Growth results in an increase in the amount of living material and the formation of new structures. All organisms ...
... Adults don’t always look like the babies of a species. All organisms begin their lives as single cells. Over time, these organisms grow and take on the characteristics of their species. Growth results in an increase in the amount of living material and the formation of new structures. All organisms ...
KINGDOM PROTISTA
... Can happen occasionally; when hyphae from two different fungi meet and fuse together to make spores ...
... Can happen occasionally; when hyphae from two different fungi meet and fuse together to make spores ...
GENETICS
... fascinating areas of biology. It has effects at all scales from the molecule to population. Its study involves a wide variety of tools, from biochemical tests to microscopy to breeding experiments. -Genetics is the science of heredity. ...
... fascinating areas of biology. It has effects at all scales from the molecule to population. Its study involves a wide variety of tools, from biochemical tests to microscopy to breeding experiments. -Genetics is the science of heredity. ...
Cell Function CC
... cell: smallest units of organisms that carry on the functions of life tissues: groups of similar cells that do the same sort of work (ex.- muscle tissue) organ: structure made up of different types of tissues (ex.- heart) organ system: a group of organs working together to do a certain job (ex. – ca ...
... cell: smallest units of organisms that carry on the functions of life tissues: groups of similar cells that do the same sort of work (ex.- muscle tissue) organ: structure made up of different types of tissues (ex.- heart) organ system: a group of organs working together to do a certain job (ex. – ca ...
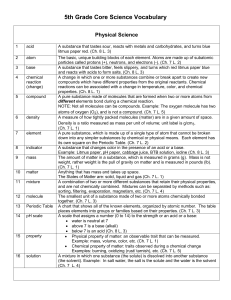
5th Grade - IUSD.org
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.