Chapter 19 – Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life
... The Three Domains of Life Like kingdoms, there are much broader groups called domains. There are three such domains. They are eukarya, archae, and bacteria. Eukarya is the newest group. The Domain Bacteria Characteristics and Kinds of Bacteria The first domain is bacteria. All organisms of the bacte ...
... The Three Domains of Life Like kingdoms, there are much broader groups called domains. There are three such domains. They are eukarya, archae, and bacteria. Eukarya is the newest group. The Domain Bacteria Characteristics and Kinds of Bacteria The first domain is bacteria. All organisms of the bacte ...
1. - OHIO SI
... 5. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. 6.Cells contain DNA, which is found specifically in the chromosome, and RNA found in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. 7. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organisms of similar species. 5. ___________________ i ...
... 5. Energy flow (metabolism and biochemistry) occurs within cells. 6.Cells contain DNA, which is found specifically in the chromosome, and RNA found in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. 7. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition in organisms of similar species. 5. ___________________ i ...
Cells - SchoolRack
... making nutrients for cells B holding cytoplasm within cells C regulating substances exiting cells D recognizing other cells ...
... making nutrients for cells B holding cytoplasm within cells C regulating substances exiting cells D recognizing other cells ...
standards - Henry County Schools
... of H2O in a lab setting with an emphasis on living systems. Synthesizing & breaking down organic macromolecules. Modeling macromolecule functions & relating them to biological systems. Demonstrate enzyme activity in a lab setting. ...
... of H2O in a lab setting with an emphasis on living systems. Synthesizing & breaking down organic macromolecules. Modeling macromolecule functions & relating them to biological systems. Demonstrate enzyme activity in a lab setting. ...
Emerging Methods in Molecular Biology and Genetics
... was founded in the mid-1950s, molecular biology and genetics were in their infancy and had little to offer neuropsychopharmacology. By 1967, when the first volume in this series was published, it still had not become apparent how greatly our field would be influenced by research on genes and on DNA. ...
... was founded in the mid-1950s, molecular biology and genetics were in their infancy and had little to offer neuropsychopharmacology. By 1967, when the first volume in this series was published, it still had not become apparent how greatly our field would be influenced by research on genes and on DNA. ...
Classification ppt - Madison County Schools
... The traits that are shown by the LEAST organisms will be the YOUNGEST because they appeared more recently; therefore, there would not have been as much time for speciation to occur creating multiple species with the trait. The traits that are shown by the MOST organisms will be the OLDEST becaus ...
... The traits that are shown by the LEAST organisms will be the YOUNGEST because they appeared more recently; therefore, there would not have been as much time for speciation to occur creating multiple species with the trait. The traits that are shown by the MOST organisms will be the OLDEST becaus ...
science vocabulary for 5th grade
... Interdependence-- the dependence of every form of life on other living things and on the natural resources in its environment, such as air, soil, and water Intestines-- Small- serves to digest and absorb nutrients/Large- absorbs water from and eliminates the residues of digestion Lungs-- two saclike ...
... Interdependence-- the dependence of every form of life on other living things and on the natural resources in its environment, such as air, soil, and water Intestines-- Small- serves to digest and absorb nutrients/Large- absorbs water from and eliminates the residues of digestion Lungs-- two saclike ...
Substance Element Molecule Compound Organic
... play in this process. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaksdown food into small molecule that the body can use, muscle line the digestive system organs and move the food materials through the system with peristalsis, Once the molecules are small enough for the cells to use they are ...
... play in this process. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaksdown food into small molecule that the body can use, muscle line the digestive system organs and move the food materials through the system with peristalsis, Once the molecules are small enough for the cells to use they are ...
Objectives
... •Organisms Living organisms are diverse but share certain characteristics. •Properties of Life Seven themes unify the science of biology: cellular structure and function, reproduction, metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, evolution, and interdependence. ...
... •Organisms Living organisms are diverse but share certain characteristics. •Properties of Life Seven themes unify the science of biology: cellular structure and function, reproduction, metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, evolution, and interdependence. ...
Cells Study Guide
... o Most cells are small because their volume is limited by how large their surface area is. o Cells produce more cells by cell division. ...
... o Most cells are small because their volume is limited by how large their surface area is. o Cells produce more cells by cell division. ...
Ch. 4 Cells
... • Chromatin is: strands of DNA and protein • Chromosomes are: densely packed, contain DNA and Protein for heredity. ...
... • Chromatin is: strands of DNA and protein • Chromosomes are: densely packed, contain DNA and Protein for heredity. ...
12C Analyze the flow of matter and energy through trophic levels
... Describe the evidence regarding the formation of key macromolecules (biomolecules) essential to life ...
... Describe the evidence regarding the formation of key macromolecules (biomolecules) essential to life ...
Dev Biol L1
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
CLASSIFICATION What is classification? Sorting out things
... kingdom classification.according to this living things are broadly grouped as: Monera-all bacteria Protista- amoeba Fungi Plants Animals ...
... kingdom classification.according to this living things are broadly grouped as: Monera-all bacteria Protista- amoeba Fungi Plants Animals ...
natural selection - faculty.fairfield.edu
... All organisms are made of cells. All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... All organisms are made of cells. All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
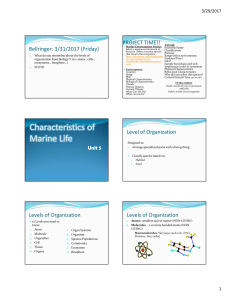
Bellringer: 3/31/2017 (Friday) PROJECT TIME!! Level of
... occur in the same place. 11. Ecosystem: a community or group of communities living in the same physical (non-living) environment. ...
... occur in the same place. 11. Ecosystem: a community or group of communities living in the same physical (non-living) environment. ...
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
... The surface area to volume ratio refers to the ratio of the cell’s total surface area in relation to its volume. Maximizing surface area to volume ratios is important so that the transport systems in cells can run efficiently ...
... The surface area to volume ratio refers to the ratio of the cell’s total surface area in relation to its volume. Maximizing surface area to volume ratios is important so that the transport systems in cells can run efficiently ...
File
... 1. All living things share certain characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. 2. The way living things carry out these processes may be different. 3. Non-living things lack the metabolic processes that maintain homeostasis. ...
... 1. All living things share certain characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. 2. The way living things carry out these processes may be different. 3. Non-living things lack the metabolic processes that maintain homeostasis. ...
Review Key
... 48. Sample Dihybrid Cross Question: The table below shows a cross between two pea plants both heterozygous for yellow seeds (Bb) and round seeds (Rr). What phenotype ratio would you expect in the offspring? ...
... 48. Sample Dihybrid Cross Question: The table below shows a cross between two pea plants both heterozygous for yellow seeds (Bb) and round seeds (Rr). What phenotype ratio would you expect in the offspring? ...
AP Biology Exam Guide
... one for a substrate and one for an inhibitor. The enzyme will oscillate between an active form and an inactive form, with an activator/inhibitor stabilizing the respective form. In feedback inhibition, inhibition the end product of a series of reactions serves as the allosteric inhibitor of an enzym ...
... one for a substrate and one for an inhibitor. The enzyme will oscillate between an active form and an inactive form, with an activator/inhibitor stabilizing the respective form. In feedback inhibition, inhibition the end product of a series of reactions serves as the allosteric inhibitor of an enzym ...
DEC 2016 BIO: some useful words File
... convert food substances into living matter Control of Keeping the internal environment stable, e.g. internal water concentration, temperature conditions Organelles membrane-bound structures in the cytoplasm of a cell which carry out particular functions. Cell basic unit of an organism Tissue a group ...
... convert food substances into living matter Control of Keeping the internal environment stable, e.g. internal water concentration, temperature conditions Organelles membrane-bound structures in the cytoplasm of a cell which carry out particular functions. Cell basic unit of an organism Tissue a group ...
Human Body Systems Unit Plan
... 1. How do organ systems interact with one another? 2. How do organ systems interact with their environment to meet basic needs? CURRICULAR COMPETENCIES ...
... 1. How do organ systems interact with one another? 2. How do organ systems interact with their environment to meet basic needs? CURRICULAR COMPETENCIES ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.