* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DEC 2016 BIO: some useful words File
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
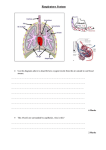
WORD DEFINITION OR NOTE Movement Change of position of the organism or parts of it Useful words for the EC1 BIOenergy EXAM from DECEMBER Respiration Releasing food 2016 Sensitivity Responding to changes in the environment Growth Getting bigger (cells grow and/or divide) Excretion Getting rid of toxic waste Nutrition The intake of food, and the processes that convert food substances into living matter Control of Keeping the internal environment stable, e.g. internal water concentration, temperature conditions Organelles membrane-bound structures in the cytoplasm of a cell which carry out particular functions. Cell basic unit of an organism Tissue a group of specialised cells carrying out the same function. Organ a group of different tissues working together to carry out a particular function. Organ systems a group of organs working together to carry out a particular function. cytoplasm jelly-like substance in cells where chemical reactions take place animal multicellular organism that is heterotrophic, made of complex cells, and has no cell walls plant multicellular organism that is autotrophic, made of complex cells, and has cell walls made of cellulose fungi single or multicellular organisms that are saprotrophic and have cell walls made of chitin bacteria very small single-celled organisms with no nucleus (prokaryotes) virus has a protein coat, smaller than a bacteria, and is a parasite (damages another organism) glycogen storage form of glucose in (most) bacteria, fungi and animals hyphae threads making up the main body (mycelium) of a multicellular fungus that perform saprotrophic nutrition autotrophic nutrition where the organism makes its own food by photosynthesis heterotrophic nutrition that consumes other organisms saprotrophic nutrition that uses enzymes to digest food externally and absorb the products vacuole space in a cell filled with fluid (in plants it is the largest part of the cell and filled with cell sap) chloroplasts structures containing chlorophyll and responsible for photosynthesis Respiration the process by which food molecules are broken down to release energy for the cells. Glucose a type of sugar, the main reactant in respiration TOPIC Useful words for the EC1 BIO EXAM DECEMBER 2016 Aerobic respiration Aerobic Mitochondria ATP Carbon dioxide Lime water Hydrogencarbonate indicator Anaerobic respiration Lactic acid food molecules broken down using oxygen to release energy for the cells. using oxygen. the site of aerobic cellular respiration in a cell. Substance that stores energy in the cell for a short time gas produced during aerobic respiration or fermentation and used up during photosynthesis solution of calcium hydroxide, used to test for carbon dioxide. chemical that turns orange/yellow where the level of carbon dioxide is high cellular respiration in the absence of oxygen. product of anaerobic respiration. it builds up in muscles with exercise. important in yoghurt and cheese making processes. Oxygen debt condition after exercise during which extra oxygen is needed to break down lactic acid Fermentation anaerobic respiration by yeast, plants or bacteria Ethanol a chemical in alcoholic drinks, produced by fermentation. Ventilation breathing in (inspiration/inhalation) and out (expiration/exhalation). Inspiration Breathing in Expiration Breathing out Thorax upper region of the body surrounded by the rib cage and the diaphragm, and containing the lungs and the heart. Diaphragm the sheet of muscle which divides the thorax from the abdomen. Trachea tube between the mouth or nose and the bronchi Bronchi tubes through which air passes, between the trachea and the smaller bronchioles Bronchioles small tubes that branch from each of the bronchi Alveoli air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place Capillaries tiny blood vessels, e.g. around alveoli Haemoglobin a protein in blood, responsible for carrying oxygen Oxyhaemoglobin formed when haemoglobin binds to oxygen molecules. Tar thick, black chemical found in tobacco smoke which can cause lung cancer, bronchitis and emphysema. Useful words for the EC1 BIO EXAM DECEMBER 2016 Nicotine Carcinogen Emphysema Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Reliable Control variable Enzyme Catalyse Substrate Denatured Active site solution solute solvent dissolve Concentration gradient Diffusion Cell membrane Semi-permeable Osmosis addictive drug found in tobacco a chemical which is known to cause cancer. condition of the lungs where walls of alveoli break down causing breathlessness using theory to predict results, e.g. ‘I think the plants will be smaller because they do not have enough water.’ the variable that you have decided to change, e.g. the temperature of the enzyme in an investigation to find out the effect of temperature on enzyme activity. the variable you are measuring as a result of changing the independent variable, e.g. the volume of CO2 produced as a result of different amounts of exercise. describes data we can trust. e.g. others get the same results. variable that might affect your result and therefore must be kept the same e.g. temperature. large molecule that catalyses a reaction in the body speed up a chemical reaction molecule that binds to an enzyme and is converted into a product enzymes that are denatured lose their shape and can no longer catalyse a reaction. the site on an enzyme where the substrates bind. when a solute is dissolved in a solution – it mixes completely and is transparent The solid material that dissolves in a solvent A liquid that dissolves a solute when a solid becomes part of a solution a difference in concentration across a membrane the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (along a concentration gradient). the membrane around the contents of a cell which controls what moves in and out of the cell. allowing only certain substances to pass through. the net movement of water from an area of high concentration (of water) to an area of low concentration (of water) across a semi- Useful words for the EC1 BIO EXAM DECEMBER 2016 permeable membrane.