File - Biology with Radjewski
... caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence ...
... caused by external or environmental factors that switch genes on and off and affect how cells read genes instead of being caused by changes in the DNA sequence ...
Diversity if Life Jeopardy Questions
... 3 This is a common name for some types of algae found in marine waters. KELP 1 Living things are classified using this ancient language. LATIN 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of th ...
... 3 This is a common name for some types of algae found in marine waters. KELP 1 Living things are classified using this ancient language. LATIN 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of th ...
File eoct review with answers
... 65. Define: species, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere. Is this the correct order for them? Organism: one specific species. Population: a group of organisms. Species: a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. Community: a group of popul ...
... 65. Define: species, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere. Is this the correct order for them? Organism: one specific species. Population: a group of organisms. Species: a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring. Community: a group of popul ...
Final Exam Review - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Protista: “the very first” List and describe several ...
... Protista: “the very first” List and describe several ...
Bio 112
... Page 8 44. Which of the following statements best describes the movements of energy and nutrients in ecosystems? a. Energy and nutrients flow through b. Energy cycles and nutrients recycle c. Energy increases and nutrients cycle d. Energy flows through and nutrients cycle e. Energy and nutrients cy ...
... Page 8 44. Which of the following statements best describes the movements of energy and nutrients in ecosystems? a. Energy and nutrients flow through b. Energy cycles and nutrients recycle c. Energy increases and nutrients cycle d. Energy flows through and nutrients cycle e. Energy and nutrients cy ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLS
... Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of ...
... Organism- any living thing Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of ...
COMMUNICATION
... 18) Briefly describe an experiment you could carry out to investigate a factor that affects the transpiration rate in plants. 19) Outline one way in which the technique of autoradiography has been used to trace the path of elements through plants or animals. 20) Explain why the caecum and colon (lar ...
... 18) Briefly describe an experiment you could carry out to investigate a factor that affects the transpiration rate in plants. 19) Outline one way in which the technique of autoradiography has been used to trace the path of elements through plants or animals. 20) Explain why the caecum and colon (lar ...
Cells and Systems Review Outine
... Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
... Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
chapter 1 - Juan Diego Academy
... build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a human gene may denote a protein hormone that stimulates growth. ○ Other human proteins include ...
... build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a human gene may denote a protein hormone that stimulates growth. ○ Other human proteins include ...
Name
... +/- a relationship between two different species in which one organism benefits while harming the other 31. What is commensalism? +/0 a relationship between two different species in which one organism benefits while the other organism is neither helped or harmed 32. What is the difference between na ...
... +/- a relationship between two different species in which one organism benefits while harming the other 31. What is commensalism? +/0 a relationship between two different species in which one organism benefits while the other organism is neither helped or harmed 32. What is the difference between na ...
Cells and Systems Notes Topic 1 1. What are five characteristics that
... 11. When an organism gets bigger, do its cells get bigger or does it add more cells? Explain why you gave the answer you gave. ...
... 11. When an organism gets bigger, do its cells get bigger or does it add more cells? Explain why you gave the answer you gave. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Lesson 1.1: Unifying Principles of
... approaches to biology generate information about phylogeny. These include the comparisons of DNA sequences conducted within molecular biology and comparisons of fossils or other records of ancient organisms in paleontology. Biologists organize and analyze evolutionary relationships through various m ...
... approaches to biology generate information about phylogeny. These include the comparisons of DNA sequences conducted within molecular biology and comparisons of fossils or other records of ancient organisms in paleontology. Biologists organize and analyze evolutionary relationships through various m ...
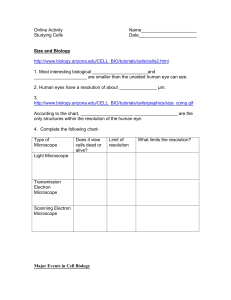
Studying cells_online activity
... 4. What type of microscope would allow you to study the orderly sequence of events that lead to the separation of chromosomes during mitosis? (Chromosomes are found inside of the cell's nucleus.) ...
... 4. What type of microscope would allow you to study the orderly sequence of events that lead to the separation of chromosomes during mitosis? (Chromosomes are found inside of the cell's nucleus.) ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functional units of life. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Define the principle of emergent properties and describe an example of it. ...
... 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functional units of life. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Define the principle of emergent properties and describe an example of it. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Key
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
... Unit 3 Test: Study Guide Living Organisms 1. What are the building blocks of all living organisms? cells 2. What are the 5 characteristics that makes something living? Made of cells, grow and develop, use energy, respond to their environment, reproduce 3. What is the difference between unicellular a ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Lesson 1: Unifying Principles of
... approaches to biology generate information about phylogeny. These include the comparisons of DNA sequences conducted within molecular biology and comparisons of fossils or other records of ancient organisms in paleontology. Biologists organize and analyze evolutionary relationships through various m ...
... approaches to biology generate information about phylogeny. These include the comparisons of DNA sequences conducted within molecular biology and comparisons of fossils or other records of ancient organisms in paleontology. Biologists organize and analyze evolutionary relationships through various m ...
Glossary - The Polesworth School
... Respiration that requires the presence of oxygen to release energy from glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water. A simple compound which, when combined with other amino acids in chains, makes proteins. There are 20 types of amino acids commonly found in living cells. Reproduction of some unicell ...
... Respiration that requires the presence of oxygen to release energy from glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water. A simple compound which, when combined with other amino acids in chains, makes proteins. There are 20 types of amino acids commonly found in living cells. Reproduction of some unicell ...
chapter 1
... DNA provides the blueprints for making proteins, and proteins serve as the tools that actually build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a ...
... DNA provides the blueprints for making proteins, and proteins serve as the tools that actually build and maintain the cell and carry out its activities. ○ For instance, the information carried in a bacterial gene may specify a certain protein in a bacterial cell membrane, while the information in a ...
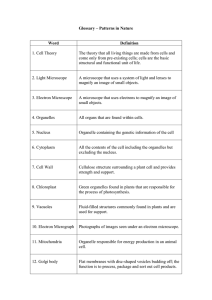
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... A chemical substance found in plant cells to strengthen cell walls. ...
... A chemical substance found in plant cells to strengthen cell walls. ...
Transport Phenomena in Cell Biology - Thermal
... • Existing models treat cells as well-mixed, but cell heterogeneity or “polarity” is essential for many important phenomena • The role of mass transport in information processing is just beginning to be explored • Reaction-diffusion dynamics are currently being explored in theory and in silico • Mor ...
... • Existing models treat cells as well-mixed, but cell heterogeneity or “polarity” is essential for many important phenomena • The role of mass transport in information processing is just beginning to be explored • Reaction-diffusion dynamics are currently being explored in theory and in silico • Mor ...
File - 5th with Smith
... grouping similar items/things together makes understanding them easier by identifying characteristics that living things share, scientists can group similar organisms together the way organisms look, live, eat, move, grow, change, and reproduce Grouping Living Things living organisms are cla ...
... grouping similar items/things together makes understanding them easier by identifying characteristics that living things share, scientists can group similar organisms together the way organisms look, live, eat, move, grow, change, and reproduce Grouping Living Things living organisms are cla ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.