* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taxonomy and Virus Review Answer Key File
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
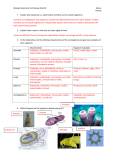
Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: 1. Explain why taxonomy is a valid system scientists use to classify organisms. Scientists use adaptations that organisms contain that differentiate them from other species. Further, scientists do not classify organisms as independent species unless they are unable to interbreed with their closest living ancestor. 2. Explain what a taxon is and why are there eight of them. Taxons are different levels of taxonomic organization and get increasingly specific as they advance. 3. In the table below, list the defining characteristics of the six kingdoms and give two examples of each organism. Characteristics Eukaryotic, multicellular, macroscopic, mobile, heterotrophic, no cell wall Organism Examples Insects, whale, tiger, human Plantae Eukaryotic, multicellular, macroscopic, immobile, autotrophic, cell wall made of cellulose, enlarged vacuole, chloroplasts present Lilly, fir tree, ivy Protista Eukaryotic, uni or multicellular, micro or macroscopic, mobile or immobile, autotrophic or heterotrophic Protozoa, diatoms, algae, slime mold Fungi Eukaryotic, multicellular, macroscopic, immobile, heterotrophic, cell wall made of chitin, decomposer, Mushrooms, penicillin producing fungus Bacteria prokaryotic, unicellular, microscopic, mobile, heterotrophic, cell wall Streptococcus, bacilli, spirilli Archaebacteria prokaryotic, multicellular, microscopic, mobile, heterotrophic, no cell wall, Halophiles, thermophiles, proteobacteria Animalia Animalia 4. Which Kingdom do the organisms below belong to? Animalia Eubacteria Protista Animalia protista Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: 5. Which two kingdoms only contain prokaryotic organisms? Archaebacteria, Eubacteria 6. Compare and contrast Plant, Animal, and Fungal Cells in the Venn Diagram below. Plant Animal Photosynthesis, autotrophs, Large vacuole, Chloroplast, cellulose cell wall, Sexual Reproduction Mobile, no cell wall, Eukaryotes, Multicellular, cell respiration Cell Wall Immobile, Asexual reproduction Heterotrophic Fungus Cell Wall Chitin Decomposer, Can be unicellular, 7. Match the description with the kingdom below. Animalia This organism must hunt for its prey making it heterotrophic. It is barely visible with the naked eye and it reproduces asexually. Protista Outside of gathering sunlight for food, there are many extraordinary features of this organism. Its cell walls are rigid among other things. Bacteria This organism mimics its surroundings in an act called camouflage. It hides from its predators and hunts during the night time. It is multicellular and eukaryotic. Fungi Plantae This organism is not very complex. It contains a plasmid and cilia. This organism is heterotrophic and immobile. It has a squishy cell wall called chitin. Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: 8. The graphic below gives the taxonomic classifications for four different species. Explain how you know that one organism is an outlier. Corn is the outlier because it does not belong in the same kingdom as the other three organisms. 9. Why is it necessary that every organism on Earth contain two names? Scientists use two names to identify different species in order to have enough combinations for the vast number of species that are out there. 10. Give two forms of the correct binomial nomenclature for the human species. Homo sapien Homo sapien 11. Give the criteria for differentiating two species when they have very similar physical features. Two organsism that are similar are considered different species when they are unable to interbreed. 12. According to the cladogram below, which organism is most closely related to chlorophyta? heptaphyta 13. What do the forks in the graph represent? Forks in the graph represent speciation as a result of a newly acquired adaptation. Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: 14. Which organisms from the graphic have remained unchanged for the longest period of time? Euglenophyta, myxomycota, dictyostelio 15. 1. 2. 3. 4. Use the dichotomous key to identify the listed organisms 1-8. Canis familiaris 5. Pinus ponderosa Taraxicum officinale 6. Balantidium sp Passer domesticus 7. Ophiophagus hannah Monodon monoceros 8. Stentor sp Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: Viruses DNA Envelope Label the virus pictured. Then answer the following questions. 16. What do both viruses and cells have in common? Both have DNA or RNA 17. What do viruses need in order to reproduce?Viruses must have a host cell to reproduce 18. Is the shape to the left the only shape that a virus comes in? No, viruses come in many different shapes. Capsid 19. Draw 2 more viruses that do not look like the one pictured. 20. Explain why a virus cannot reproduce on its own. Viruses lack the organelles needed to perform life functions. They do not have the ability to make protein, use energy or grow. They must use the machinery of the cell to be able to do those things. Biology Taxonomy Test Revie Name: Period: 21. Draw the cycle for a virus infecting a cell. Give a brief description of what is happening at each step.Step A= Virus attaches to host cell. Step B=virus injects DNA into the host cell. Step C= Cell makes new viral proteins. Step D= Cell assembles new viruses. Step E= New viruses are released as the cell bursts 22. 23. What type of cell does the HIV virus infect? What happens to the immune system of people with HIV virus?HIV infects white blood cells. White blood cells are part of the immune system. A lowered immunity leads to secondary infections 24. AIDS is short for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. What does it mean to have AIDS? AIDS means that your immune system has lost it's ability to protect you from pathogens and diseases.