File - Chereese Langley
... 2006, it was shown that this rule applies to four of the five types of double stranded genomes; specifically it applies to the eukaryotic chromosomes, the bacterial chromosomes, the double stranded DNA viral genomes, and the archival chromosomes. ...
... 2006, it was shown that this rule applies to four of the five types of double stranded genomes; specifically it applies to the eukaryotic chromosomes, the bacterial chromosomes, the double stranded DNA viral genomes, and the archival chromosomes. ...
Lab 6 DNA ISOLN
... For the selective isolation of plasmid DNA, cells are exposed to NaOH and a strong detergent (alkaline lysis) to denature de Chromosomal DNA (i.e. the 2 strands are separated). An acidic solution of sodium acetate is then added to neutralize the solution. At this point, most of the cell membrane mat ...
... For the selective isolation of plasmid DNA, cells are exposed to NaOH and a strong detergent (alkaline lysis) to denature de Chromosomal DNA (i.e. the 2 strands are separated). An acidic solution of sodium acetate is then added to neutralize the solution. At this point, most of the cell membrane mat ...
Organism Genome (kb) Form
... complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different types - euchromatin (where most of the active genes are) and heteroc ...
... complexes of the 4 histone proteins (2 molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) to form “beads on string” arrangement - the beads are nucleosomes • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different types - euchromatin (where most of the active genes are) and heteroc ...
Prediction practice - unlinked
... • Used to separate fragments of DNA or proteins according to size (uses an electric field to separate charge molecules) DNA is all negatively charged so everything moves in the same direction. Small fragments move faster, so in a given time they will move a greater distance. ...
... • Used to separate fragments of DNA or proteins according to size (uses an electric field to separate charge molecules) DNA is all negatively charged so everything moves in the same direction. Small fragments move faster, so in a given time they will move a greater distance. ...
No Slide Title
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
DNA extraction activity
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
A Comparison of Concentration Methods for Low Copy Number
... samples these methods are highly controversial as a result of stochastic effects which complicate the data analysis interpretation process. However, LCN typing techniques may be avoided or reduced by improved processes prior to amplification of purified DNA such as improved sample storage, DNA colle ...
... samples these methods are highly controversial as a result of stochastic effects which complicate the data analysis interpretation process. However, LCN typing techniques may be avoided or reduced by improved processes prior to amplification of purified DNA such as improved sample storage, DNA colle ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... II. MANY PROTEINS WORK TOGETHER IN DNA REPLICATION AND REPAIR A. The Basic Principle: Base Pairing to a Template Strand 1. Template mechanism for DNA replication - ...
... II. MANY PROTEINS WORK TOGETHER IN DNA REPLICATION AND REPAIR A. The Basic Principle: Base Pairing to a Template Strand 1. Template mechanism for DNA replication - ...
HtoN
... sequence, they use it to construct a primer by synthesizing the single stranded DNA If the sequence is unknown, they use DNA from the same gene of a closley related species that has already been isolated ...
... sequence, they use it to construct a primer by synthesizing the single stranded DNA If the sequence is unknown, they use DNA from the same gene of a closley related species that has already been isolated ...
APC004 DNA Quantification/Nanodrop
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
Prostate cancer stem cells Ongoing Projects 3
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
DNA technology
... – Antifreeze gene from cold water fish introduced to tobacco and potato plants ...
... – Antifreeze gene from cold water fish introduced to tobacco and potato plants ...
Slide 1 - Brookwood High School
... DNA extraction – opening cell to separate DNA from rest of cell parts Restriction enzymes – used to cut DNA at specific points to make small fragments Gel electrophoresis – used to separate DNA fragments on the basis of their length ...
... DNA extraction – opening cell to separate DNA from rest of cell parts Restriction enzymes – used to cut DNA at specific points to make small fragments Gel electrophoresis – used to separate DNA fragments on the basis of their length ...
Biology, Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Study Guide 1. What two
... 8. Compare the nucleotide sequences of bacteria, oak trees, mice, and humans. 9. How is DNA replication important for organisms? ...
... 8. Compare the nucleotide sequences of bacteria, oak trees, mice, and humans. 9. How is DNA replication important for organisms? ...
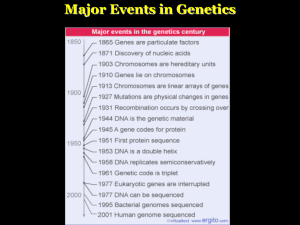
Major Events in Genetics
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
DISCOVERY OF DNAhandout
... 3. Treated with deoxyribonuclease, which eliminates all DNA The result: ...
... 3. Treated with deoxyribonuclease, which eliminates all DNA The result: ...
Genetic Changes = Mutations
... Differences: Body cell DNA mutations affect the individual Sex cell DNA mutations affect the next generation 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. T ...
... Differences: Body cell DNA mutations affect the individual Sex cell DNA mutations affect the next generation 6. cancer … uncontrolled cell division 7. Point mutation: a change in a single N-base pair in DNA a. End result: a change in ONE of the amino acids in the sequence b. THE DOG BIT THE CAT c. T ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.