
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... • After discovering the technique of genetic fingerprinting at the University of Leicester, he continued to work there as a professor in the Department of Genetics. • Sir Alec Jeffreys's methods were soon applied to the public when two young women were raped and murdered in Leicestershire. • One man ...
... • After discovering the technique of genetic fingerprinting at the University of Leicester, he continued to work there as a professor in the Department of Genetics. • Sir Alec Jeffreys's methods were soon applied to the public when two young women were raped and murdered in Leicestershire. • One man ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... Ch.16-17 Quiz: Review of Basic Biology 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how ...
... Ch.16-17 Quiz: Review of Basic Biology 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how ...
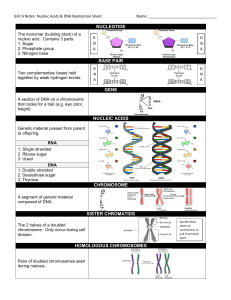
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
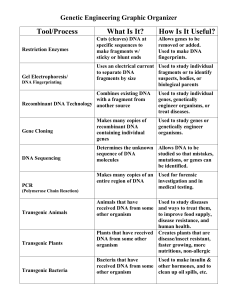
DNA Technology Tools Graphic Organizer KEY
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
... Makes many copies of an Used for forensic entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates ...
Italian Association for Cancer Research NETWORK OF
... Principal investigators Dr. Eugenia Dogliotti, Dr. Margherita Bignami, and Dr. Alessandro Giuliani The overall goals of the Network are: (a) to create a network of researchers involved in the identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epide ...
... Principal investigators Dr. Eugenia Dogliotti, Dr. Margherita Bignami, and Dr. Alessandro Giuliani The overall goals of the Network are: (a) to create a network of researchers involved in the identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epide ...
Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
... Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing ( ...
... Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing ( ...
CALF THYMUS DNA, ACTIVATED - Sigma
... 1 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 3.31 mg/ml DNA Ratio A260/A280: 1.8 Nick Translation Assay and Result 10 µg of D4522 were incubated at 37EC for 30 minutes in a 100 Fl reaction containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.2; 10 mM MgSO4; 1 mM DTT; 0.5 mg/ml BSA; 32.5 FM of dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and TT ...
... 1 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 3.31 mg/ml DNA Ratio A260/A280: 1.8 Nick Translation Assay and Result 10 µg of D4522 were incubated at 37EC for 30 minutes in a 100 Fl reaction containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.2; 10 mM MgSO4; 1 mM DTT; 0.5 mg/ml BSA; 32.5 FM of dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and TT ...
DNA to Protein - Duplin County Schools
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... Hint: look at the navigation bar at the top, you’ll need to click on “What is a Gene” to continue. 6. What is a gene? ...
... Hint: look at the navigation bar at the top, you’ll need to click on “What is a Gene” to continue. 6. What is a gene? ...
Practice Question for Replication, Genetics and Biotechnology
... 28. A trait that expresses itself as a heterozygote is ______________ (dominant or recessive). 29. Sex linked traits are found on the _____________________ chromosome. 30. People who have one copy of an allele for a recessive disorder, but do not exhibit symptoms are called _________ 31. Is blood ty ...
... 28. A trait that expresses itself as a heterozygote is ______________ (dominant or recessive). 29. Sex linked traits are found on the _____________________ chromosome. 30. People who have one copy of an allele for a recessive disorder, but do not exhibit symptoms are called _________ 31. Is blood ty ...
Gene Isolation and Manipulation
... The region of DNA that encodes tyrosinase in “normal” mouse genomic DNA contains two EcoRI sites. Thus, after EcoRI digestion, three different-sized fragments hybridize to the cDNA clone. When genomic DNA from certain albino mice is subjected to similar analysis, there are no DNA fragments that cont ...
... The region of DNA that encodes tyrosinase in “normal” mouse genomic DNA contains two EcoRI sites. Thus, after EcoRI digestion, three different-sized fragments hybridize to the cDNA clone. When genomic DNA from certain albino mice is subjected to similar analysis, there are no DNA fragments that cont ...
Genetic Engineering
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
... Positive mutations desirable characteristics; can be increased by ____________, ____________, etc. (ex: seedless oranges) ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • the master copy of an organism’s information code that contains the instructions used to form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • the master copy of an organism’s information code that contains the instructions used to form all of an organism’s enzymes and structural proteins. ...
Molecuar Structure of DNA Questions
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.











![Recombinant DNA technology.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022508436_1-26bb714d45e9a2e7cd265480e0da1a03-300x300.png)









