Hypothyroidism in Children
... give is called Synthroid or levothyroxine sodium. It is important to take this pill at the same time every day at as part of your daily routine so you don’t forget to take it. Each person or family should find the right routine that works for them. Be careful not to give this pill at the same time w ...
... give is called Synthroid or levothyroxine sodium. It is important to take this pill at the same time every day at as part of your daily routine so you don’t forget to take it. Each person or family should find the right routine that works for them. Be careful not to give this pill at the same time w ...
by Mrs. Bailey
... thyroxine from the thyroid gland. The brain and skeleton fail to develop properly, resulting in mental retardation and dwarfism. Symptoms: gradual development of a characteristic coarse, dry skin, a slightly swollen face and tongue, umbilical hernia, and an open mouth that drools. The baby is usuall ...
... thyroxine from the thyroid gland. The brain and skeleton fail to develop properly, resulting in mental retardation and dwarfism. Symptoms: gradual development of a characteristic coarse, dry skin, a slightly swollen face and tongue, umbilical hernia, and an open mouth that drools. The baby is usuall ...
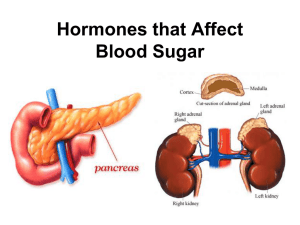
8.2 Hormones that Affect Blood Sugar - Ms. Pasic
... – Both need iodine to be produced. – Used to oxidize sugar and other nutrients. – More T4 in the blood will “boost metabolism” ...
... – Both need iodine to be produced. – Used to oxidize sugar and other nutrients. – More T4 in the blood will “boost metabolism” ...
Endocrine disease
... • ↑ T4 are converted to the reverse T3. • Reduction in thyroid hormone activity does not result in an increased serum TSH concentration. • TSH secretion is suppressed→ ↓ T4 and T3. • TBG decrease ...
... • ↑ T4 are converted to the reverse T3. • Reduction in thyroid hormone activity does not result in an increased serum TSH concentration. • TSH secretion is suppressed→ ↓ T4 and T3. • TBG decrease ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: MATCHING EXERCISE
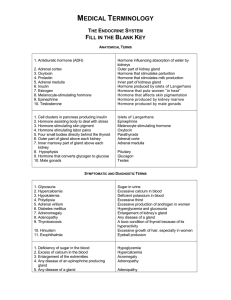
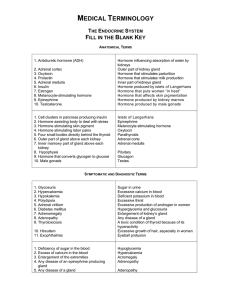
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
fill in blank key
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
... Sugar in urine Excessive calcium in blood Deficient potassium in blood Excessive thirst Excessive production of androgen in women Hyperglycemia and glucosuria Enlargement of kidney’s gland Any disease of a gland A toxic condition of thyroid because of its hyperactivity Excessive growth of hair, espe ...
ANSWERS: CHAPTER 15
... 3. Superior thyroid arteries; inferior thyroid arteries 4. Superior; middle; inferior 5. Posterior lateral; longus colli 6. Triiodothyronine (T3); thyroxine (T4); calcitonin; iodine 7. Hypothalmus; pituitary 8. Hyperthyroidism; hypothyroidism 9. Homogeneous; hyperechoic 10. Th ...
... 3. Superior thyroid arteries; inferior thyroid arteries 4. Superior; middle; inferior 5. Posterior lateral; longus colli 6. Triiodothyronine (T3); thyroxine (T4); calcitonin; iodine 7. Hypothalmus; pituitary 8. Hyperthyroidism; hypothyroidism 9. Homogeneous; hyperechoic 10. Th ...
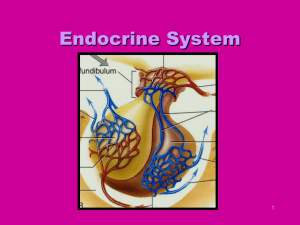
The Pituitary Gland
... Posterior lobe – stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. 1. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – released into blood and targets kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, thi ...
... Posterior lobe – stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. 1. antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – released into blood and targets kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, thi ...
A Closer Look at Some Hormones 1. Melatonin $ produced by
... They work together, when one is high the other is low and they cycle back and forth, thereby maintaining homeostasis. ...
... They work together, when one is high the other is low and they cycle back and forth, thereby maintaining homeostasis. ...
Lobes of thyroid gland and carotid sheath (with its contents).
... Its apex extends upward to the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, and its base reaches down to the 4-5 tracheal ring. It isthmus extends across the midline in front of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th tracheal rings. A pyramidal lobe may be present. ...
... Its apex extends upward to the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, and its base reaches down to the 4-5 tracheal ring. It isthmus extends across the midline in front of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th tracheal rings. A pyramidal lobe may be present. ...
BioBases Exam 2
... Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: growth and metabolism Parathyroid: calcium regulation Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions – located “on top of kidneys” 1) Releases 3 major classes of hormones (a) Andro ...
... Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: growth and metabolism Parathyroid: calcium regulation Thymus: immune system (children) Pancreas: blood sugar control Adrenal: stress, many other functions – located “on top of kidneys” 1) Releases 3 major classes of hormones (a) Andro ...
Endocrine System
... Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
... Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
Thyroid gland
... • It is formed by the ventral primary divisions of the first four cervical nerves. • Each nerve, except the first, divides into the superior branch and the inferior branch. • C1 joins the upper branch of C2 • the adjacent upper and lower branches of C2 and C3 fuse • Each nerve receives a gray ramus ...
... • It is formed by the ventral primary divisions of the first four cervical nerves. • Each nerve, except the first, divides into the superior branch and the inferior branch. • C1 joins the upper branch of C2 • the adjacent upper and lower branches of C2 and C3 fuse • Each nerve receives a gray ramus ...
Week 4 (Neck) Clinical case A 37 year old teacher consults her
... Question 4: Which lymph nodes should the physician examine for metastases if a malignant tumor is suspected? Question 5: What structures can be damaged during thyroidectomy if the surgeon is not careful? Question 6: What do you think caused patient’s sore throat? Question 7: What was the likely caus ...
... Question 4: Which lymph nodes should the physician examine for metastases if a malignant tumor is suspected? Question 5: What structures can be damaged during thyroidectomy if the surgeon is not careful? Question 6: What do you think caused patient’s sore throat? Question 7: What was the likely caus ...
File
... • Endocrinologist: a medical doctor that deals with disease of the endocrine system • Endocrinology: the branch of medicine concerned with hormone imbalances • Parts: ducts, glands, hormones • Functions: to regulate various body functions and keep the internal environment of the body stable • Regula ...
... • Endocrinologist: a medical doctor that deals with disease of the endocrine system • Endocrinology: the branch of medicine concerned with hormone imbalances • Parts: ducts, glands, hormones • Functions: to regulate various body functions and keep the internal environment of the body stable • Regula ...
File
... • Exocrine glands: release secretions through a duct (tube). • Endocrine: release secretions into blood to be transported. ...
... • Exocrine glands: release secretions through a duct (tube). • Endocrine: release secretions into blood to be transported. ...
Endocrine System
... lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have important effects on the way in which energy is stored and food is used and on chemicals in the blood. The pancreas gland secretes digestive juices which break down ...
... lymphocytes into T-cells that play an important part in fighting infections and disease. The adrenal glands release hormones which have important effects on the way in which energy is stored and food is used and on chemicals in the blood. The pancreas gland secretes digestive juices which break down ...
8Aldosterone 8Na + secretion 8 H 2 O reabsorption9 urine volume
... – hair loss, – lethargy, && more frequently affected than %% ...
... – hair loss, – lethargy, && more frequently affected than %% ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.