Biology 30 Notes October 9, 2014 (DID NOT FINISH CONITNUE ON
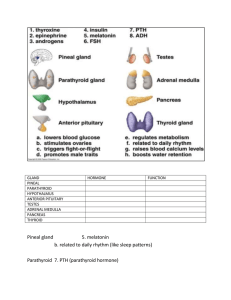
... (amount) of calcium in the blood. When the concentration of calcium gets too high in the blood calcitonin stimulates the uptake of calcium in the bones, thus reducing the amount of calcium in the blood. THE PARATHYROID GLANDS Four small glands attached to the thyroid. It produces a hormone called PT ...
... (amount) of calcium in the blood. When the concentration of calcium gets too high in the blood calcitonin stimulates the uptake of calcium in the bones, thus reducing the amount of calcium in the blood. THE PARATHYROID GLANDS Four small glands attached to the thyroid. It produces a hormone called PT ...
Dear «PrefName» «Surname» this work is due in 7 days from 6/10
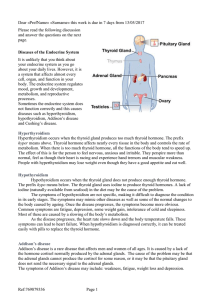
... about your daily lives. However, it is a system that affects almost every cell, organ, and function in your body. The endocrine system regulates mood, growth and development, metabolism, and reproductive processes. Sometimes the endocrine system does not function correctly and this causes diseases s ...
... about your daily lives. However, it is a system that affects almost every cell, organ, and function in your body. The endocrine system regulates mood, growth and development, metabolism, and reproductive processes. Sometimes the endocrine system does not function correctly and this causes diseases s ...
Thyroid Gland
... The thyroid gland operates as part of a feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. First, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland through a hormone called TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone). When the pituitary gland receives this signal, it releases TSH (t ...
... The thyroid gland operates as part of a feedback mechanism involving the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. First, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the pituitary gland through a hormone called TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone). When the pituitary gland receives this signal, it releases TSH (t ...
Thyroid gland
... Thyroglobulin - synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and then enter the colloid in the lumen of the thyroid follicle by exocytosis. Sodium-iodide (Na/I) symporter pumps iodide (I-) into the cell This iodide enters the follicular lumen from the cytoplasm by the ...
... Thyroglobulin - synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and then enter the colloid in the lumen of the thyroid follicle by exocytosis. Sodium-iodide (Na/I) symporter pumps iodide (I-) into the cell This iodide enters the follicular lumen from the cytoplasm by the ...
Uses
... Loading dose – of T4 – 300-400micrograms I/V initially f/by `50micrograms daily I/V T3 – more cardiotoxic and difficult to moniter ...
... Loading dose – of T4 – 300-400micrograms I/V initially f/by `50micrograms daily I/V T3 – more cardiotoxic and difficult to moniter ...
Disorders of the Endocrine System
... Low blood sugar, which can cause anxiety, tremors, weakness, and even unconsciousness and death. Hypothyroidism Undersecretion of thyroxine, resulting in a very low metabolic rate and sluggish activity, sometimes accompanied by obesity. Myxedema Accumulation of water in skin resulting from thyroid h ...
... Low blood sugar, which can cause anxiety, tremors, weakness, and even unconsciousness and death. Hypothyroidism Undersecretion of thyroxine, resulting in a very low metabolic rate and sluggish activity, sometimes accompanied by obesity. Myxedema Accumulation of water in skin resulting from thyroid h ...
The Endocrine System
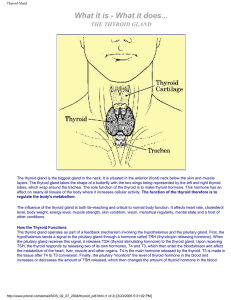
... The thyroid gland is located in the front of the windpipe called the (trachea) and just below the larynx or Adams Apple on the neck. The Thyroid gland regulates your (Metabolism) or your ability to break down food and use it for energy. ...
... The thyroid gland is located in the front of the windpipe called the (trachea) and just below the larynx or Adams Apple on the neck. The Thyroid gland regulates your (Metabolism) or your ability to break down food and use it for energy. ...
Hyperthyroidism FAQ - American Thyroid Association
... by overactive thyroid cells and destroys them. The radioiodine that is not taken up by the Further details on this and other thyroid-related topics are available in the patient thyroid cells disappears from the body within days. Radioiodine often takes several weeks information section on the Americ ...
... by overactive thyroid cells and destroys them. The radioiodine that is not taken up by the Further details on this and other thyroid-related topics are available in the patient thyroid cells disappears from the body within days. Radioiodine often takes several weeks information section on the Americ ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine System • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream to control body functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. ...
... Endocrine System • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream to control body functions such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. ...
Normal Thyroid and Scanning Technique
... ROLE OF ULTRASOUND: Ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool in assessing the following indications; Classification of a palpated lump. eg solid, cystic, mixed Evaluate adjacent structures Determining the location of a palpable lump (within or outside of the thyroid) Identifying a cause for ...
... ROLE OF ULTRASOUND: Ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool in assessing the following indications; Classification of a palpated lump. eg solid, cystic, mixed Evaluate adjacent structures Determining the location of a palpable lump (within or outside of the thyroid) Identifying a cause for ...
1-The immune system and endocrine disorders 2017)
... carefully regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland. ...
... carefully regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland. ...
Anatomy of thyroid gland Introduction • Brownish
... Brownish-‐red and soft during life Usually weighs about 25-‐ 30g (larger in women) Surrounded by a thin, fibrous capsule of connective tissue External to this is a “false capsule” formed by pretrache ...
... Brownish-‐red and soft during life Usually weighs about 25-‐ 30g (larger in women) Surrounded by a thin, fibrous capsule of connective tissue External to this is a “false capsule” formed by pretrache ...
AACE/ACE Principles of Endocrine Neck Sonography Course
... AACE/ACE Principles of Endocrine Neck ...
... AACE/ACE Principles of Endocrine Neck ...
Pituitary gland
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
... Thyroiditis Thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid gland, can be: ...
... Thyroiditis Thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid gland, can be: ...
The Endocrine System (Chap 11)
... ability to break down food and store it as energy Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) - increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium ...
... ability to break down food and store it as energy Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & Tri-iodothyronine (T3) - increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates Calcitonin – regulates the blood concentration of calcium ...
Thyroid Gland - Fort Bend ISD
... Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ...
... Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, Raises ...
Endocrine System
... Steroid Hormones consists of complex rings of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They are insoluble in water and are carried in the bloodstream weakly bound to plasma proteins in a way that allows them to be released in decent sized quantities within the same area as their target cells. ...
... Steroid Hormones consists of complex rings of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They are insoluble in water and are carried in the bloodstream weakly bound to plasma proteins in a way that allows them to be released in decent sized quantities within the same area as their target cells. ...
The Endocrine System (Chap 11) 11.1
... Nonsteroid hormones – binding site, activity site (cyclic AMP, cAMP = secondary messenger) Prostoglandins – act locally, affecting only the organ where they are produces 11.4 Control of Hormonal Secretions Hypothalamus (releasing hormone) Pituitary (stimulating hormone) Target Gland (secretes ho ...
... Nonsteroid hormones – binding site, activity site (cyclic AMP, cAMP = secondary messenger) Prostoglandins – act locally, affecting only the organ where they are produces 11.4 Control of Hormonal Secretions Hypothalamus (releasing hormone) Pituitary (stimulating hormone) Target Gland (secretes ho ...
Endocrine System Anatomy
... – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
... – Follicle stimulating (luteinizing) = regulates development, growth and functions of the ovaries and testes. ...
The Endocrine system
... • Thyroid- produces hormones that control metabolism and calcium in blood. • Thyroid gland must have any source of iodine – goiter- not enough iodine – hyperthyroidism – hypothyroidism ...
... • Thyroid- produces hormones that control metabolism and calcium in blood. • Thyroid gland must have any source of iodine – goiter- not enough iodine – hyperthyroidism – hypothyroidism ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.