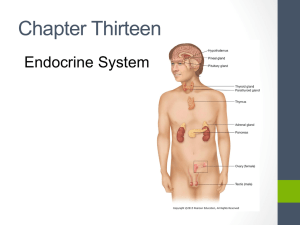
Endocrine System
... – Pine cone shape. – In the epithalamus. – Covered by a capsule made of pia mater. ...
... – Pine cone shape. – In the epithalamus. – Covered by a capsule made of pia mater. ...
Endocrine System
... • Secrete hormones into the extracellular spaces around their cells, which diffuse into capillaries and are carried away by blood. • The science of this system is called Endocrinology. ...
... • Secrete hormones into the extracellular spaces around their cells, which diffuse into capillaries and are carried away by blood. • The science of this system is called Endocrinology. ...
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
... hyperplastic glands secretion 5-15x TSH decreased to 0 thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) bind with the same membrane receptors that bind TSH (lasting for as long as 12 hours) an autoimmune disease result from a adenoma – remainder inhibited ...
... hyperplastic glands secretion 5-15x TSH decreased to 0 thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) bind with the same membrane receptors that bind TSH (lasting for as long as 12 hours) an autoimmune disease result from a adenoma – remainder inhibited ...
Thyroid Profile
... test report, linking symptoms, hormone usage and basal temperatures, provide physicians with more diagnostic clues. For example, a test result showing free T3, free T4, and TSH within normal range, but symptoms (e.g. a low basal temperature) consistent with a hypothyroid state, points to a "function ...
... test report, linking symptoms, hormone usage and basal temperatures, provide physicians with more diagnostic clues. For example, a test result showing free T3, free T4, and TSH within normal range, but symptoms (e.g. a low basal temperature) consistent with a hypothyroid state, points to a "function ...
الشريحة 1
... As shown in the following diagram, the thyroid hormones are basically two tyrosines linked together with the critical addition of iodine at three or four positions on the aromatic rings. The number and position of the iodines is important. Several other iodinated molecules are generated that have li ...
... As shown in the following diagram, the thyroid hormones are basically two tyrosines linked together with the critical addition of iodine at three or four positions on the aromatic rings. The number and position of the iodines is important. Several other iodinated molecules are generated that have li ...
Histology Ch 21 755-762 [4-20
... 6. Resorption of Colloid – in response to TSH, follicular cells take up thyroglobulin from colloid by endocytosis, after which it follows one of 2 intracellular pathways: a. Lysosomal Pathway – internalized thyroglobulin transported to early endosomes which mature or fuse to lysosomes; resorption c ...
... 6. Resorption of Colloid – in response to TSH, follicular cells take up thyroglobulin from colloid by endocytosis, after which it follows one of 2 intracellular pathways: a. Lysosomal Pathway – internalized thyroglobulin transported to early endosomes which mature or fuse to lysosomes; resorption c ...
Graves` Disease
... your life to have normal hormone levels. Radioactive iodine treatment may make the symptoms of Graves’ ophthalmopathy worse but it’s often treatable with a steroid medication (prednisone). • Surgery involves the removal of the thyroid (thyroidectomy). It is a permanent solution, but not usually pref ...
... your life to have normal hormone levels. Radioactive iodine treatment may make the symptoms of Graves’ ophthalmopathy worse but it’s often treatable with a steroid medication (prednisone). • Surgery involves the removal of the thyroid (thyroidectomy). It is a permanent solution, but not usually pref ...
Chapter 9 Concept Map Review
... Write today’s assignments in your planner. Write down and answer the following: What is the hormone that is present in the urine during pregnancy that is detectable by home pregnancy tests? ...
... Write today’s assignments in your planner. Write down and answer the following: What is the hormone that is present in the urine during pregnancy that is detectable by home pregnancy tests? ...
File
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
... • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. ...
Dissection of the Superior Thyroid Pole
... "tips out" facilitates avoidance of inadvertent injury to the external laryngeal nerve as it crosses in this plane. Taking such precautions to prevent injury to the nerve, referred to as the "Amelita Gala Curci nerve" is mandatory to avoid loss of highpitched sounds After creation of the space, the ...
... "tips out" facilitates avoidance of inadvertent injury to the external laryngeal nerve as it crosses in this plane. Taking such precautions to prevent injury to the nerve, referred to as the "Amelita Gala Curci nerve" is mandatory to avoid loss of highpitched sounds After creation of the space, the ...
Endocrine system notes
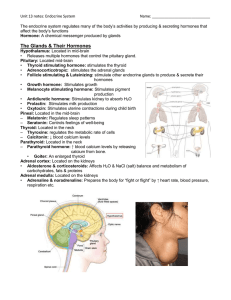
... • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: stimulate other endocrine glands to produce & secrete their hormones • Growth hormone: Stimulates growth • Melanocyte stimulating hormone: Stimulates pigme ...
... • Thyroid stimulating hormone: stimulates the thyroid • Adrenocorticotropic: stimulates the adrenal glands • Follicle stimulating & Luteinizing: stimulate other endocrine glands to produce & secrete their hormones • Growth hormone: Stimulates growth • Melanocyte stimulating hormone: Stimulates pigme ...
Iodination of Tyrosine and Formation of the Thyroid Hormones
... – large numbers of closed follicles (100 to 300 micrometers in diameter) – filled with a secretory substance called colloid and – lined with cuboidal epithelial cells that secrete into the interior of the follicles. – The major constituent of colloid is the large glycoprotein thyroglobulin, which co ...
... – large numbers of closed follicles (100 to 300 micrometers in diameter) – filled with a secretory substance called colloid and – lined with cuboidal epithelial cells that secrete into the interior of the follicles. – The major constituent of colloid is the large glycoprotein thyroglobulin, which co ...
Endocrinology
... Largest Endocrine organ in the body Involved in production, storage, and release of thyroid hormone Function influenced by ...
... Largest Endocrine organ in the body Involved in production, storage, and release of thyroid hormone Function influenced by ...
Common form is Graves disease May result in goiter (enlarged thyroid)
... – Caused by tumor or interruption of gland’s blood supply – Widespread effects • Lack of ADH – Results in diabetes insipidus • Kidneys with diminished ability to conserve ...
... – Caused by tumor or interruption of gland’s blood supply – Widespread effects • Lack of ADH – Results in diabetes insipidus • Kidneys with diminished ability to conserve ...
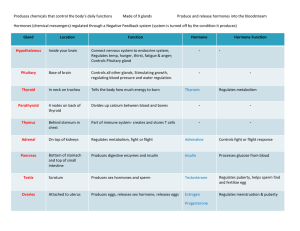
Produces chemicals that control the body`s daily functions Made of 9
... Produces chemicals that control the body’s daily functions ...
... Produces chemicals that control the body’s daily functions ...
Thyroid Gland
... The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of the (trachea) The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. Thyroid ...
... The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of the (trachea) The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. Thyroid ...
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands make hormones • Hormones are chemical messengers transported in the bloodstream. • Hormones bring about a response, or change, in cells with matching receptors called target cells. ...
... • Endocrine glands make hormones • Hormones are chemical messengers transported in the bloodstream. • Hormones bring about a response, or change, in cells with matching receptors called target cells. ...
The Neck
... A. Each side of the neck is divided into two triangles by muscle 1. Anterior triangle – bounded above by mandible, laterally by sternomastoid, medially by midline of body 2. Posterior triangle – extends from sternomastoid to trapezius. Bounded below by clavicle; portion of omohyoid muscle crosses lo ...
... A. Each side of the neck is divided into two triangles by muscle 1. Anterior triangle – bounded above by mandible, laterally by sternomastoid, medially by midline of body 2. Posterior triangle – extends from sternomastoid to trapezius. Bounded below by clavicle; portion of omohyoid muscle crosses lo ...
Congenital anomalies of the face
... Thyroid gland develops from the thyroglossal duct which passes from the foramen caecum to the isthmus of thyroid. Parafollicular cells (C-cells) develops from the neural crest. Surgical anatomy: The gland is formed from two lateral lobes, isthmus, and pyramidal lobe. Weight is about 20-25 gm. The lo ...
... Thyroid gland develops from the thyroglossal duct which passes from the foramen caecum to the isthmus of thyroid. Parafollicular cells (C-cells) develops from the neural crest. Surgical anatomy: The gland is formed from two lateral lobes, isthmus, and pyramidal lobe. Weight is about 20-25 gm. The lo ...
2. Thyroid Gland T 4 and T 3
... 2. Thyroid Gland • located anteriorly in cervical region, just inferior to thyroid cartilage; two lobes connected by thin isthmus • largest purely endocrine gland in body • consists of follicles (cuboidal or simple squamous epithelium) filled with colloid (combination of protein [thyroglobulin] cont ...
... 2. Thyroid Gland • located anteriorly in cervical region, just inferior to thyroid cartilage; two lobes connected by thin isthmus • largest purely endocrine gland in body • consists of follicles (cuboidal or simple squamous epithelium) filled with colloid (combination of protein [thyroglobulin] cont ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
... structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
... structure of the thyroid gland. List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.