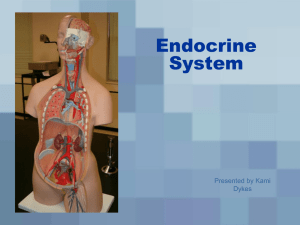
endocrinesystemshort
... A tissue or group of tissues that makes and releases chemicals is called a gland. The chemical product of an endocrine glands is called a hormone. Endocrine glands produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
... A tissue or group of tissues that makes and releases chemicals is called a gland. The chemical product of an endocrine glands is called a hormone. Endocrine glands produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. ...
Endocrine Quiz Review
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
... -Autocrines: Act on cells that secrete them vs. Paracrines: Act on cells nearby -Endocrine glands become less effective with age Hormones: Steroid or amino acid based -Stimulate or inhibit target cell -Mechanisms: alter membrane permeability, enzyme synthesis, secretion, and mitosis -Many interact w ...
Objective: You will be able to identify all of the glands of the
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
... • Read all of p. 591 • How are the functions of LH and FSH different in males and females? ...
Endocrine Notes 2
... tiiodothyronine (T3). These hormones control metabolic rate. It also releases calcitonin, which lowers blood calcium levels. Thyroxine is released when metabolic decreases signal the release of thryoid-releasing factors (TRH), which stimulate the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormon ...
... tiiodothyronine (T3). These hormones control metabolic rate. It also releases calcitonin, which lowers blood calcium levels. Thyroxine is released when metabolic decreases signal the release of thryoid-releasing factors (TRH), which stimulate the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormon ...
File
... d) retention of electrolytes by the kidneys e) increases osteoclast activity 8) This hormone acts on the intestines and causes increased calcium absorption: a) calcitonin b) calcitriol c) thyroxine d) pancreatic polypeptide e) corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) 9) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) ...
... d) retention of electrolytes by the kidneys e) increases osteoclast activity 8) This hormone acts on the intestines and causes increased calcium absorption: a) calcitonin b) calcitriol c) thyroxine d) pancreatic polypeptide e) corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) 9) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) ...
Endocrine Disease in the White House
... Thyroid gland • Tissue consists of follicles • Follicles are hollow spheres lined with epithelial cells (follicle cells) • Follicular cells take up Iodine from circulation and produce thryoglobulin (the precursor to thyroid hormone) • Thyroglobulin is stored in the colloid of follicle • C cells pro ...
... Thyroid gland • Tissue consists of follicles • Follicles are hollow spheres lined with epithelial cells (follicle cells) • Follicular cells take up Iodine from circulation and produce thryoglobulin (the precursor to thyroid hormone) • Thyroglobulin is stored in the colloid of follicle • C cells pro ...
Endocrine System
... The endocrine glands secrete what? __________ hormones They are transported in ___________through body fluids ductless glands that act together with the nervous system. By controlling cellular activities, endocrine glands play important roles in the maintenance homeostasis of _____________. The hypo ...
... The endocrine glands secrete what? __________ hormones They are transported in ___________through body fluids ductless glands that act together with the nervous system. By controlling cellular activities, endocrine glands play important roles in the maintenance homeostasis of _____________. The hypo ...
TSH Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Thyotropin
... TSH then causes the thyroid gland to make T3 triiodothyronine or T4 thyroxine Somatostatin decreases or inhibits the release of TSH ...
... TSH then causes the thyroid gland to make T3 triiodothyronine or T4 thyroxine Somatostatin decreases or inhibits the release of TSH ...
Lecture 15
... INHIBITORY and RELEASING hormones from hypothalamus III. Thyroid Gland A. Location, Structure and Hormones 1. anterior neck region, overlying the trachea 2. two lateral lobes connected by the isthmus a. thyroid hormone (TH) - regulates rate of metabolism; Iodine key part of hormone b. calcitonin - l ...
... INHIBITORY and RELEASING hormones from hypothalamus III. Thyroid Gland A. Location, Structure and Hormones 1. anterior neck region, overlying the trachea 2. two lateral lobes connected by the isthmus a. thyroid hormone (TH) - regulates rate of metabolism; Iodine key part of hormone b. calcitonin - l ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... messages within the body are called… A: What are hormones? ...
... messages within the body are called… A: What are hormones? ...
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
... Graves’ Disease • How grave is Graves’ disease? • Graves’ disease is most common type • Autoimmune, 30-60 years old, family history of thyroid abnormalities • Thyroid-stimulating antibodies bind to TSH receptors • Thyroid storm (thyrotoxic crisis) Overproduction of T3 and T4 increased SNS activity ...
... Graves’ Disease • How grave is Graves’ disease? • Graves’ disease is most common type • Autoimmune, 30-60 years old, family history of thyroid abnormalities • Thyroid-stimulating antibodies bind to TSH receptors • Thyroid storm (thyrotoxic crisis) Overproduction of T3 and T4 increased SNS activity ...
Introduction to Health Science
... body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
... body cells where it can be used for energy which leads to increased hunger. ...
Thyroxine - Chavis Biology
... Through a series of steps, the decrease in body temperature causes the release of thyroxine from the thyroid Thyroxine triggers increased metabolism in all body cells (chemical reactions in cells) Metabolism increases the generation of body heat ...
... Through a series of steps, the decrease in body temperature causes the release of thyroxine from the thyroid Thyroxine triggers increased metabolism in all body cells (chemical reactions in cells) Metabolism increases the generation of body heat ...
Chapter 17
... gland and may be associated with hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or euthyroidism – In many third-word countries dietary iodine intake is inadequate; the resultant low level of thyroid hormone in the blood stimulates secretion of TSH, which causes thyroid gland enlargement ...
... gland and may be associated with hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or euthyroidism – In many third-word countries dietary iodine intake is inadequate; the resultant low level of thyroid hormone in the blood stimulates secretion of TSH, which causes thyroid gland enlargement ...
The Endocrine System
... breathing airway (trachea) and below your Adam's apple. The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & ...
... breathing airway (trachea) and below your Adam's apple. The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products with a release of energy in the process. Thyroid Hormones Thyroxin (T4) & ...
Endocrine Review
... 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in blood glucose d. a hormone secreted by the pituitary e. an increase in blood glucose 3. Which of the following hormones have antagonistic (opposite) ...
... 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in blood glucose d. a hormone secreted by the pituitary e. an increase in blood glucose 3. Which of the following hormones have antagonistic (opposite) ...
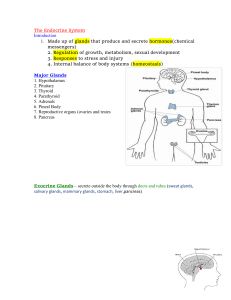
glands of the human body
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
Endocrine System Lecture
... f .Constant exchange of calcium and phosphate between bone and blood g. Parathyroid hormone plays an important function in maintaining proper level of circulating calcium 4. Disorders of the Parathyroid Glands a. Hyperparathyroidism (1) Over-activity of the parathyroid gland resulting in an overprod ...
... f .Constant exchange of calcium and phosphate between bone and blood g. Parathyroid hormone plays an important function in maintaining proper level of circulating calcium 4. Disorders of the Parathyroid Glands a. Hyperparathyroidism (1) Over-activity of the parathyroid gland resulting in an overprod ...
Handout 7a2
... It consists of two laminæ the anterior borders of which are fused with each other at an acute angle in the middle line of the neck, and form a subcutaneous projection named the laryngeal prominence ( Adams apple). ...
... It consists of two laminæ the anterior borders of which are fused with each other at an acute angle in the middle line of the neck, and form a subcutaneous projection named the laryngeal prominence ( Adams apple). ...
Human Endocrine System
... least 208 cm (6 feet 10 in) tall and believed by many to have been over 213 cm (7 feet) at his tallest. His great size was a result of excessive growth hormone, a condition known as pituitary gigantism, and led to him being dubbed "The Eighth Wonder of the World[1][2]." ...
... least 208 cm (6 feet 10 in) tall and believed by many to have been over 213 cm (7 feet) at his tallest. His great size was a result of excessive growth hormone, a condition known as pituitary gigantism, and led to him being dubbed "The Eighth Wonder of the World[1][2]." ...
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
... • Hypothyroidism – Thyroid deficiency (decreased T3 and T4) metabolic processes slow (may be problem with thyroid, pituitary, or hypothalamus) – Primary hypothyroidism – due to disorder of thryoid – Secondary hypothyroidism –due to failure to stimulate thyroid – Causes: thyroidectomy, radiation, n ...
... • Hypothyroidism – Thyroid deficiency (decreased T3 and T4) metabolic processes slow (may be problem with thyroid, pituitary, or hypothalamus) – Primary hypothyroidism – due to disorder of thryoid – Secondary hypothyroidism –due to failure to stimulate thyroid – Causes: thyroidectomy, radiation, n ...
Surgical importance of Thyroid Gland
... Superior Suprarenal artery, from inferior phrenic a. (which are branches of the aorta) Middle Suprarenal artery from the aorta, and Inferior Suprarenal artery from the renal a. Suprarenal veins - On the right side opens into the inferior vena cava, - On the left into the renal vein. Lymphatics end i ...
... Superior Suprarenal artery, from inferior phrenic a. (which are branches of the aorta) Middle Suprarenal artery from the aorta, and Inferior Suprarenal artery from the renal a. Suprarenal veins - On the right side opens into the inferior vena cava, - On the left into the renal vein. Lymphatics end i ...
15. thyroid2010-10-01 03:41779 KB
... Structure : it is the largest endocrine gland in the body. It has butterfly shape. It consists of 2 lateral ( right & left ) lobes connected by a narrow isthmus. ...
... Structure : it is the largest endocrine gland in the body. It has butterfly shape. It consists of 2 lateral ( right & left ) lobes connected by a narrow isthmus. ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.