Biology 30 Assignment 6 Endocrine System and Hormones
... assignments will not be accepted for full marks. Key Terms: 21 marks Pituitary Gland Posterior Pituitary Anterior Pituitary Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Thyroid Gland Thyroxine (T4) Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Goitre Adrenal Glands Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Norep ...
... assignments will not be accepted for full marks. Key Terms: 21 marks Pituitary Gland Posterior Pituitary Anterior Pituitary Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Thyroid Gland Thyroxine (T4) Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Goitre Adrenal Glands Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Norep ...
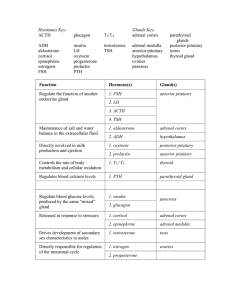
Endocrine System Hormones
... • The major organs of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands, the islets of the pancreas, the adrenal glands, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
... • The major organs of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands, the islets of the pancreas, the adrenal glands, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
anatomy_lec15_29_3_2011 - Post-it
... recurrent laryngeal nerve " between the esophagus and trachea". Lymphatics : Follow the arteries to deep cervical lymph nodes. Sympathetic innervation : most from the middle sympathetic ganglion through the inferior thyroid artery .They act as vasoconstrictors . Functions : the entire functional con ...
... recurrent laryngeal nerve " between the esophagus and trachea". Lymphatics : Follow the arteries to deep cervical lymph nodes. Sympathetic innervation : most from the middle sympathetic ganglion through the inferior thyroid artery .They act as vasoconstrictors . Functions : the entire functional con ...
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE - Welcome to Hansen Nursing
... In this form of the disease, the body does not make any insulin at all. It occurs most often in children and young adults. The islet cells of Langerhans are destroyed in type I diabetes mellitus. This occurs probably as a consequence of a genetic susceptibility, followed by the onset of autoimmune d ...
... In this form of the disease, the body does not make any insulin at all. It occurs most often in children and young adults. The islet cells of Langerhans are destroyed in type I diabetes mellitus. This occurs probably as a consequence of a genetic susceptibility, followed by the onset of autoimmune d ...
Endocrine System
... thyroid gland -releases Prolactin (PRL) = stimulates production of breast milk -releases Endorphins= natural pain and stress fighters -releases Growth Hormone (GH) = stimulates growth -releases Gonadotropic Hormones = stimulates gonads ...
... thyroid gland -releases Prolactin (PRL) = stimulates production of breast milk -releases Endorphins= natural pain and stress fighters -releases Growth Hormone (GH) = stimulates growth -releases Gonadotropic Hormones = stimulates gonads ...
Submandibular gland
... entered the groove and lies posterior to inf. Thyroid artery. Right nerve:- recurves around the right subclavian artery at the root of the neck may be more lateral to the trachea, . passing anterior or posterior to the inferior thyroid artery or in between its branches ...
... entered the groove and lies posterior to inf. Thyroid artery. Right nerve:- recurves around the right subclavian artery at the root of the neck may be more lateral to the trachea, . passing anterior or posterior to the inferior thyroid artery or in between its branches ...
Dr Watson Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... Body’s response to this very low level of calcium: ___________________________________ Low blood level of calcium (medical term): ________________________________ 11. What is a tumor of a gland called? 12. If calcium moves from the bones faster than new calcium can replace it (in hypersecretion), wh ...
... Body’s response to this very low level of calcium: ___________________________________ Low blood level of calcium (medical term): ________________________________ 11. What is a tumor of a gland called? 12. If calcium moves from the bones faster than new calcium can replace it (in hypersecretion), wh ...
AMA 176 powerpoint
... Produces thymosin and T-cells and is responsible for immune responses (more so in childhood, shrinks as we age). ...
... Produces thymosin and T-cells and is responsible for immune responses (more so in childhood, shrinks as we age). ...
Nervous System Practice
... b) It is stored and released by the posterior pituitary gland. c) It keeps excessive amounts of water from being lost in the urine. d) All of the above. ...
... b) It is stored and released by the posterior pituitary gland. c) It keeps excessive amounts of water from being lost in the urine. d) All of the above. ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their hormones into the blood stream. ...
Unit Four - Regulation Unit 4- REGULATORY
... of the thyroid hormones. Causes may include other thyroid disease processes, non-cancerous growths in the pituitary gland or thyroid gland, inflammation of the thyroid, or excessive ingestion of iodine. ...
... of the thyroid hormones. Causes may include other thyroid disease processes, non-cancerous growths in the pituitary gland or thyroid gland, inflammation of the thyroid, or excessive ingestion of iodine. ...
Chapter 9: The endocrine system
... Thyroid deficiency • Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is most often caused by autoimmune disease that attacks the thyroid • Symptoms include fatigue, persistent feeling of cold, bloating and weight gain, dry skin, and mental slowness • Can be very well treated by taking thyroid hormone pills • ...
... Thyroid deficiency • Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is most often caused by autoimmune disease that attacks the thyroid • Symptoms include fatigue, persistent feeling of cold, bloating and weight gain, dry skin, and mental slowness • Can be very well treated by taking thyroid hormone pills • ...
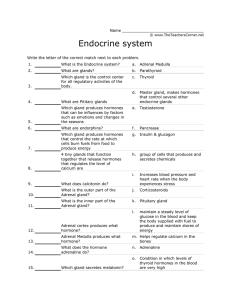
Name Endocrine system Matching! Write the letter of the correct
... _____ 5. Which gland produces hormones that can be influences by factors such as emotions and changes in the seasons ...
... _____ 5. Which gland produces hormones that can be influences by factors such as emotions and changes in the seasons ...
Endocrine match worksheet
... Which gland is the control center for all regulatory activites of the body. ...
... Which gland is the control center for all regulatory activites of the body. ...
Endocrine system - aandersonbiology
... maintain a steady level of glucose in the blood and keep the body supplied with fuel to produce and maintain ...
... maintain a steady level of glucose in the blood and keep the body supplied with fuel to produce and maintain ...
Lecture 2
... – Regulate organic metabolism & H2O & electrolyte balance – Induce adaptive changes to help body cope with stressful situations – Promote smooth, sequential growth & development – Control reproduction – Regulate red blood cell production – Along with autonomic nervous system, control & integrate bot ...
... – Regulate organic metabolism & H2O & electrolyte balance – Induce adaptive changes to help body cope with stressful situations – Promote smooth, sequential growth & development – Control reproduction – Regulate red blood cell production – Along with autonomic nervous system, control & integrate bot ...
MCB 135K Discussion
... Failure of up-regulation of T3 nuclear receptors in antithyroid antibodies, present even in the absence of manifestations of hypothyroidism ...
... Failure of up-regulation of T3 nuclear receptors in antithyroid antibodies, present even in the absence of manifestations of hypothyroidism ...
Chapter 45 Essentials
... endocrine system Intro- hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads, pineal gland Relation Between the Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland- posterior pituitary gland, tropic hormones, anterior pituitary Posterior Pituitary Hormones- oxyto ...
... endocrine system Intro- hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads, pineal gland Relation Between the Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland- posterior pituitary gland, tropic hormones, anterior pituitary Posterior Pituitary Hormones- oxyto ...
Self governing- serves internal organs and glands
... Autonomic Nervous SystemSelf governing- serves internal organs and glands Both systems work together- emotional and involuntary behavior ...
... Autonomic Nervous SystemSelf governing- serves internal organs and glands Both systems work together- emotional and involuntary behavior ...
Endocrine System
... enzymes that depolymerize (break apart) glycogen and release glucose back into the blood stream so it can go where it is needed in the body’s cells for mitochondrial cellular respiration to make ATP. • High blood levels of amino acids (after eating a protein –rich meal), cause glucagon to convert ex ...
... enzymes that depolymerize (break apart) glycogen and release glucose back into the blood stream so it can go where it is needed in the body’s cells for mitochondrial cellular respiration to make ATP. • High blood levels of amino acids (after eating a protein –rich meal), cause glucagon to convert ex ...
File
... cells can respond to a hormone. Target cells have specific receptors that other cells do not have. ...
... cells can respond to a hormone. Target cells have specific receptors that other cells do not have. ...
The system that consists of group of ductless glands
... body size & short extremities: 4. Decrease in secretion of antidiuretic hormone (causes polyuria, excessive thirst, weakness, & dehydration): ...
... body size & short extremities: 4. Decrease in secretion of antidiuretic hormone (causes polyuria, excessive thirst, weakness, & dehydration): ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.