AIM: What system of the human body regulates hormones?
... hormone by endocrine glands for a determined length of time (inhibited by negative feedback). • Ex. Oxytocin and Prolactinencourages lactation of milk from mammary glands of nursing ...
... hormone by endocrine glands for a determined length of time (inhibited by negative feedback). • Ex. Oxytocin and Prolactinencourages lactation of milk from mammary glands of nursing ...
Agenesis of Isthmus of Thyroid Gland – A Cadaveric Study
... Abstract: The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland, situated in the lower part of the front and sides of the neck. The gland consists of right and left lobes that are joined to each other by Isthmus lying anterior to the second, third and fourth tracheal rings. A number of morphological variations an ...
... Abstract: The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland, situated in the lower part of the front and sides of the neck. The gland consists of right and left lobes that are joined to each other by Isthmus lying anterior to the second, third and fourth tracheal rings. A number of morphological variations an ...
Document
... The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. “Local hormones” include paracrine secretions that are released to interstitial fluid and affect only nearby cells, and autocrine secretions that influence the cell secreting the hormone. C. ...
... The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. “Local hormones” include paracrine secretions that are released to interstitial fluid and affect only nearby cells, and autocrine secretions that influence the cell secreting the hormone. C. ...
the endocrine system
... -also called the Master Gland -located at the base of the brain -has 2 lobes -stimulates other endocrine glands to release their hormones ...
... -also called the Master Gland -located at the base of the brain -has 2 lobes -stimulates other endocrine glands to release their hormones ...
Notes
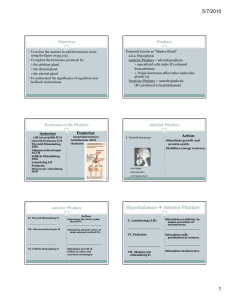
... treatments now include HGH therapy during childhood 2. Gigantism (see figure 13.9 p.429) an excess of HGH production prior to puberty; causes uncontrolled growth (long bones in the skeleton) usually caused by a tumor on the pituitary gland can be treated with surgery on the pituitary gland 3. Acrome ...
... treatments now include HGH therapy during childhood 2. Gigantism (see figure 13.9 p.429) an excess of HGH production prior to puberty; causes uncontrolled growth (long bones in the skeleton) usually caused by a tumor on the pituitary gland can be treated with surgery on the pituitary gland 3. Acrome ...
Thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH receptor Regulation of thyroid
... only a slight effect on metabolism. T4 is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the active hormone that stimulates metabolism. About 80% of this conversion is in the liver and other organs, and 20% in the thyroid itself.TSH is secreted throughout life but particularly ...
... only a slight effect on metabolism. T4 is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the active hormone that stimulates metabolism. About 80% of this conversion is in the liver and other organs, and 20% in the thyroid itself.TSH is secreted throughout life but particularly ...
Agenesis of isthmus of thyroid gland with bilateral levator glandulae
... developmental anomalies ranging from common to rare. Common anomalies include persistence of pyramidal lobe and thyroglossal duct cyst. Rare anomalies are agenesis or hemi-agenesis of thyroid gland, agenesis of isthmus alone or aberrant thyroid glands [1,2] In all the higher primates and human, the ...
... developmental anomalies ranging from common to rare. Common anomalies include persistence of pyramidal lobe and thyroglossal duct cyst. Rare anomalies are agenesis or hemi-agenesis of thyroid gland, agenesis of isthmus alone or aberrant thyroid glands [1,2] In all the higher primates and human, the ...
ppt - Stritch School of Medicine
... the hypothalamus and transported to the pars nervosa where processing is completed ...
... the hypothalamus and transported to the pars nervosa where processing is completed ...
2016_02_03_exam_key_revised
... be caused by any of the following except a. chronically elevated TSH levels b. excessive iodine intake – YES c. thyroid gland tumor d. thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) e. ANY of the above could cause this problem. ...
... be caused by any of the following except a. chronically elevated TSH levels b. excessive iodine intake – YES c. thyroid gland tumor d. thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) e. ANY of the above could cause this problem. ...
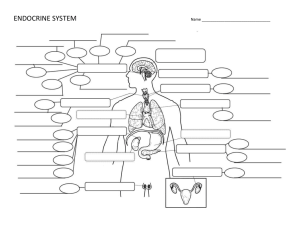
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Protein and catecholamine hormones act by binding to receptors located on the cell membranes of target cells Hormones act as the 1st messenger which in turn activates a series of events involving cAMP as the 2nd messenger cAMP activates protein kinases G-proteins link the first messenger and the sec ...
... Protein and catecholamine hormones act by binding to receptors located on the cell membranes of target cells Hormones act as the 1st messenger which in turn activates a series of events involving cAMP as the 2nd messenger cAMP activates protein kinases G-proteins link the first messenger and the sec ...
Name
... Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - cortex and medulla.. Pancreas - islets of Langerhans and acinar cells. ...
... Thyroid gland - colloid-filled follicles, follicle cells, parafollicular cells. Parathyroid gland - chief cells. Adrenal gland - cortex and medulla.. Pancreas - islets of Langerhans and acinar cells. ...
Thyroid gland (level 3 discussion)
... butterfly shaped or H –shaped. The gland is closely plastered to the voice box and upper airway by the pretracheal fascia and its isthmus is attached to the cricoid cartilage by the ligaments named after Berry as berry’s ligament (The recurrent laryngeal nerves ascend in the tracheo-esophageal grove ...
... butterfly shaped or H –shaped. The gland is closely plastered to the voice box and upper airway by the pretracheal fascia and its isthmus is attached to the cricoid cartilage by the ligaments named after Berry as berry’s ligament (The recurrent laryngeal nerves ascend in the tracheo-esophageal grove ...
TAKE HOME EXAM –URINARY SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
Endocrine System
... • The main functioning unit of the endocrine system is the hormone. – Travels through interstitial fluid and blood to reach target cells. – Secreted by endocrine glands. • Ex: Pituitary, Thyroid, etc. ...
... • The main functioning unit of the endocrine system is the hormone. – Travels through interstitial fluid and blood to reach target cells. – Secreted by endocrine glands. • Ex: Pituitary, Thyroid, etc. ...
UPPER AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION & TRACHEOTOMY
... Upper airway obstruction Obstructive sleep apnea Bilateral vocal cord paralysis Inability to intubate Major head & neck surgery or trauma ...
... Upper airway obstruction Obstructive sleep apnea Bilateral vocal cord paralysis Inability to intubate Major head & neck surgery or trauma ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Name 1. Gland in the brain that is the control
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
... 1. Gland in the brain that is the control center for all regulatory activities of the body: ____________________________ 2. Condition in which levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low: _________________________ __ 3. Helps regulate when you sleep at night and when you wake in the mornin ...
Endocrine System
... Estrogen – stimulates uterine lining, development of primary and secondary female characteristics Progesterone – Uterine lining growth, helps maintain pregnancy ...
... Estrogen – stimulates uterine lining, development of primary and secondary female characteristics Progesterone – Uterine lining growth, helps maintain pregnancy ...
Thyroid
... Most of the secreted thyroid hormone (90%) is thyroxine but is converted to the more active form, triiodothyronine, by peripheral target tissues. The kidney and liver are important deiodinators of thyroxin and convert it to the functionally more potent triiodothyronine. Triiodothyronine then bids to ...
... Most of the secreted thyroid hormone (90%) is thyroxine but is converted to the more active form, triiodothyronine, by peripheral target tissues. The kidney and liver are important deiodinators of thyroxin and convert it to the functionally more potent triiodothyronine. Triiodothyronine then bids to ...
Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Anatomy
... - The colloid, or stored thyroglobulin, fills the lumen. When stimulated by pituitary TSH, the colloid is ingested and broken down to release thyroid hormones. - The “scalloping” or bubbly appearance of the colloid near the edge of the colloid is characteristic of the follicular cells ingesting the ...
... - The colloid, or stored thyroglobulin, fills the lumen. When stimulated by pituitary TSH, the colloid is ingested and broken down to release thyroid hormones. - The “scalloping” or bubbly appearance of the colloid near the edge of the colloid is characteristic of the follicular cells ingesting the ...
The thyroid hormones
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.