The Endocrine System
... Hormone producing cells are sent information from sensing and signaling systems - permit regulation of amount and duration of hormone release ...
... Hormone producing cells are sent information from sensing and signaling systems - permit regulation of amount and duration of hormone release ...
The Endocrine System
... The endocrine system is the chemical control of your body (aka hormones) Endocrine glands are found throughout the body Hormones are chemicals that are made in one part of the body and affect another part of the body ...
... The endocrine system is the chemical control of your body (aka hormones) Endocrine glands are found throughout the body Hormones are chemicals that are made in one part of the body and affect another part of the body ...
chapter 18 study guide
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
... ADH – antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) causes kidneys to return more water to the blood rather than going to urine output decreases water loss through perspiration raises blood pressure by constricting arterioles ...
chapt14-endocrine system
... If iodine is available in limited quantities, a simple goiter develops; if the thyroid is overactive, an exophthalmic goiter develops. Thyroid hormones generally increase metabolic rate. If the thyroid fails to develop properly, cretinism results. Hypothyroidism in adults causes myxedema. Calcitonin ...
... If iodine is available in limited quantities, a simple goiter develops; if the thyroid is overactive, an exophthalmic goiter develops. Thyroid hormones generally increase metabolic rate. If the thyroid fails to develop properly, cretinism results. Hypothyroidism in adults causes myxedema. Calcitonin ...
Endocrine System Glands - Fall River Public Schools
... • Endocrine function – produces insulin and glucagon, which helps to keep the level of glucose in the blood stable – Insulin stimulates cells in the liver and muscles to remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat – Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glu ...
... • Endocrine function – produces insulin and glucagon, which helps to keep the level of glucose in the blood stable – Insulin stimulates cells in the liver and muscles to remove sugar from the blood and store it as glycogen or fat – Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen and release glu ...
PowerPoint - Pennsylvania Pharmacists Association
... responsible for the regulation of metabolism. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormone (T3) and (T4) and responds by releasing (TRH). The TRH stimulates the pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid ...
... responsible for the regulation of metabolism. The hypothalamus senses low circulating levels of thyroid hormone (T3) and (T4) and responds by releasing (TRH). The TRH stimulates the pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroid ...
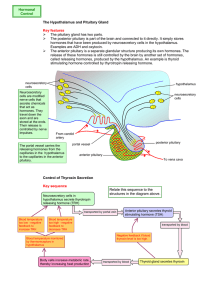
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Key features The pituitary
... hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular structure producing its own hormones. The release of these hormones is still controlled by the brain by another set of hormones, called releasin ...
... hormones that have been produced by neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Examples are ADH and oxytocin. The anterior pituitary is a separate glandular structure producing its own hormones. The release of these hormones is still controlled by the brain by another set of hormones, called releasin ...
High Yield Hints-Endocrine Glands
... High Yield Hints – Endocrine Glands ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. Hormones are “ Informational molecules “ produced from the endocrine cells. These may be proteins, amines or steroids. 2. Thyroxin is an iodine-containing hormone (4 iodine per molecule). It is a derivative of Tyrosine amino acid. Thyroxin is t ...
... High Yield Hints – Endocrine Glands ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. Hormones are “ Informational molecules “ produced from the endocrine cells. These may be proteins, amines or steroids. 2. Thyroxin is an iodine-containing hormone (4 iodine per molecule). It is a derivative of Tyrosine amino acid. Thyroxin is t ...
Endocrine System Facts Review
... A small pine cone - shaped structure located deep in the center of the brain which produces melatonin. Abnormal production of this hormone may result in mood disorders and depression , a disorder called SADS. The part of the brain that acts as the main control center for the autonomic nervous system ...
... A small pine cone - shaped structure located deep in the center of the brain which produces melatonin. Abnormal production of this hormone may result in mood disorders and depression , a disorder called SADS. The part of the brain that acts as the main control center for the autonomic nervous system ...
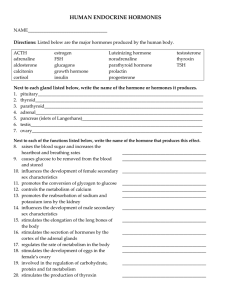
human endocrine hormones
... Next to each gland listed below, write the name of the hormone or hormones it produces. 1. pituitary_________________________________________________________________________ 2. thyroid__________________________________________________________________________ 3. parathyroid___________________________ ...
... Next to each gland listed below, write the name of the hormone or hormones it produces. 1. pituitary_________________________________________________________________________ 2. thyroid__________________________________________________________________________ 3. parathyroid___________________________ ...
Name______________________________________ Due Date
... Compare and contrast Endocrine glands and Exocrine glands Compare and contrast Endocrine system and Nervous system Know the Endocrine glands location on a diagram of the Human Body (Diagram in notes) Describe the terms Receptor and Target cell and how they apply to the endocrine system Describe the ...
... Compare and contrast Endocrine glands and Exocrine glands Compare and contrast Endocrine system and Nervous system Know the Endocrine glands location on a diagram of the Human Body (Diagram in notes) Describe the terms Receptor and Target cell and how they apply to the endocrine system Describe the ...
Thyroid Disorders
... associated with other autoimmune disease such as pernicious anaemia, vitiligo and other endocrine deficiencies . In some instances intermittent hypothyroidism occurs with recovery from disease; antibodies which block the TSH receptor may sometimes be involved in the aetiology. ...
... associated with other autoimmune disease such as pernicious anaemia, vitiligo and other endocrine deficiencies . In some instances intermittent hypothyroidism occurs with recovery from disease; antibodies which block the TSH receptor may sometimes be involved in the aetiology. ...
Human Endocrine System
... Negative Feedback is how the endocrine system regulates hormone levels. •The level of one hormone in the blood stimulates or inhibits the production of a second hormone. •The blood level of the second hormone in turn stimulates or inhibits the production of the first. •TSH (secreted by the pituitary ...
... Negative Feedback is how the endocrine system regulates hormone levels. •The level of one hormone in the blood stimulates or inhibits the production of a second hormone. •The blood level of the second hormone in turn stimulates or inhibits the production of the first. •TSH (secreted by the pituitary ...
Endocrine Pharmacology
... • A chemical substance secreted into body fluids by one cell or group of cells • Exerts a physiological control effect on other cells in the body • General vs. local hormones • General hormones may effect all cells [e.g. GH] or some effect specific tissues ...
... • A chemical substance secreted into body fluids by one cell or group of cells • Exerts a physiological control effect on other cells in the body • General vs. local hormones • General hormones may effect all cells [e.g. GH] or some effect specific tissues ...
• Two hormones are produced: (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland The
... Hormones are secreted from two different areas of the gland, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla ...
... Hormones are secreted from two different areas of the gland, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla ...
The Endocrine System - Greer Middle College Charter
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
... melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Thymus Gland – large in young children, gradually shrinks with age, secretes thymosins, important to immune function Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... These hormones maintain the reproductive system and develop sexual characteristics ...
... These hormones maintain the reproductive system and develop sexual characteristics ...
Aspects regarding the morphological variability of superior thyroid
... of thyroid lobe and two inferior thyroid arteries, which irrigate inferior and inferomedial part of the gland. The study was made in the Laboratory of Anatomy at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Victor Babes. Timisoara. on 120 corpses. To point out superior thyroid artery, we used the method ...
... of thyroid lobe and two inferior thyroid arteries, which irrigate inferior and inferomedial part of the gland. The study was made in the Laboratory of Anatomy at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Victor Babes. Timisoara. on 120 corpses. To point out superior thyroid artery, we used the method ...
Endocrine System
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
8.1 endocrine gland note
... found in the neck, below the Adam's apple The thyroid controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls how sensitive the body should be to other hormones. ...
... found in the neck, below the Adam's apple The thyroid controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls how sensitive the body should be to other hormones. ...
Endocrine System
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
SAP 1 – Students will analyze anatomical structures in
... if too much is released during adulthood, a condition called acromegaly results ...
... if too much is released during adulthood, a condition called acromegaly results ...
CASE 34
... the tyrosines are still part of the thyroglobulin molecule and is catalyzed by thyroperoxidase. Normally, this storage form of thyroid hormone is sufficient to provide the body with adequate amounts of hormone for 1 to 3 months. Secretion of thyroid hormones begins with the uptake of thyroglobulin b ...
... the tyrosines are still part of the thyroglobulin molecule and is catalyzed by thyroperoxidase. Normally, this storage form of thyroid hormone is sufficient to provide the body with adequate amounts of hormone for 1 to 3 months. Secretion of thyroid hormones begins with the uptake of thyroglobulin b ...
The Endocrine System - Lawndale High School
... • A chemical that inhibits or prevents urine production • In large amounts, can increase blood pressure ...
... • A chemical that inhibits or prevents urine production • In large amounts, can increase blood pressure ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.