* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
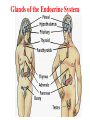
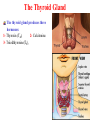
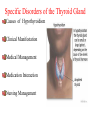
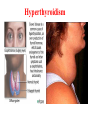
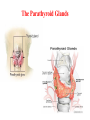
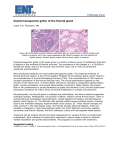
Assessment Patients and Management of With Endocrine Disorders Prepared by Dr. Iman Abdalla Out line Glands of the Endocrine System Classification and Action of Hormones The Thyroid Gland Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Function of Thyroid Hormone Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Storm (Thyrotoxic Crisis) Thyroiditis Thyroid Tumors Out line Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Management prevention Nodular Goiter Thyroid Cancer The Parathyroid Glands Pathophysiology Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism Learning Objectives On completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe the functions of each of the endocrine glands and their hormones. Compare hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism: their causes, clinical manifestations, management, and nursing interventions. Develop a plan of nursing care for the patient undergoing thyroidectomy. compare hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism: their causes, clinical manifestations, management, and nursing interventions. Glands of the Endocrine System Classification and Action of Hormones Hormones are classified as: Steroid hormones ( hydrocortisone ) Peptide or protein hormones ( insulin ) Amine hormones ( epinephrine ) Fatty acids derivatives ( retinoids ) The Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland produces three hormones: 1- Thyroxin (T4), 2- Calcitonine. 3- Triiodthyronine(T3), Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Function of Thyroid Hormone Calcitonin Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Specific Disorders of the Thyroid Gland Causes of Hypothyroidism Clinical Manifestation Medical Management Medication Interaction Nursing Management Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism Clinical Manifestation Medical Management Pharmacotherapy Surgical Management Nursing Process The Patient With Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Storm (Thyrotoxic Crisis) Causes :It is precipitated by stress, injury, infection, thyroidectomy, tooth extraction, insulin reaction, diabetic ketoacidosis, pregnancy, abrupt withdrawal of antithyroid medications Clinical manifestations Management Thyroiditis Thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid gland, can be: acute, subacute, or chronic. Thyroid Tumors Tumors of the thyroid gland are classified on the basis of being benign or malignant. If the enlargement is sufficient to cause a visible swelling in the neck, the tumor is referred to as goiter. All grades of goiter are encountered, from those, that are barely visible to those producing disfigurement. Goiter either symmetrical and diffuse or nodular. It might accompanied by hyperthyroidism (toxin); others are non toxic goiters Endemic (Iodine-Deficient) Goiter Management Many goiters of this type decreased after correction of iodine insufficiency. When surgery is recommended, post operative complications can be minimized by pre operative iodide administration to reduce the size & vascularity of goiter. Prevention Providing children in iodine-poor region with iodine compounds. Use of iodized salt. Nodular Goiter Thyroid Cancer Causes Types Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Medical Management Nursing Management The Parathyroid Glands Pathophysiology Excess parathormone can result in markedly increased levels of serum calcium, a potentially life- threatening situation. When the product of serum calcium and serum phosphorus (calcium x phosphorus) rises, calcium phosphorus may precipitate in various organs of the body (kidneys) and cause tissue calcification. Hyperparathyroidism Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. Clinical Manifestation Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Medical Management Nursing Management Complications Hypercalcemic Crisis Hypoparathyroidism Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestation Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Medical Management Nursing Management Reference Brunner, L. and Suddarath, D. (2010). Text Book of Medical Surgical Nursing. 12th Edition. J.B. Lippincott Williams & Wilikins, Library of Congress Catalging-in-Publication Data.] . Thank you