Test questions used for assessment
... a. is a complex protein network running through the cytosol b. functions in support, organization and movement of the cell c. is made up of microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and the microtrabecular lattice d. all of the above e. a and c 6. Which of the following are true? a. micro ...
... a. is a complex protein network running through the cytosol b. functions in support, organization and movement of the cell c. is made up of microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and the microtrabecular lattice d. all of the above e. a and c 6. Which of the following are true? a. micro ...
SMicroChapter5
... 2. Metabolism requires energy from light or from catabolism of nutrients 3. Energy is stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 4. Cells catabolize nutrients to form precursor metabolites 5. Precursor metabolites, energy from ATP, and enzymes used in anabolic reactions 6. Enzymes plus ATP form macromol ...
... 2. Metabolism requires energy from light or from catabolism of nutrients 3. Energy is stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 4. Cells catabolize nutrients to form precursor metabolites 5. Precursor metabolites, energy from ATP, and enzymes used in anabolic reactions 6. Enzymes plus ATP form macromol ...
Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your
... Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your own words. 1. In cellular respiration oxidation, hydrogen is transferred from glucose to oxygen. 2. Substrate-level phosphorylation is a simple transfer of a phosphate group from the substrate molecule to the ADP. 3. Glycolysis ...
... Key Terms and Ideas: Fill in the blanks or provide a definition in your own words. 1. In cellular respiration oxidation, hydrogen is transferred from glucose to oxygen. 2. Substrate-level phosphorylation is a simple transfer of a phosphate group from the substrate molecule to the ADP. 3. Glycolysis ...
CELL RESPIRATION
... adenosine monophosphate (AMP) inorganic phosphate anaerobic glycolysis coupled reactions NAD pyruvic acid fermentation lactic acid ethanol aerobic cellular respiration acetyl-CoA Krebs citric acid cycle FAD chemiosmosis electron-transport chain chemiosmotic gradient Q10 substrate level phosphorylati ...
... adenosine monophosphate (AMP) inorganic phosphate anaerobic glycolysis coupled reactions NAD pyruvic acid fermentation lactic acid ethanol aerobic cellular respiration acetyl-CoA Krebs citric acid cycle FAD chemiosmosis electron-transport chain chemiosmotic gradient Q10 substrate level phosphorylati ...
Photosynthesis 6.2
... – Principal energy supply molecule for cellular functions of all living cells ...
... – Principal energy supply molecule for cellular functions of all living cells ...
Cellular Respiration 3 Parts Glycolysis Kreb`s Cycle
... types of organisms must convert the carbohydrate to ATP, the energy currency of the cell, in order to carry out metabolic activity. ...
... types of organisms must convert the carbohydrate to ATP, the energy currency of the cell, in order to carry out metabolic activity. ...
Name: Date: 1. The is the source of most of the cellular energy. A
... metabolic pathways can be interconnected, and glucose could enter more than one ...
... metabolic pathways can be interconnected, and glucose could enter more than one ...
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration - SBI
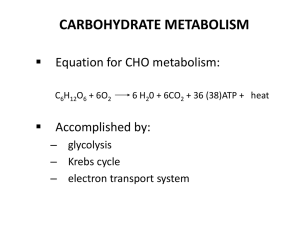
... • Glucose reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and energy (ATP) • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP) • For one molecule of glucose, 36 molecules of ATP are formed ...
... • Glucose reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and energy (ATP) • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP) • For one molecule of glucose, 36 molecules of ATP are formed ...
Jeopardy Review Enzyme/Energetics
... The process of breaking down pyruvates in the absence of oxygen to obtain energy ...
... The process of breaking down pyruvates in the absence of oxygen to obtain energy ...
Exam 2 Practice #3
... a. NADH and ATP; Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle b. NADH and ATP; Krebs Cycle c. ATP; Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain d. ATP; Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle 13. When chlorophyll absorbs a photon of light, what initially happens to the energy of the ...
... a. NADH and ATP; Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle b. NADH and ATP; Krebs Cycle c. ATP; Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain d. ATP; Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle 13. When chlorophyll absorbs a photon of light, what initially happens to the energy of the ...
Standard 3
... as a SIMPLE SUGAR, which acts as a building block for larger carbohydrates such as starches. Example: GLUCOSE ____ Nucleic Acid ...
... as a SIMPLE SUGAR, which acts as a building block for larger carbohydrates such as starches. Example: GLUCOSE ____ Nucleic Acid ...
Cellular Respiration Check-in Questions: THESE Questions are
... 4. Drugs known as uncouplers facilitate diffusion of protons across the membrane. When such a drug is added, what will happen to ATP synthesis and oxygen consumption, if the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle stay the same? a. Both ATP synthesis and oxygen consumption will decrease. b. AT ...
... 4. Drugs known as uncouplers facilitate diffusion of protons across the membrane. When such a drug is added, what will happen to ATP synthesis and oxygen consumption, if the rates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle stay the same? a. Both ATP synthesis and oxygen consumption will decrease. b. AT ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... or w/o presence of O2 • 2 phases: – Investment phase: use 2 ATP to break up glucose into 2 PGAL (C-C-C-p) – Payoff phase: each PGAL turns into pyruvate (C-C-C) • Each PGAL pyruvate change makes 2 ATPs via substrate level phosphorylation and 1 NADH via redox ...
... or w/o presence of O2 • 2 phases: – Investment phase: use 2 ATP to break up glucose into 2 PGAL (C-C-C-p) – Payoff phase: each PGAL turns into pyruvate (C-C-C) • Each PGAL pyruvate change makes 2 ATPs via substrate level phosphorylation and 1 NADH via redox ...
If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel
... • Significance: Allows 2 ATPs to be made as well as breaks the glucose molecule down into a more usable form ...
... • Significance: Allows 2 ATPs to be made as well as breaks the glucose molecule down into a more usable form ...
Nov_16
... o Same concept deliever electrons from asparatate to moxaloacetate to form malate.. This gives you NADH Oxaloacetate can not enter mitochondrial miatriax….so we have to make asparatate (?) Shuttles are just mechanisms to transfer compounds across the membrane… o 12.7 o Kinase they phosphorylat ...
... o Same concept deliever electrons from asparatate to moxaloacetate to form malate.. This gives you NADH Oxaloacetate can not enter mitochondrial miatriax….so we have to make asparatate (?) Shuttles are just mechanisms to transfer compounds across the membrane… o 12.7 o Kinase they phosphorylat ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... 2. Cells use the energy of energy-rich food molecules to form ATP. Which of the following represents a state of high energy? A) the C-H bonds in food molecules B) the H (electrons and H+) loaded onto NADH C) the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane D) the ATP formed E) all of the above ...
... 2. Cells use the energy of energy-rich food molecules to form ATP. Which of the following represents a state of high energy? A) the C-H bonds in food molecules B) the H (electrons and H+) loaded onto NADH C) the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane D) the ATP formed E) all of the above ...
Water - University of California, Los Angeles
... Under standard conditions, measurement against the standard hydrogen half cell (1M H+, 1ATM H2) gives standardE (E 0 for H+ + e- ½ H2) ...
... Under standard conditions, measurement against the standard hydrogen half cell (1M H+, 1ATM H2) gives standardE (E 0 for H+ + e- ½ H2) ...
Honors Biology Ch 6 Review sheet
... 7) What percent of energy is used from the glucose molecule?_____ 8) Which produces more ATP? Anaerobic or aerobic respiration?_________________________ 9) What is the function of lactic acid fermentation? Where? With or without O2? With or without mitochondria? What is produced? What cells? What is ...
... 7) What percent of energy is used from the glucose molecule?_____ 8) Which produces more ATP? Anaerobic or aerobic respiration?_________________________ 9) What is the function of lactic acid fermentation? Where? With or without O2? With or without mitochondria? What is produced? What cells? What is ...
Chapter 8 study guide
... What happens to the reducing agent in a redox reactions? What is the balanced equation for cellular respiration? What is being reduced? What is being oxidized? Where does glycoysis take place? What event or process in cellular respiration is oxygen directly involved in? What process happens with or ...
... What happens to the reducing agent in a redox reactions? What is the balanced equation for cellular respiration? What is being reduced? What is being oxidized? Where does glycoysis take place? What event or process in cellular respiration is oxygen directly involved in? What process happens with or ...
Cell Metabolism Review
... oxidative decarboxylation), then the Citric Acid Cycle (also known as Kreb’s Cycle). For each pyruvate, one CO2 is lost during AcCoA formation, the other 2 are lost during the Citric Acid Cycle. From one original molecule of glucose, two more ATPs are produced during the Citric Acid Cycle. Electrons ...
... oxidative decarboxylation), then the Citric Acid Cycle (also known as Kreb’s Cycle). For each pyruvate, one CO2 is lost during AcCoA formation, the other 2 are lost during the Citric Acid Cycle. From one original molecule of glucose, two more ATPs are produced during the Citric Acid Cycle. Electrons ...
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme often called the ""molecular unit of currency"" of intracellular energy transfer.ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of photophosphorylation, cellular respiration, and fermentation and used by enzymes and structural proteins in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions, motility, and cell division. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by a wide variety of enzymes, including ATP synthase, from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and various phosphate group donors. Substrate-level phosphorylation, oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration, and photophosphorylation in photosynthesis are three major mechanisms of ATP biosynthesis.Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors. ATP is therefore continuously recycled in organisms: the human body, which on average contains only 250 grams (8.8 oz) of ATP, turns over its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day.ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and lipids. It is also used by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP. The ratio between ATP and AMP is used as a way for a cell to sense how much energy is available and control the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in signaling and energy metabolism, ATP is also incorporated into nucleic acids by polymerases in the process of transcription. ATP is the neurotransmitter believed to signal the sense of taste.The structure of this molecule consists of a purine base (adenine) attached by the 9' nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon atom of a pentose sugar (ribose). Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the addition and removal of these phosphate groups that inter-convert ATP, ADP and AMP. When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.ATP was discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and independently by Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow of Harvard Medical School, but its correct structure was not determined until some years later. It was proposed to be the intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and energy-requiring reactions in cells by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. It was first artificially synthesized by Alexander Todd in 1948.