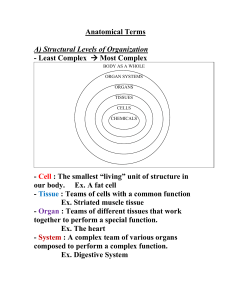
Anatomical Terms - Mr. Lesiuk
... - Body As A Whole : Unification of all the teams that work together to ensure healthy survival. ...
... - Body As A Whole : Unification of all the teams that work together to ensure healthy survival. ...
Name Sports Medicine I—Introduction to Anatomy Study Guide
... Classification of Synovial Joints Match each type of synovial joint to its definition and example. Synovial Joint _____50. ...
... Classification of Synovial Joints Match each type of synovial joint to its definition and example. Synovial Joint _____50. ...
The Study of Human Anatomy
... Gross Anatomy: anatomical position; anatomical terminology, body cavities, 9 regions and 4 quadrants of abdomen, Microscopic Anatomy: preparation and examination of slides with a light microscope An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of Structure or form of body and body parts and their relati ...
... Gross Anatomy: anatomical position; anatomical terminology, body cavities, 9 regions and 4 quadrants of abdomen, Microscopic Anatomy: preparation and examination of slides with a light microscope An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of Structure or form of body and body parts and their relati ...
I am to the back
... What is the force exerted on the surface of the body by the weight of air called? I am Where are the arms relative to the chest? atmospheric pressure I am lateral In which of the following regions is the shoulder blade found? I am scapular What is a cut made along the horizontal plane? I am transver ...
... What is the force exerted on the surface of the body by the weight of air called? I am Where are the arms relative to the chest? atmospheric pressure I am lateral In which of the following regions is the shoulder blade found? I am scapular What is a cut made along the horizontal plane? I am transver ...
big ideas - Hobbs High School
... MATCHING: Organ system to a function and to organs (digestive, endocrine, circulatory, respiratory, reproductive, nervous, urinary, lymphatic) Body Regions: 1. Cervical 2. Cephalic 3. Brachial 4. Pedal 7. Abdominopelvic and regions within the 9 abdominopelvic regions ...
... MATCHING: Organ system to a function and to organs (digestive, endocrine, circulatory, respiratory, reproductive, nervous, urinary, lymphatic) Body Regions: 1. Cervical 2. Cephalic 3. Brachial 4. Pedal 7. Abdominopelvic and regions within the 9 abdominopelvic regions ...
Anatomical dissection vocab File
... The body can be broken into planes i.e. top and bottom, left and right, middle and outside, front and back etc. These words can be used to help determine the placement of body parts. ...
... The body can be broken into planes i.e. top and bottom, left and right, middle and outside, front and back etc. These words can be used to help determine the placement of body parts. ...
Unit 2 The Anatomical Positions 1. Warm – up
... 5. to keep someone at arm's length d) to avoid being close or friendly e) to get angry very easily ...
... 5. to keep someone at arm's length d) to avoid being close or friendly e) to get angry very easily ...
Allied Health I
... Anatomy studies the shape an structure of an organisms body and the relationship of one body part to another. Physiology studies the function of each body part and how the functions of the various body parts coordinate to form a complete living organism. For our purposes in this unit it is the study ...
... Anatomy studies the shape an structure of an organisms body and the relationship of one body part to another. Physiology studies the function of each body part and how the functions of the various body parts coordinate to form a complete living organism. For our purposes in this unit it is the study ...
MMHS Anatomy and Physiology
... Energy Sources ATP can run out and must be regenerated. a. creatine phosphate is 4-6 times more abundant than ATP b. creatine phosphate converts ADP back to ATP. ...
... Energy Sources ATP can run out and must be regenerated. a. creatine phosphate is 4-6 times more abundant than ATP b. creatine phosphate converts ADP back to ATP. ...
Muscle movements, types, and names Types of body movements
... muscles are working in tandem with our skeletal system. ...
... muscles are working in tandem with our skeletal system. ...
MCQs on introduction to Anatomy [PPT]
... Q.1) Which system involves the study of skin and its appendages ? a) Locomotor system b) Endocrine system c) Integumentary system d) Skeletal system ...
... Q.1) Which system involves the study of skin and its appendages ? a) Locomotor system b) Endocrine system c) Integumentary system d) Skeletal system ...
10 great views inside the human body
... The renal arteries of the circulatory system deliver blood to the kidneys. The kidneys remove waste from the blood; this waste then passes into the renal pelvis and to the ureters. ...
... The renal arteries of the circulatory system deliver blood to the kidneys. The kidneys remove waste from the blood; this waste then passes into the renal pelvis and to the ureters. ...
Ch01 Anatomy basics
... iliac Body Areas – Internal cardiac heart pulmonary lung cutaneous skin Terms of Direction: superior toward the head inferior toward the feet cephalic toward the head caudal toward the tail anterior toward the front posterior toward the back ventral toward the front dorsal toward the back ...
... iliac Body Areas – Internal cardiac heart pulmonary lung cutaneous skin Terms of Direction: superior toward the head inferior toward the feet cephalic toward the head caudal toward the tail anterior toward the front posterior toward the back ventral toward the front dorsal toward the back ...
Chapter 1
... structure lies beneath another Superior Above in relation to another structure (towards the head) ...
... structure lies beneath another Superior Above in relation to another structure (towards the head) ...
Section 1- The Anatomical Position.pptx
... direction of movement at joints: v Longitudinal (polar) axis: In a “north-south” relationship to the anatomical position v Horizontal (bilateral) axis: In an “east-west” relationship to the anatomical position v Antero-posterior axis: In a “front-to-back” relationship to the anatomical p ...
... direction of movement at joints: v Longitudinal (polar) axis: In a “north-south” relationship to the anatomical position v Horizontal (bilateral) axis: In an “east-west” relationship to the anatomical position v Antero-posterior axis: In a “front-to-back” relationship to the anatomical p ...
Functions Protection for organs of the inferior abdominopelvic
... Body, superior and inferior rami Pubic crest and pubic tubercles Attachment of abd muscles and inguinal ligaments (Abercrombie line) respectively ...
... Body, superior and inferior rami Pubic crest and pubic tubercles Attachment of abd muscles and inguinal ligaments (Abercrombie line) respectively ...
Abdomen and Pelvis
... 2. A lower root (C8 & T1) injury of the brachial plexus may cause loss of precision movements of the fingers and thumb. 3. As well as being an elbow flexor, biceps is also a powerful pronator of the forearm. 4. The brachial pulse may be found deep to biceps on the lateral aspect of the arm. 5. The r ...
... 2. A lower root (C8 & T1) injury of the brachial plexus may cause loss of precision movements of the fingers and thumb. 3. As well as being an elbow flexor, biceps is also a powerful pronator of the forearm. 4. The brachial pulse may be found deep to biceps on the lateral aspect of the arm. 5. The r ...
Anatomical Planes
... Abduction moving away from the median plane except digits Adduction moving towards the median plane ...
... Abduction moving away from the median plane except digits Adduction moving towards the median plane ...
Directional Terms, Anatomical Planes
... 16. Directional Terms, Anatomical Planes , Regions, and Additional Terms EXERCISE 16- 1 Match the terms in the first column with the correct definitions in the second column. The answers in the second column may be used more than once. 1. anterior a. toward the top 2. caudal ...
... 16. Directional Terms, Anatomical Planes , Regions, and Additional Terms EXERCISE 16- 1 Match the terms in the first column with the correct definitions in the second column. The answers in the second column may be used more than once. 1. anterior a. toward the top 2. caudal ...
Can we study anatomy without studying
... Refers to the body in anatomical position Standardized terms of direction are paired terms ...
... Refers to the body in anatomical position Standardized terms of direction are paired terms ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.













![MCQs on introduction to Anatomy [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006962811_1-c9906f5f12e7355e4dc103573e7f605b-300x300.png)